版权声明:本文系博主原创,未经博主许可,禁止转载。保留所有权利。
引用网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhizaixingzou/p/10140762.html
目录



1. MyBatis
1.1. 简介
MyBatis是一个持久层框架。
1.2. 开发实例
1.2.1. 创建数据库和表
在MySQL数据库服务器上创建一个数据库,并建立一张表。
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS examples;
USE examples;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `order` (
`id` BIGINT (20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id',
`goods` VARCHAR (24) NOT NULL COMMENT 'goods name',
`seller` VARCHAR (24) NOT NULL COMMENT 'seller',
`buyer` VARCHAR (24) NOT NULL COMMENT 'buyer',
`create_time` datetime (3) NOT NULL COMMENT 'create time',
`remark` VARCHAR (64) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'remark',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE = INNODB DEFAULT CHARSET = utf8mb4 COMMENT = 'the table create order info';
并往表插入一条记录。
INSERT INTO `examples`.`order` (`goods`, `seller`, `buyer`, `create_time`, `remark`)
VALUES('basket ball', 'cjw', 'BK Ltc.', '2011-02-23', '');
1.2.2. 与表对应的POJO
package com.cjw.learning.examples;
import java.util.Date;
public class Order {
private int id;
private String goods;
private String seller;
private String buyer;
private Date createTime;
private String remark;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(String goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public String getSeller() {
return seller;
}
public void setSeller(String seller) {
this.seller = seller;
}
public String getBuyer() {
return buyer;
}
public void setBuyer(String buyer) {
this.buyer = buyer;
}
public Date getCreateTime() {
return createTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date createTime) {
this.createTime = createTime;
}
public String getRemark() {
return remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order [id=" + id + ", goods=" + goods + ", seller=" + seller + ", buyer=" + buyer + "]";
}
}
1.2.3. DAO接口
package com.cjw.learning.examples;
import java.util.List;
public interface OrderDao {
Order selectById(int id);
List<Order> selectAllOrders();
}
1.2.4. POM配置
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cjw.learning</groupId>
<artifactId>examples</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.11</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
1.2.5. MyBatis配置
mybatis.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Order" type="com.cjw.learning.examples.Order"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="local">
<environment id="local">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/examples?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mybatis/OrderMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
1.2.6. Mapper配置
OrderMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mappers.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.cjw.learning.examples.OrderDao">
<resultMap id="orMap" type="com.cjw.learning.examples.Order">
<result column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="goods" property="goods"/>
<result column="seller" property="seller"/>
<result column="buyer" property="buyer"/>
<result column="create_time" property="createTime"/>
<result column="remark" property="remark"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="orMap">
SELECT `order`.`id`,
`order`.`goods`,
`order`.`seller`,
`order`.`buyer`,
`order`.`create_time`,
`order`.`remark`
FROM `examples`.`order` WHERE `order`.`id`=#{id}
</select>
<select id="selectAllOrders" resultMap="orMap">
SELECT `order`.`id`,
`order`.`goods`,
`order`.`seller`,
`order`.`buyer`,
`order`.`create_time`,
`order`.`remark`
FROM `examples`.`order`
</select>
</mapper>
1.2.7. 客户端调用
package com.cjw.learning.examples;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo01 {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
public static SqlSession getSqlSession() throws IOException {
if (sqlSessionFactory == null) {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
}
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
sqlSession = getSqlSession();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Configuration file not found");
}
if (sqlSession == null) {
return;
}
OrderDao orderDao = sqlSession.getMapper(OrderDao.class);
List<Order> orders = orderDao.selectAllOrders();
sqlSession.commit();
for (Order order : orders) {
System.out.println(order.toString());
}
Order order = orderDao.selectById(1);
sqlSession.commit();
System.out.println(order.toString());
sqlSession.close();
}
}
1.2.8. 应用的总体结构

1.2.9. 运行结果

1.3. MyBatis源码
https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/tree/mybatis-3.4.5


1.4. 源码解读
1.4.1. MyBatis和Mapper配置中的DTD
MyBatis配置引用了一个DTD文档:
http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd

DTD是文档类型定义的简称,它一般内嵌于XML文档中,指定了一个XML文档所能合法使用的构建节点,即可以使用哪些元素来定义XML文档的结构。可以看到,DTD是XML文档关于自身格式的描述,有了它:1)借助IDE内置了DTD的解析器,我们在编辑XML文档时就能得到这些预先定义的构建节点的输入提示,2)便于交换数据的校验,如果XML使用了DTD定义以外的构建节点,则XML解析器会抛错。
<!ELEMENT,声明元素。元素可以包含哪些子元素,以及各个子元素的多少使用类似Java正则表达式中的量词表达。
<!ATTLIST,声明属性。
#REQUIRED,属性值是必须的。
#IMPLIED,属性值不是必须的。
CDATA 是不会被解析器解析的字符数据。
有兴趣了解更多细节见:http://www.runoob.com/dtd/dtd-tutorial.html
Mapper配置也引用了一个DTD文档:
http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
1.4.2. 读取MyBatis配置
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
MyBatis使用类加载器的如下方法来读取配置文件,它要求这个配置文件的路径是相对于.\src\main\resources的相对路径。
InputStream returnValue = cl.getResourceAsStream(resource);
而类加载器可以使用如下几种(封装为一个ClassLoaderWrapper,表现得像一个ClassLoader一样,类似于使用了组合模式),任何一种读取成功都算成功,但优先使用自定义的:
ClassLoader[] getClassLoaders(ClassLoader classLoader) {
return new ClassLoader[]{
classLoader,
defaultClassLoader,
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),
getClass().getClassLoader(),
systemClassLoader};
}
1.4.3. 构建会话工厂
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
解析配置文件得到配置。
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
然后用此配置创建默认的会话工厂。
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
1.4.4. 创建XPath解析器并读取配置为DOM文档
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
在这个过程中,会使用XPath语言进行解析,并根据DTD检查文档的合法性。
private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) {
// important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setValidating(validation);
factory.setNamespaceAware(false);
factory.setIgnoringComments(true);
factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false);
factory.setCoalescing(false);
factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true);
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver);
builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() {
@Override
public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
throw exception;
}
@Override
public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException {
}
});
return builder.parse(inputSource);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}
1.4.5. 构建XML配置
XML配置构建器:
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
指定了XPath解析器,并初始化了一个配置,里面事先定义了一些类的别名配置:
public Configuration() {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("PERPETUAL", PerpetualCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("FIFO", FifoCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LRU", LruCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SOFT", SoftCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("WEAK", WeakCache.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("XML", XMLLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("RAW", RawLanguageDriver.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("SLF4J", Slf4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("COMMONS_LOGGING", JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J", Log4jImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("LOG4J2", Log4j2Impl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDK_LOGGING", Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("STDOUT_LOGGING", StdOutImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("NO_LOGGING", NoLoggingImpl.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("CGLIB", CglibProxyFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JAVASSIST", JavassistProxyFactory.class);
languageRegistry.setDefaultDriverClass(XMLLanguageDriver.class);
languageRegistry.register(RawLanguageDriver.class);
}
接着,使用XPath解析器解析MyBatis配置。
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
解析得到的每个节点都内置了同一个XPath解析器,用于节点的递归解析。
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}
1.4.6. DOM文档的解析过程
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder#parseConfiguration
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
即对应如下部分的解析(结合着DTD文档来阅读代码更方面):

关于每个配置的意义,见MyBatis官方的描述(会有稍许出入,此时以代码为准):
http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/configuration.html
1.4.6.1. properties
从如下DTD可知,MyBatis可以有1或0个properties子元素。
<!ELEMENT configuration (properties?,
properties子元素可以有0或多个property子元素,可以有resource、url属性。
<!ELEMENT properties (property*)>
<!ATTLIST properties
resource CDATA #IMPLIED
url CDATA #IMPLIED
>
每个property则可以配置name、value的配置键值对。
<!ELEMENT property EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST property
name CDATA #REQUIRED
value CDATA #REQUIRED
>
从具体代码看:
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
resource和url属性只能二居其一。而且,用户调用build方法传入的参数配置优先级最高,其次是resource或url指定的,最后是property指定的。
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
property集合的读取过程如下:
public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (XNode child : getChildren()) {
String name = child.getStringAttribute("name");
String value = child.getStringAttribute("value");
if (name != null && value != null) {
properties.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
return properties;
}
代码上看,这些配置会进入到XPath解析器,也就是说,后续解析中用到解析器的地方都可以用到这些配置,同时刷新已有配置。
这些属性可以在整个配置文件中被用来替换需要动态配置的属性值,即${name},可以为此占位符提供默认值${name:default},前提是配置了:
<property name="org.apache.ibatis.parsing.PropertyParser.enable-default-value" value="true"/>
1.4.6.2. settings
这个子元素可以有若干setting子元素,都配置了name、value键值对,如:
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
解析时,这些name必须是配置类有setter的,否则抛异常停止解析,这些配置时大小写敏感的。

特别是vfsImpl配置,用英文逗号隔开若干VFS实现类的全限定名,解析后组成一个VFS的集合。
这些集合会根据具体的字符串值,得到具体的类型的具体值并放到配置中去。
private void settingsElement(Properties props) throws Exception {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), false));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setDefaultFetchSize(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultFetchSize"), null));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends TypeHandler> typeHandler = (Class<? extends TypeHandler>)resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultEnumTypeHandler"));
configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(typeHandler);
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), true));
configuration.setReturnInstanceForEmptyRow(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("returnInstanceForEmptyRow"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class<? extends Log> logImpl = (Class<? extends Log>)resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl"));
configuration.setLogImpl(logImpl);
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
1.4.6.3. typeAliases
这里为全限定名的类定义一个简短的别名,后续配置可以使用别名。
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
<package name="domain.blog"/>
对于typeAlias配置的:
如果没有指定alias属性,那么使用指定类型的Alias注解的值为别名,如果没有这个注解,则使用类型的简单名作为别名。别名最后都变为全小写做键,类做值,遇到同一个别名配置了两个不同的类则异常。
对于package配置的:
通过VFS服务,加载这个包下的类(不包含子包下的类),如果是Object的子类则加入到待处理集合。针对每一个类,只要不是匿名类,不是接口或成员类,则当做没有指定alisa那样处理。
1.4.6.4. plugins
<plugin interceptor="org.mybatis.example.ExamplePlugin">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</plugin>
@Intercepts({@Signature(
type= Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class,Object.class})})public class ExamplePlugin implements Interceptor {
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
return invocation.proceed();
}
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}}
这里的interceptor可以是类型别名,如果没有配置,则只当做全限定名来处理。每个拦截器都可以定义键值对列表。如果定义了多个则依次加入到配置的拦截器链上。拦截器主要用来拦截指定的方法。
1.4.6.5. objectFactory
<objectFactory type="org.mybatis.example.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/></objectFactory>
对象工厂的用来创建结果对象,如果没有指定,则使用默认的,指定了则使用这个指定的,只能配置一个。
1.4.6.6. objectWrapperFactory
与objectFactory类似的处理形式,但无属性设置。
1.4.6.7. reflectorFactory
与objectWrapperFactory类似的处理形式。
在处理settings的时候,已经用到过发射子工厂,用来判断是否键值对合法是通过判断是否有对应的setXXX来的,而自定义的反射子工厂则可以不拘泥于这个形式。
1.4.6.8. environments
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="..." value="..."/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment></environments>
一个会话工厂只能使用到一个environment。想连接两个数据库,就需要创建两个 SqlSessionFactory 实例,每个数据库对应一个。
可以配置多个environment子元素,但实际上只会解析id与默认相同的那个。
指定了事务管理器,也叫事务管理工厂。有两种,对应下面的两个类:
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JDBC", JdbcTransactionFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("MANAGED", ManagedTransactionFactory.class);
指定了数据源类型如下,以及对应的参数:
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("JNDI", JndiDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("POOLED", PooledDataSourceFactory.class);
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("UNPOOLED", UnpooledDataSourceFactory.class);
1.4.6.9. databaseIdProvider
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR">
<property name="SQL Server" value="sqlserver"/>
<property name="DB2" value="db2"/>
<property name="Oracle" value="oracle" /></databaseIdProvider>
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias("DB_VENDOR", VendorDatabaseIdProvider.class);
可以根据不同的厂商执行不同的SQL语句。
根据environment的数据源可以得到产品名,然后根据上面的配置从中选出对应的databaseId,即上面的value值。
1.4.6.10. typeHandlers
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.mybatis.example.ExampleTypeHandler"/></typeHandlers>
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.VARCHAR)public class ExampleTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
在预处理和结果输出时都涉及到Java与DB的类型转换问题,typeHandler就是处理这种问题的。
类型处理器配置可以指定Java类型、JDBC类型和处理器,另外可以通过package的形式指定。
1.4.6.11. mappers
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
对于前3属性,只能选择之一。
1.4.7. Mapper文档的解析过程
对于class,只能是接口,会保存为接口与其动态代理的映射,如果存在了则抛异常,也就是说不能定义多次。
解析过程定义如下:
org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLMapperBuilder#parse

相关配置读取的时候,有时还要在实例构造后在读一次,即Pending字样的解析。
1.4.7.1. cache-ref
引用其他命名空间(即其他Mapper)的缓存配置,这个主要用于在多个Mapper间共享相同的缓存数据。
命名空间实际上是一个Mapper接口的全限定名。
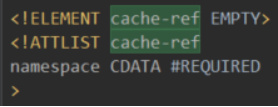
此缓存引用会存入到配置实例的缓存应用映射中(<Mapper的命名空间,被引用的命名空间>)。
1.4.7.2. cache
1.4.7.2.1. 缓存的作用
MyBatis默认开启一级缓存,配置了此元素则开启二级缓存。
1.4.7.2.2. 组成
cache元素的组成:
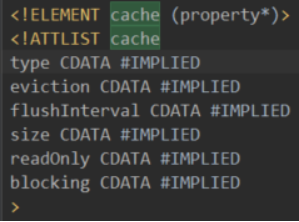
一个命名空间只能配置一个二级缓存,并且以命名空间名作为其id。
type指定了缓存的具体实现类,默认PerpetualCache。
eviction指定移除缓存记录时采用的策略,默认是LRU,即最近最久未使用的先移除。
flushInterval指定了每隔多少毫秒自动刷新,即清空缓存一次。
size指定了最多存多少条缓存记录。
另外就是readOnly、blocking,还有通过子元素可以指定若干配置。
1.4.7.2.3. 接口形式和默认实现
缓存的接口org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache。

如果没有指定type,则默认是下面的缓存实现(判等是通过id来的):

1.4.7.2.4. 缓存实例的构造过程
结合使用了构建者模式和修饰者模式。
org.apache.ibatis.mapping.CacheBuilder#build
缓存接口实现时要求必须具备一个含String类型参数的构造方法。构造type类型的缓存时就是通过反射,得到此构造方法来创建实例的,这个String实际上是Mapper的命名空间名。
实例创建后,就通过配置属性给该缓存具有的相应字段赋值。赋值前通过缓存类是否含有与配置对应的setter来判断是否赋值,然后通过此setter和字段判断值类型,然后赋值。
如果使用的是默认的缓存实现,则使用修饰者模式得到最后缓存。
修饰者缓存含一个构造方法,以缓存为参数,也是通过反射得到,然后也是应用配置的属性。只是这里的修饰者组成了一个列表,依次进行缓存封装和属性设置得到最终缓存。
接下来就是使用标准的修饰者:
flushInterval

如果不是readOnly,则修饰为序列化存储值。
也封装为key记录了请求多少次,有几次命中的缓存LoggingCache。
blocking为true,则读取缓存时需要获得锁,获得锁可以有超时设置,没有设置,则使用同步锁。

1.4.7.2.5. 缓存构造后存到配置实例中
构造得到的缓存,最后存到配置的缓存映射中,命名空间为id。
1.4.7.3. parameterMap
可以有多个这样的子元素,每一个都包含下面的组成。
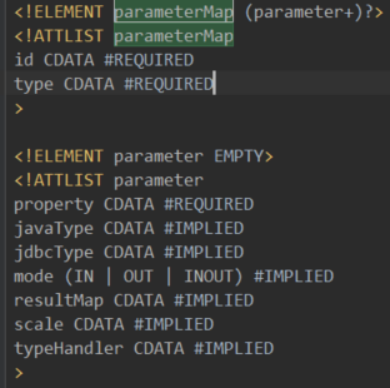
type一般就是POJO。
property为POJO字段名。
如果没有指定javaType,那么MyBatis自动解析:如果jdbcType为游标,则该字段当做ResultSet,对于此种类型resultMap是不能缺少的;如果type是一个Map,则字段为Object类;否则通过反射得到字段的类型。
如果没有指定typeHandler就不用了,如果指定了,那么它是一个类。这个类可以根据具体的Java类型创建一个对应的处理器实例(有缓存,所以一个Java类只对应一个处理器实例)。
最后的参数映射被修饰为不可修改的,指定了id=Mapper命名空间.id,POJO类,及对应的字段类型映射及处理器。
1.4.7.4. resultMap

里面很繁杂,但主要在于配置POJO和数据表的映射关系,以及数据构造的参数等。
1.4.7.5. sql
作用与resultMap类似,主要目的在于去重多个语句的相同部分,做到“一处变多处变”的效果。
1.4.7.6. select|insert|update|delete
这些配置用来生成SQL语句。
其中的id要求对应的Mapper有声明相应的方法。
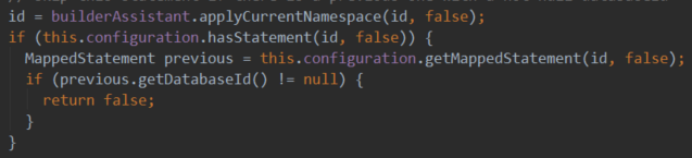
最后的生成的是一个结构体,存放在配置实例中,根据这可以很快构造出语句:
Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements

1.4.8. 会话
1.4.8.1. 会话工厂创建会话
org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSession()
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
根据配置得到事务工厂,并根据数据源、事务隔离级别、是否自动提交得到一个事务。
然后根据事务和配置,并创建指定类型的执行器:
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH
}
如果允许缓存,则封装一下。
添加拦截器列表。
得到默认的会话:
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
1.4.8.2. 通过会话得到Mapper实例
org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession#getMapper
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}

public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
Mapper实例使用动态代理创建。
1.4.8.3. Mapper方法调用
org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy#invoke
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
如果方法是Object的,则直接调用。
代理的执行过程是:
根据方法,得到对应的MapperMethod
new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());

然后执行:
org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod#execute
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
比如插入:
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
首先获取参数名与值的对应param,
然后根据语句id和此参数执行语句:
@Override
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
try {
dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.update(ms, wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
最后会话提交,提交实际上是调用事务的提交。
1.4.9. 语句执行的体系结构
1.4.9.1. 类型处理器
1.4.9.1.1. Jdbc类型的封装
org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType
public enum JdbcType {
ARRAY(Types.ARRAY),
……
CURSOR(-10), // Oracle
SQLXML(Types.SQLXML), // JDK6
DATETIMEOFFSET(-155); // SQL Server 2008
public final int TYPE_CODE;
}
Jdbc类型将Java SE核心库的java.sql.Types做了枚举封装(原来只是int型常量来表示通用的SQL类型),并添加了非通用的SQL类型。
1.4.9.1.2. 类型处理器体系的类图

1.4.9.1.3. 类型处理器:Java类型与Jdbc类型间的转换
org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandler
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
要执行SQL语句,对应数据的Java类型要转换为Jdbc类型,这发生在参数设置处,而SQL语句执行后,返回的结果要由Jdbc类型转换为Java类型,便于后续处理。与之对应,类型处理器提供了两个主要功能:1)预编译SQL语句参数设置。2)返回指定结果。在这两处,提供了类型转换操作。也可以看到,它直接使用了Java SE核心库提供的SQLException、PreparedStatement、ResultSet、CallableStatement等类型。
org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler,此基类实现了类型处理器。
对于参数设置,如果参数为null,则必须给出JdbcType。如果参数不为null,则由各个具体的基类的子类来完成参数设置(此时的JdbcType几乎都没有用到,根据Java类型直接对应了具体的设置),比如:
public class BigIntegerTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<BigInteger> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, BigInteger parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setBigDecimal(i, new BigDecimal(parameter));
}
再比如:
public class BlobTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<byte[]> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, byte[] parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(parameter);
ps.setBinaryStream(i, bis, parameter.length);
}
对于返回指定结果,基类如下:
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
T result;
try {
result = getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
而具体的执行则也由基类的具体子类完成,如上面与参数设置对应的如下:
@Override
public BigInteger getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = rs.getBigDecimal(columnName);
return bigDecimal == null ? null : bigDecimal.toBigInteger();
}
再如:
@Override
public byte[] getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
Blob blob = rs.getBlob(columnName);
byte[] returnValue = null;
if (null != blob) {
returnValue = blob.getBytes(1, (int) blob.length());
}
return returnValue;
}
1.4.9.2. 参数处理器
org.apache.ibatis.executor.parameter.ParameterHandler
public interface ParameterHandler {
Object getParameterObject();
void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps)
throws SQLException;
}
它只有一个实现:org.apache.ibatis.scripting.defaults.DefaultParameterHandler
setParameters用来给语句设置所有的IN参数,用到了类型处理器。
getParameterObject对应设置OUT参数。
1.4.9.3. 结果集处理器
org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.ResultSetHandler
public interface ResultSetHandler {
<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> handleCursorResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException;
}
只有一个实现:org.apache.ibatis.executor.resultset.DefaultResultSetHandler
handleResultSets,处理语句执行结果集(可能多个),返回Java形式的数据,如果只有一个结果集,则元素即对应的记录,如果是多个结果集,则元素是一个结果集。期间有用到配置的表属性与POJO的字段映射关系。创建的POJO实例都是通过反射来的。
返回游标情况下,对应的表属性与POJO的字段映射关系只能有一个。
handleOutputParameters用结果集来设置OUT参数。
1.4.9.4. 语句处理器
1.4.9.4.1. 语句处理器体系的类图
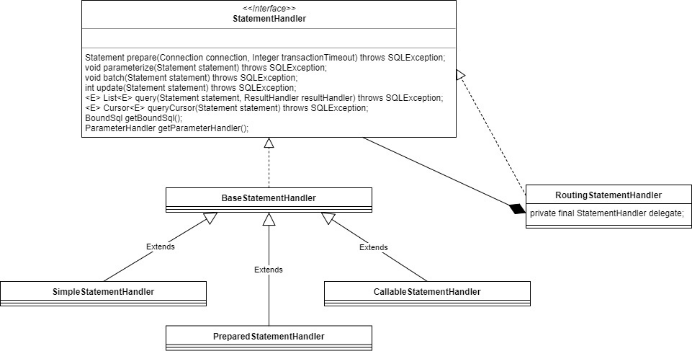
实际处理语句的是3个子类。另外,定义了一个路由语句处理器,它的作用是根据语句处理器参数构造具体的3种语句处理器中的一种。然后所有的处理都路由到这个上面去,这实际上是一个代理模式的应用。
1.4.9.4.2. 语句处理器的功能
org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler
public interface StatementHandler {
Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout)
throws SQLException;
void parameterize(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
void batch(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
int update(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
<E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)
throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(Statement statement)
throws SQLException;
BoundSql getBoundSql();
ParameterHandler getParameterHandler();
}
prepare,用连接创建语句。期间用到了配置的结果集类型,如游标只能前移、可回滚(又分结果可变敏感和不敏感)、结果集不可变更(并发模式)。也可能用到键和SQL语句。
parameterize,使用ParameterHandler根据配置为需要参数的SQL语句设置参数,CallableStatement还要注册返回参数。
update,执行SQL语句,填充自动生成的键,对于CallableStatement还要设置返回的参数以具体的值。
query,执行查询语句,并使用ResultSetHandler处理语句执行结果集(可能多个),返回Java形式的数据,如果只有一个结果集,则元素即对应的记录,如果是多个结果集,则元素是一个结果集。期间有用到配置的表属性与POJO的字段映射关系。ResultHandler参数实际上没有用到,算是开发者的疏忽吧。
1.4.9.5. 执行器
1.4.9.5.1. 执行器体系类图
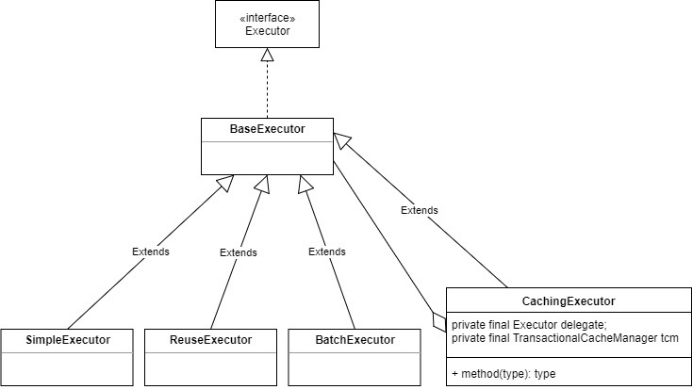
1.4.9.5.2. 执行器功能
org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor

update,清空本地缓存。得到配置,从配置创建语句处理器。接下来,Simple类型则用语句处理器准备语句、参数化语句、执行更新操作,执行完后关闭语句。而Reuse类型,则看是否之前有缓存指定SQL串的语句,有则取出,无则准备并缓存,然后参数化语句,然后执行。而Batch则判断SQL串是否最后一次添加的语句,是则重新参数化,不是则准备并参数化,然后添加到批量列表的末尾。由此也可以看出ReuseExecutor会缓存上次执行的语句,但参数化用最新的,而Batch则山将语句先存于语句列表。
Query,如果对应的语句之前缓存过结果则直接取出,否则去DB查询出来。剩下的过程也分3种情况。
FlushStatements,Simple直接返回空;Reuse关闭所有的缓存的语句,并清空缓存,也返回空;Batch则执行所有语句并返回结果,要关闭所有语句并清空缓存。
1.4.10. 总结
首先,根据配置文件和映射配置文件构建出Configuration实例,它是全局性的,几乎用到的所有配置都包含在里面了,而且它的作用范围包括了从底层到底层执行。同时会构建出会话工厂SqlSessionFactory。
接着,通过会话工厂SqlSessionFactory构建出一个会话SqlSession。
根据Mapper接口,从配置中得到动态代理工厂,继而创建出动态代理,这个动态代理包含了这个会话SqlSession实例。
在执行Mapper接口的某个方法时,实际上会调用动态代理的invoke方法,相当于拦截了,然后执行这个动态代理的方法。执行过程中,就用上了此会话和方法对应的传入参数。
执行时,会根据配置知道这是增删还是改查,构建的会话里包含了执行器Executor,接着使用语句处理器StatementHandler完成特定的执行操作,即使用参数处理器ParameterHandler将传入参数设置进SQL语句,此间借助TypeHandler完成了从Java类型到JDBC类型的转换,接着调用Java SE核心库执行,执行完成返回的结果或结果集通过ResultSetHandler处理,得到最后要返回的数据的Java类型,这个过程中,如果语句涉及到过程调用且有OUT参数的,也会借助ParameterHandler得到对应的值。
关于这个流程、框架图,请见:
https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/40422941
1.5. 参考资料
https://www.yiibai.com/mybatis/
http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/luoxn28/p/6417892.html
https://blog.csdn.net/abc5232033/article/details/79048663
https://baike.baidu.com/item/MyBatis/2824918?fr=aladdin
https://blog.csdn.net/luanlouis/article/details/40422941
http://www.mybatis.cn/category/mybatis-source/





