20172311 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第九周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
本周对异常和递归进行了学习
- 异常的处理方式有两种:一种是直接抛出,并从异常处终止程序;另一种是捕获并处理异常,从而使程序继续运行。
- 捕获和处理异常主要运用
try-catch语句。 - 通过继承
Exception类可以自定义一个新的异常 - 处理IO异常的常用方法是抛出异常。
- 对于某些问题,递归是最精炼和适当的解法,但对于其他问题,递归则不如迭代方法直接。
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
问题:什么是IO操作
- 问题一解决方案:通过上网查阅资料了解到:
所谓IO,也就是Input与Output的缩写
对于文件内容的操作主要分为两大类分别是:
1.字符流
2.字节流
其中,字符流有两个抽象类:Writer Reader
其对应子类FileWriter和FileReader可实现文件的读写操作
BufferedWriter和BufferedReader能够提供缓冲区功能
,用以提高效率
同样,字节流也有两个抽象类:InputStream OutputStream
其对应子类有FileInputStream和FileOutputStream实现文件读写
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream提供缓冲区功能。
- 字符流写入的例子:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args ) {
//创建要操作的文件路径和名称
//其中,File.separator表示系统相关的分隔符,Linux下为:/ Windows下为:\\
String path = File.separator + "home" + File.separator + "siu" +
File.separator + "work" + File.separator + "demo.txt";
//由于IO操作会抛出异常,因此在try语句块的外部定义FileWriter的引用
FileWriter w = null;
try {
//以path为路径创建一个新的FileWriter对象
//如果需要追加数据,而不是覆盖,则使用FileWriter(path,true)构造方法
w = new FileWriter(path);
//将字符串写入到流中,\r\n表示换行想有好的
w.write("Nerxious is a good boy\r\n");
//如果想马上看到写入效果,则需要调用w.flush()方法
w.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//如果前面发生异常,那么是无法产生w对象的
//因此要做出判断,以免发生空指针异常
if(w != null) {
try {
//关闭流资源,需要再次捕捉异常
w.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- 字符流读取的实例:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args ) {
String path = File.separator + "home" + File.separator + "siu" +
File.separator + "work" + File.separator + "demo.txt";
FileReader r = null;
try {
r = new FileReader(path);
//方式一:读取单个字符的方式
//每读取一次,向下移动一个字符单位
int temp1 = r.read();
System.out.println((char)temp1);
int temp2 = r.read();
System.out.println((char)temp2);
//方式二:循环读取
//read()方法读到文件末尾会返回-1
/*
while (true) {
int temp = r.read();
if (temp == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.print((char)temp);
}
*/
//方式三:循环读取的简化操作
//单个字符读取,当temp不等于-1的时候打印字符
/*int temp = 0;
while ((temp = r.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)temp);
}
*/
//方式四:读入到字符数组
/*
char[] buf = new char[1024];
int temp = r.read(buf);
//将数组转化为字符串打印,后面参数的意思是
//如果字符数组未满,转化成字符串打印后尾部也许会出现其他字符
//因此,读取的字符有多少个,就转化多少为字符串
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,temp));
*/
//方式五:读入到字符数组的优化
//由于有时候文件太大,无法确定需要定义的数组大小
//因此一般定义数组长度为1024,采用循环的方式读入
/*
char[] buf = new char[1024];
int temp = 0;
while((temp = r.read(buf)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buf,0,temp));
}
*/
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(r != null) {
try {
r.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
更多示例见参考资料:
java中的IO操作总结
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
问题1:做pp12.1时使用while语句出现逻辑错误
- 错误的判断是否为回文的方法代码如下:
public static boolean Palindrome(String str1){
int left=0;
int right=str1.length()-1;
boolean result;
while (str1.charAt(left) == str1.charAt(right) && left < right) {
str1 = str1.substring(1, str1.length() - 1);
Palindrome(str1);
}
if (left>=right)
result=true;
else
result=false;
return result;
}
- 问题1解决方案:自己写的方法通过单步调试仍未找到解决方法
通过询问同学找到适用的方法代码如下:
public static boolean Palindrome(String str){
if(str.length()==1)
return true ;
else
if(str.length()==2)
{
if(str.charAt(0)==str.charAt(str.length()-1))
return true ;
else
return false ;
}
else
if(str.charAt(0)==str.charAt(str.length()-1))
return Palindrome(str.substring(1,str.length()-1)) ;
else
return false;
}
问题2:做pp12.9时遇到较大麻烦,不知道怎样使用递归方法输出杨辉三角
问题2解决方案:
- 网上查阅资料找到一个生成10行杨辉三角的代码如下:
//递归输出杨辉三角
public class Yanghuitriangle {
public static int digui(int i,int j)
{
if(j==0||j==i)
return 1;
else
return digui(i-1,j)+digui(i-1,j-1);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int tri[][];
tri=new int[10][10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++)
tri[i][j]=digui(i,j);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
System.out.println();
for(int n=10-i;n>=1;n--)
System.out.print(" ");
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++)
System.out.print(tri[i][j]+" ");
}
}
}
参考资料的链接:
java实现递归输出杨辉三角
- 修改后实现生成指定行数N的杨辉三角并可以输出第N行的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Pascal {
public static int digui(int i, int j) {
if (j == 0 || j == i)
return 1;
else
return digui(i - 1, j) + digui(i - 1, j - 1);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入杨辉三角的行数: ");
int raw = scan.nextInt();
int tri[][] = new int[raw][raw];
for (int i = 0; i < raw; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
tri[i][j] = digui(i, j);
System.out.println("共有N行的杨辉三角为: ");
for (int i = 0; i < raw; i++) {
System.out.println();
for (int n = raw - i; n >= 1; n--)
System.out.print(" ");
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
System.out.print(+tri[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("共有N行的杨辉三角的第N行为: ");
for (int j = 0; j < raw; j++)
System.out.print(tri[(raw - 1)][j] + " ");
}
}
代码托管

上周考试错题总结
-
错题1

理解:D: 异常不会被抛出到异常类中 -
错题2

理解:不理解!原因如下: 这确实是按顺序输出的啊!!

-
错题3
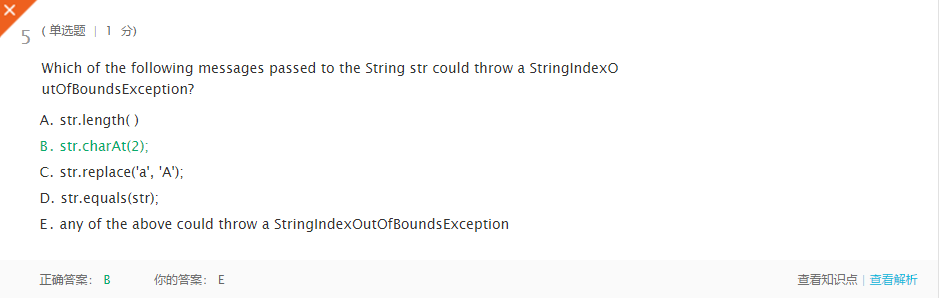
理解:如果字符串方法的参数引用字符串中超出字符串边界的位置,则会抛出StringIndexOutOfBoundsException。可以发生在charAt方法中。 -
错题4

理解:可以保存任何给定的对象以供将来使用。这种特性称为持久性,通过将对象的实例数据保存到文件中来实现这一点 -
错题5
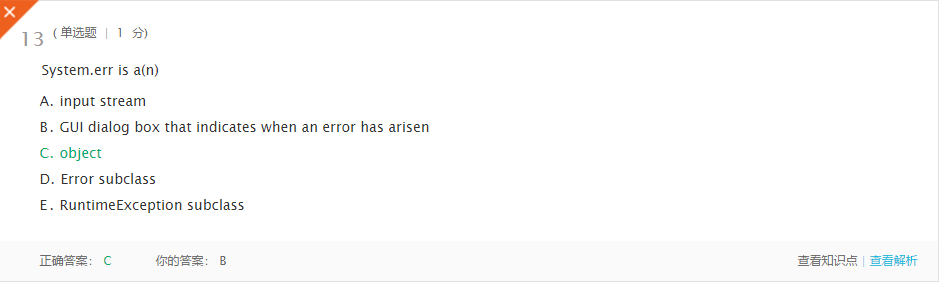
理解:System.err是一个对象。 -
错题6
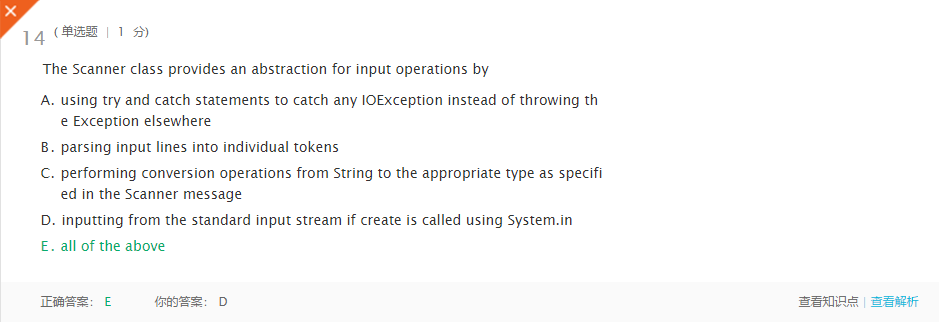
错因:概念理解欠缺。 -
错题7
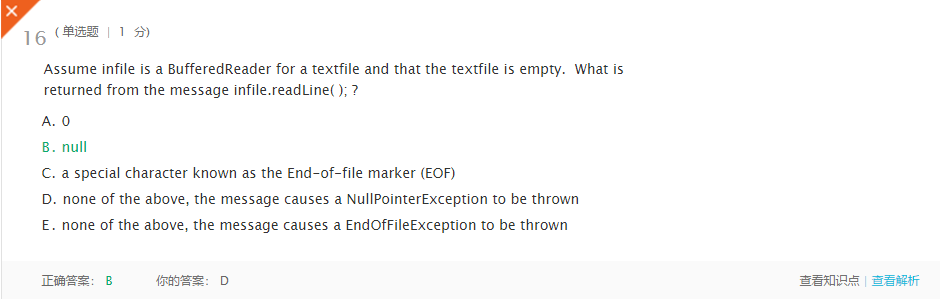
理解:能使用readLine()方法说明文件已经有了,readLine()方法用于返回字符串,该字符串等于文件中的下一个文本项;如果文件为空,则返回null -
错题8

理解:PrintWriter是专门为文件而设计的,因此有错误检查机制,而PrintStream没有 -
错题9
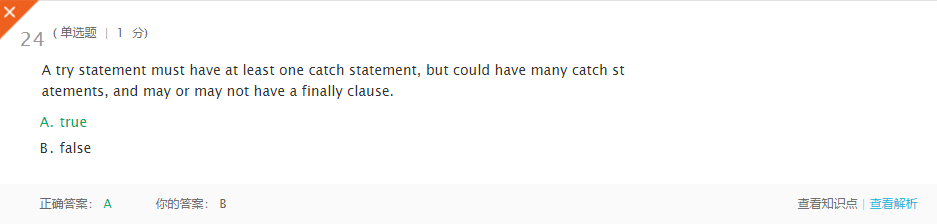
错因:笔误!!!! -
错题10

验证:

确实只是执行了第一个错误!
结对及互评
黄宇瑭小伙伴编码能力的提升很大,继续加油吧!!!
点评过的同学博客和代码
- 本周结对学习情况
感悟
坚持到底就是胜利!
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 28/28 | 1/1 | 16/16 | |
| 第二周 | 710/738 | 1/2 | 20/36 | |
| 第三周 | 426/1164 | 1/3 | 16/52 | |
| 第四周 | 1068/2232 | 2/5 | 20/72 | |
| 第五周 | 604/2928 | 1/6 | 22/94 | |
| 第六周 | 609/3537 | 1/7 | 22/116 | |
| 第七周 | 599/4136 | 1/8 | 18/134 | |
| 第八周 | 1052/5188 | 3/11 | 20/154 | |
| 第九周 | 866/6054 | 1/12 | 20/174 |
-
计划学习时间:18小时
-
实际学习时间:20小时
-
改进情况:努力提前完成作业,留出更多时间扩展。



