在图像上直方图和条形图相似,但是直方图是用来统计数据在某个值上的数量。
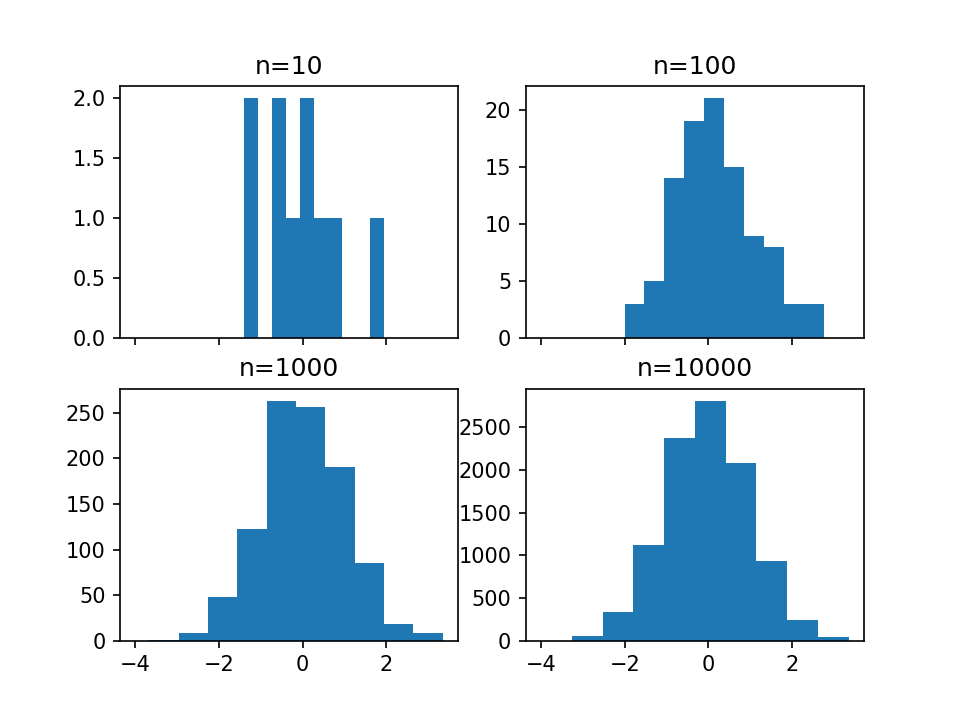
1 # 创建2*2的图像分块,并获取每个分块 2 fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True) 3 axs = [ax1,ax2,ax3,ax4] 4 5 # 分别用正态分布得到10,100,1000,10000个点 6 for n in range(0,len(axs)): 7 sample_size = 10**(n+1) 8 sample = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=sample_size) 9 axs[n].hist(sample) 10 axs[n].set_title('n={}'.format(sample_size))
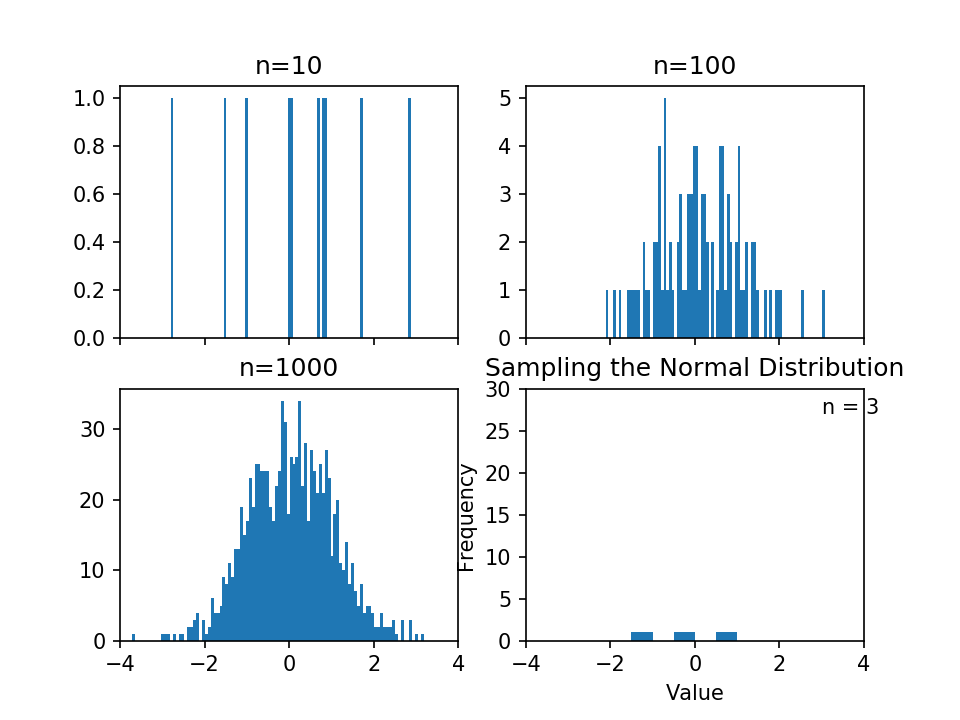
1 # 调整bins到100,增加横坐标的数量 2 fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True) 3 axs = [ax1,ax2,ax3,ax4] 4 5 for n in range(0,len(axs)): 6 sample_size = 10**(n+1) 7 sample = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=sample_size) 8 #通过修改bins更改横坐标的数量 9 axs[n].hist(sample, bins=100) 10 axs[n].set_title('n={}'.format(sample_size))
1 plt.figure() 2 Y = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=10000) 3 X = np.random.random(size=10000) 4 plt.scatter(X,Y)

1 # use gridspec to partition the figure into subplots 2 import matplotlib.gridspec as gridspec 3 4 plt.figure()
#通过把图分成3*3的9块区域,来自定义子图 5 gspec = gridspec.GridSpec(3, 3) 6 7 top_histogram = plt.subplot(gspec[0, 1:]) 8 side_histogram = plt.subplot(gspec[1:, 0]) 9 lower_right = plt.subplot(gspec[1:, 1:])
对中间的图进行绘制
1 Y = np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=10000) 2 X = np.random.random(size=10000) 3 lower_right.scatter(X, Y) 4 top_histogram.hist(X, bins=100) 5 s = side_histogram.hist(Y, bins=100, orientation='horizontal')
1 # 对上面和左侧的图进行绘制 2 top_histogram.clear() 3 top_histogram.hist(X, bins=100, normed=True) 4 side_histogram.clear() 5 side_histogram.hist(Y, bins=100, orientation='horizontal', normed=True) 6 # flip the side histogram's x axis 7 side_histogram.invert_xaxis()
1 # 改变坐标的限制 2 for ax in [top_histogram, lower_right]: 3 ax.set_xlim(0, 1) 4 for ax in [side_histogram, lower_right]: 5 ax.set_ylim(-5, 5)

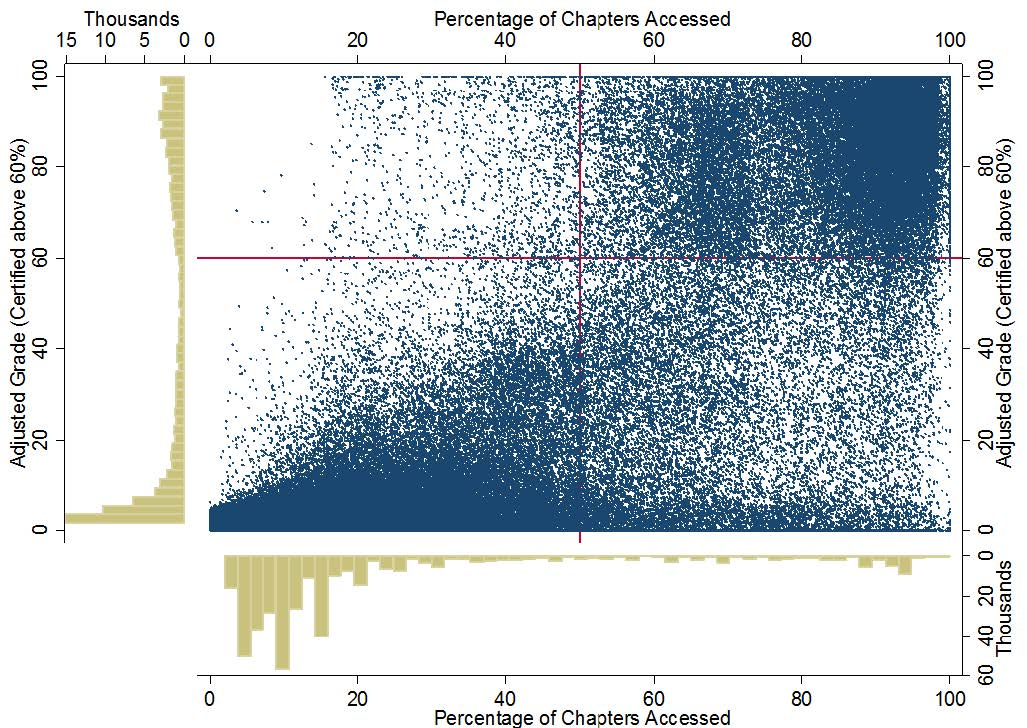
1 %%HTML 2 <img src='http://educationxpress.mit.edu/sites/default/files/journal/WP1-Fig13.jpg' />