Let's define logical OR as an operation on two logical values (i. e. values that belong to the set {0, 1}) that is equal to 1 if either or both of the logical values is set to 1, otherwise it is 0. We can define logical OR of three or more logical values in the same manner:
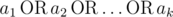 where
where 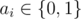 is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
Nam has a matrix A consisting of m rows and n columns. The rows are numbered from 1 to m, columns are numbered from 1 to n. Element at row i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) and column j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) is denoted as Aij. All elements of A are either 0 or 1. From matrix A, Nam creates another matrix B of the same size using formula:
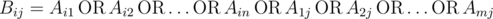 .
.
(Bij is OR of all elements in row i and column j of matrix A)
Nam gives you matrix B and challenges you to guess matrix A. Although Nam is smart, he could probably make a mistake while calculating matrix B, since size of A can be large.
The first line contains two integer m and n (1 ≤ m, n ≤ 100), number of rows and number of columns of matrices respectively.
The next m lines each contain n integers separated by spaces describing rows of matrix B (each element of B is either 0 or 1).
In the first line, print "NO" if Nam has made a mistake when calculating B, otherwise print "YES". If the first line is "YES", then also print mrows consisting of n integers representing matrix A that can produce given matrix B. If there are several solutions print any one.
2 2
1 0
0 0
NO
2 3
1 1 1
1 1 1
YES
1 1 1
1 1 1
2 3
0 1 0
1 1 1
YES
0 0 0
0 1 0
题意是一个矩阵B的b[i][j]是所有A矩阵的a[i][k]和a[k][j]或起来的值,给一个B矩阵,问是否存在这样的A矩阵,并输出方案
因为是或……所以在B中出现的0必须在A中一横一竖都为0
所以先把B中0的情况搞完,然后判一下现在的B矩阵中1的位置对应的A的一行一列是否存在至少一个1
15分钟……有些慢了,你看卓神6分钟A掉
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<deque>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<ctime>
#define LL long long
#define inf 0x7ffffff
#define pa pair<int,int>
#define pi 3.1415926535897932384626433832795028841971
using namespace std;
int mat[110][110];
int a[110][110];
int n,m;
inline LL read()
{
LL x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
void ex()
{
printf("NO");
exit(0);
}
int main()
{
n=read();m=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
mat[i][j]=1;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
a[i][j]=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
int x=a[i][j];
if (!x)
{
for (int k=1;k<=n;k++)
mat[k][j]=0;
for (int k=1;k<=m;k++)
mat[i][k]=0;
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
if(a[i][j])
{
bool mrk=0;
for (int k=1;k<=n;k++)if (mat[k][j])mrk=1;
for (int k=1;k<=m;k++)if (mat[i][k])mrk=1;
if (!mrk)ex();
}
printf("YES\n");
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
printf("%d ",mat[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号