上下文管理
- threading.local
- 为每个线程开辟空间,使得线程之间进行数据隔离。
- 应用:DBUtils中为每个线程创建一个数据库连接时使用。
Local是threading.local的加强版,它不光对线程,对协程也开辟了自己的空间;
# __getattr__ (是在 obj.xxx 的取值的时候调用的 ); __setattr__(obj.xxx = 123 设置值的时候调用的)
# threading.local 的加强版 (不仅包含线程 也包含协程 )
try:
from threading import get_ident
# from greenlet import getcurrent as get_ident
except Exception:
from greenlet import getcurrent as get_ident
class Local(object):
#__slots__ 里面定义的字符串,才能 self. ; 没有定义的就不能
__slots__ = ("__storage__", "__ident_func__")
def __init__(self):
object.__setattr__(self, "__storage__", {})
object.__setattr__(self, "__ident_func__", get_ident)
def __getattr__(self, item):
try:
return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][item]
except Exception:
return None
def __setattr__(self, key, value):
ident = self.__ident_func__()
storage = self.__storage__
try:
storage[ident][key] = value
except Exception:
storage[ident] = {key: value}
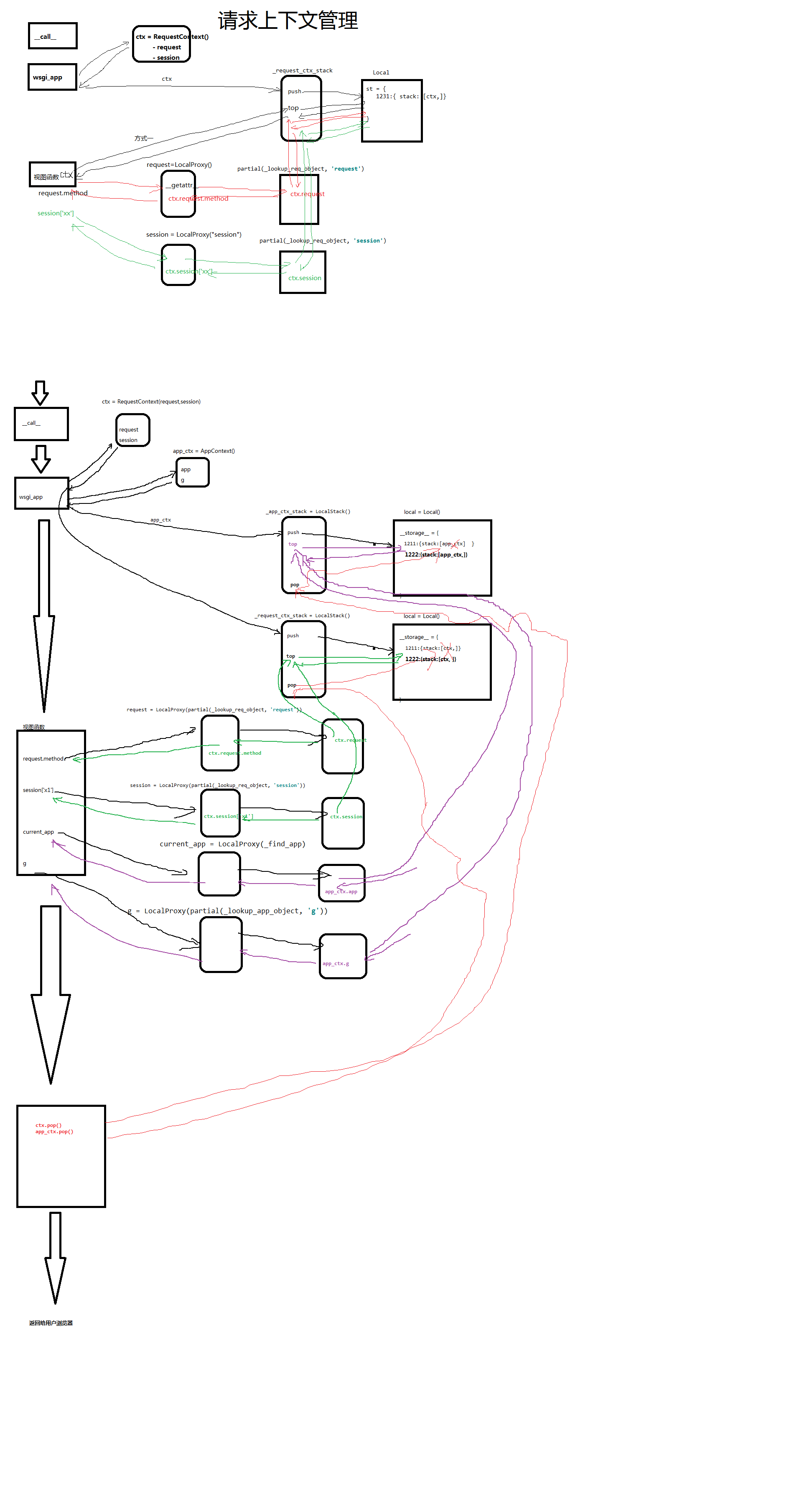
2. 上下文管理:
- 请求上下文(ctx=RequestContext()):request/session
- App上下文(app_ctx=AppContext()): app/g
- 程序启动:
两个Local:
local1 = {
}
local2 = {
}
两个LocalStack:
_request_ctx_stack
_app_ctx_stack
- 请求到来
对数据进行封装:
ctx = RequestContext(request,session)
app_ctx = AppContext(app,g)
保存数据:
将包含了(app,g)数据的app_ctx对象,利用 _app_ctx_stack=LocalStack()将app_ctx添加到Local中
storage = {
1231:{stack:[app_ctx(app,g),]}
}
将包含了request,session数据的ctx对象,利用_request_ctx_stack=LocalStack(),将ctx添加到Local中
storage = {
1231:{stack:[ctx(request,session),]}
}
- 视图函数处理:
from flask import Flask,request,session,current_app,g
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/index')
def index():
# 去请求上下文中获取值 _request_ctx_stack
request.method
session['xxx']
# request = LocalProxy(partial(_lookup_req_object, "request"))
# 去app上下文中获取值:_app_ctx_stack
print(current_app)
print(g)
return "Index"
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
app.wsgi_app
- 结束
_app_ctx_stack.pop()
_request_ctx_stack.pop()
问题:
1. Flask中g的生命周期?
每一次请求过来的时候,创建g ,该请求结束后 g 就消失了
2. g和session一样吗?
不一样,当下一次请求来的时候,上个请求的g 不存在,而session存在,session是以加密的形式存放到cookie中的
3. g和全局变量一样吗?
不一样; 全局变量 是项目一启动的时候就创建的,而g则是请求来以后创建的.
全局变量 是存放到内存中的,不会消失;而g会随着请求结束后消失.
自己写的
try:
from threading import get_ident
# from greenlet import getcurrent as get_ident
except Exception:
from greenlet import getcurrent as get_ident
class Local(object):
#__slots__ 里面定义的字符串,才能 self. ; 没有定义的就不能
__slots__ = ("__storage__", "__ident_func__")
def __init__(self):
object.__setattr__(self, "__storage__", {})
object.__setattr__(self, "__ident_func__", get_ident)
def __getattr__(self, item):
try:
return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][item]
except Exception:
return None
def __setattr__(self, key, value):
ident = self.__ident_func__()
storage = self.__storage__
try:
storage[ident][key] = value
except Exception:
storage[ident] = {key: value}
#LocalStack是帮助我们方便的去维护Local 里面的栈
class LocalStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self._local = Local()
#往栈里面添加值
def push(self,obj):
rv = getattr(self._local,"stack",None)
if rv is None:
#用对象.stack =[] 来触发 Local类下面的__setattr__
self._local.stack = rv = []
rv.append(obj)
return rv
#取值,先进后出
def pop(self):
#stack >[]
stack = getattr(self._local, "stack", None)
if stack is None:
return None
elif len(stack) == 1:
return stack[-1]
else:
return stack.pop()
def top(self):
try:
return self._local.stack[-1]
except Exception:
return None
import functools
_request_ctx_stack = LocalStack()
class RequestContext(object):
def __init__(self):
self.session = "session"
self.request = "request"
ctx = RequestContext()
#_request_ctx_stack 帮助我们维护一个 __storage__ = {}
_request_ctx_stack.push(ctx)
'''
__storage__:{
123:{"stack":[ctx(session/request)]},
113:{"stack":[]}
}
'''
def _lookup_req_object(arg):
ctx = _request_ctx_stack.top()
return getattr(ctx,arg)
#偏函数 ,自动的帮你传入参数
session = functools.partial(_lookup_req_object,"session")
request = functools.partial(_lookup_req_object,"request")
print(request())



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号