运算符重载
运算符重载概念:对已有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型
4.5.1 加号运算符重载
作用:实现两个自定义数据类型相加的运算

成员函数加法重载运算
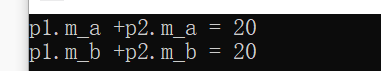
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int a = 10; 4 int b = 10; 5 int c = a + b; 6 class person 7 { 8 public: 9 int m_a; 10 int m_b; 11 person operator+ (person& p) 12 { 13 person tempt; 14 tempt.m_a = m_a + p.m_a; 15 tempt.m_b = m_b + p.m_b; 16 return tempt; 17 } 18 }; 19 int main() 20 { 21 person p1; 22 p1.m_a = 10; 23 p1.m_b = 10; 24 person p2; 25 p2.m_a = 10; 26 p2.m_b = 10; 27 person p3 = p1 + p2; //本质上是 :p1.operaor+(p2)
28 cout <<"p1.m_a +p2.m_a = " << p3.m_a << endl 29 << "p1.m_b +p2.m_b = " << p3.m_b << endl; 30 }
全局函数加法重载运算
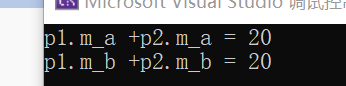
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int a = 10; 4 int b = 10; 5 int c = a + b; 6 class person 7 { 8 public: 9 int m_a; 10 int m_b; 11 }; 12 person operator+ (person& p1, person& p2) 13 { 14 person tempt; 15 tempt.m_a = p1.m_a + p2.m_a; 16 tempt.m_b = p1.m_b + p2.m_b; 17 return tempt; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 person p1; 22 p1.m_a = 10; 23 p1.m_b = 10; 24 person p2; 25 p2.m_a = 10; 26 p2.m_b = 10; 27 person p3 = p1 + p2 ;//本质上是operator+(p1,p2)
28 cout <<"p1.m_a +p2.m_a = " << p3.m_a << endl 29 << "p1.m_b +p2.m_b = " << p3.m_b << endl; 30 }
运算符的函数重载
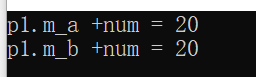
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 int a = 10; 4 int b = 10; 5 int c = a + b; 6 class person 7 { 8 public: 9 int m_a; 10 int m_b; 11 }; 12 person operator+ (person& p1, int num ) 13 { 14 person tempt; 15 tempt.m_a = p1.m_a + num ; 16 tempt.m_b = p1.m_b + num; 17 return tempt; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 person p1; 22 p1.m_a = 10; 23 p1.m_b = 10; 24 person p3 = p1 + 10; 25 cout <<"p1.m_a +num = " << p3.m_a << endl 26 << "p1.m_b +num = " << p3.m_b << endl; 27 }
总结1:对于内置的数据类型(比如int类型)的表达式的的运算符是不可能改变的
总结2:不要滥用运算符重载(比如加法写成减法等等,会让人看不懂)
左移运算符重载
作用:可以输出自定义数据类型
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //左移运算重载符 4 class person 5 { 6 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, person& p); 7 //friend void test01();可以这样做也可以下面那样做 8 public://也可以这样做 9 person(int a, int b) 10 { 11 m_a = a; 12 m_b = b; 13 } 14 private: 15 //利用成员函数重载 左移运算符 16 //如果不知道函数会返回什么先写void 17 //如果是这样void operator<<(person& p),那么就会变成p.operator<<(p) 18 //如果是这样void operator<<(cout),那么就会变成p.operator<<(cout),简化版本为,p<<cout,与希望的cout << p不符 19 //通常不会用成员函数调用重载<<运算符,因为无法实现cout在左侧 20 /*void operator<<(person&p) 21 { 22 23 }*/ 24 int m_a; 25 int m_b; 26 }; 27 //只能利用全局函数重载左移运算符 28 ostream &operator<<(ostream& cout, person& p)//本质是 operator << (cout , p) 简化 cout << p 29 { 30 cout << "m_a = " << p.m_a << ",m_b = " << p.m_b << endl; 31 return cout; 32 } 33 //ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, person& p)//本质是 operator << (cout , p) 简化 cout << p 34 //{ 35 // out << "m_a = " << p.m_a << ",m_b = " << p.m_b << endl; 36 // return out; 也可以 ,因为引用的就是给它起别名,这本质上还是cout 37 //} 38 void test01() 39 { 40 person p(10,10); 41 /*p.m_a = 10; 42 p.m_b = 10;*/ 43 cout << p << endl; 44 } 45 int main() 46 { 47 test01(); 48 }总结:重载左移运算符配合友元可以实现输出自定义数据类型
递增运算符重载
作用: 通过重载递增运算符,实现自己的整型数据
前置递增
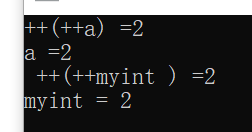
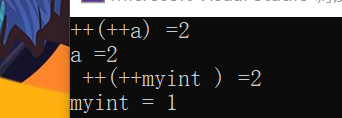
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class myinteger 4 { 5 /*friend void test01();*/ 6 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, myinteger myint); 7 public: 8 myinteger() 9 { 10 m_num = 0; 11 } 12 //重载前置++运算符,先输出原数据在加1 13 myinteger& operator++() //地址传递,指向的是地址,不会创建新副本,对该地址持有者进行直接更改 14 { 15 //先进行++运算 16 m_num++; 17 //再将自身做返回 18 return *this; 19 } 20 21 private: 22 int m_num; 23 }; 24 //重载左移运算符 25 ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, myinteger myint) 26 { 27 cout << myint.m_num; 28 return cout; 29 } 30 void test01() 31 { 32 int a = 0; 33 cout << "++(++a) =" << ++(++a) << endl; 34 cout << "a =" << a << endl; 35 myinteger myint; 36 cout << " ++(++myint ) =" <<++(++myint) << endl; 37 cout <<"myint = " << myint << endl; 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 test01(); 43 }
1 myinteger operator++() 2 { 3 //先进行++运算 4 m_num++; 5 //再将自身做返回 6 return *this; 7 } 8 9 void test01() 10 { 11 int a =0; //内置数据类型,所以++都是对同一个a进行的 12 cout << "++(++a) =" << ++(++a) << endl; 13 cout << "a =" << a << endl;//所以结果也是2 14 myinteger myint;//通过值传递进行,每执行完一次操作后都会创造新的副本 15 cout << " ++(++myint ) =" <<++(++myint) << endl;//(++myint )后创造一个新的myint在进行++操作,也就是说相当于,对同一个myint只进行了一次++操作,所以++(++myint ) = 2,但是myint却只等于1 16 cout <<"myint = " << myint << endl; 17 }
后置递增
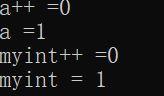
1 myinteger operator++(int)//后置递增需要返回 值,而不是地址,因为返回的是局部对象 2 { 3 //先记录当时结果 4 myinteger temp = *this;//,操作完之后就被释放掉了,后面返回操作就是非法的了 5 //后进行递增运算 6 m_num++; 7 //最后将记录的结果返回 8 return temp; 9 } 10 void test02() 11 { 12 int a = 0; 13 cout << "a++ =" << a++ << endl; 14 cout << "a =" << a << endl; 15 myinteger myint; 16 cout << "myint++ =" << myint++<< endl;//因为值传递每次执行后会创建新副本所以不能(myint++)++链式相加 17 cout << "myint = " << myint << endl; 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 test02(); 22 }
总结: 前置递增返回引用,后置递增返回值
赋值运算符重载
c++编译器至少给一个类添加4个函数
- 默认构造函数(无参,函数体为空)
- 默认析构函数(无参,函数体为空)
- 默认拷贝构造函数,对属性进行值拷贝
- 赋值运算符 operator=, 对属性进行值拷贝
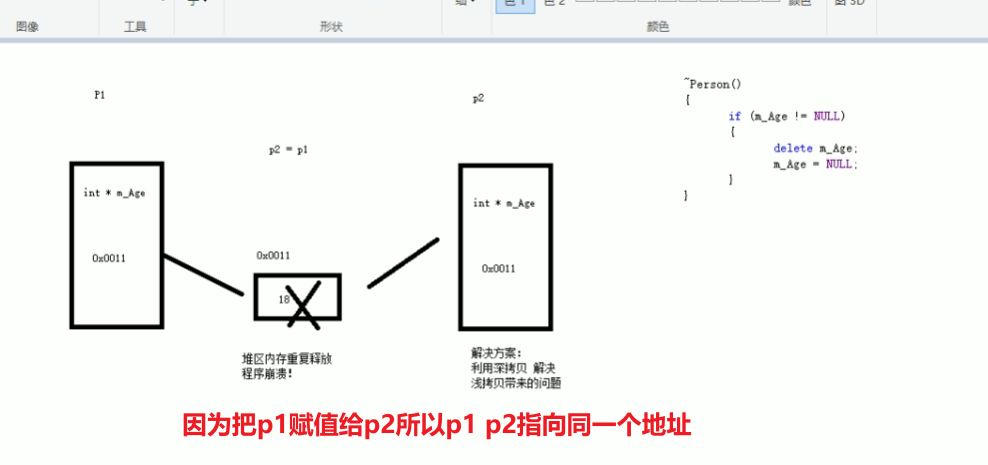
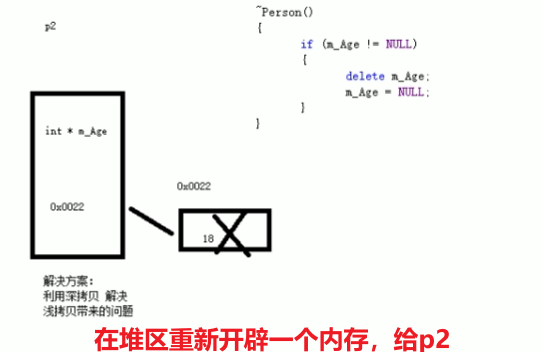
如果类中有属性指向堆区,做赋值操作时也会出现深浅拷贝问题
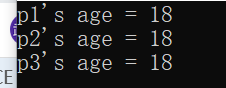
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //赋值运算符重载 4 class person 5 { 6 public: 7 person(int age) 8 { 9 m_age = new int(age); 10 } 11 ~person() 12 { 13 if (m_age != NULL) 14 { 15 delete m_age ; 16 m_age = NULL; 17 } 18 } 19 //重载 赋值运算符 20 person& operator = (person& p) 21 { 22 //编译器提供浅拷贝 23 //m_age= p.m_age 24 //先判断是否有属性在堆区,如果有先释放干净,然后进行深拷贝 25 if (m_age != NULL) 26 { 27 delete m_age; 28 m_age = NULL; 29 } 30 //深拷贝 31 m_age = new int(*p.m_age); 32 //返回对象本身 33 return *this;//this指向对象本身 34 } 35 int* m_age; 36 }; 37 void test01() 38 { 39 person p1(18); 40 person p2(20); 41 person p3(30); 42 p3 = p2 = p1;//赋值操作 43 cout << "p1's age = " << *p1.m_age << endl; 44 cout << "p2's age = " << *p2.m_age << endl; 45 cout << "p3's age = " << *p3.m_age << endl; 46 } 47 int main() 48 { 49 test01(); 50 //对于内置的数据类型默认可以运行连等于操作 51 /*int a = 10; 52 int b = 20; 53 int c = 30; 54 c = b = a; 55 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 56 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 57 cout << "c = " << c << endl;*/ 58 }
关系运算符重载
**作用:**重载关系运算符,可以让两个自定义类型对象进行对比操作
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 //重载关系运算符 4 class person 5 { 6 public: 7 person(string name, int age) 8 { 9 m_name = name; 10 m_age = age; 11 } 12 bool operator==(person &p) 13 { 14 if (this->m_name == p.m_name && this->m_age == p.m_age) 15 { 16 return true; 17 } 18 else 19 return false; 20 } 21 bool operator!=(person& p) 22 { 23 if (this->m_name != p.m_name && this->m_age != p.m_age) 24 { 25 return true; 26 } 27 return false; 28 } 29 string m_name; 30 int m_age; 31 }; 32 void test01() 33 { 34 person p1("tom", 18); 35 person p2("tom", 18); 36 if (p1 == p2) 37 { 38 cout << "p1 == p2 " << endl; 39 } 40 } 41 void test02() 42 { 43 person p3("tom", 18); 44 person p4("jerry", 18); 45 if (p3 == p4) 46 { 47 cout << "p3 == p4 " << endl; 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 cout << "p3 != p4 " << endl; 52 } 53 } 54 void test03() 55 { 56 person p5("tom", 18); 57 person p6("jerry", 18); 58 if (p5 != p6) 59 { 60 cout << "p5 != p6 " << endl; 61 } 62 else 63 { 64 cout << "p5 == p6 " << endl; 65 } 66 } 67 int main() 68 { 69 test01(); 70 test02(); 71 test03(); 72 }
函数调用运算符重载
- 函数调用运算符 () 也可以重载
- 由于重载后使用的方式非常像函数的调用,因此称为仿函数
- 仿函数没有固定写法,非常灵活
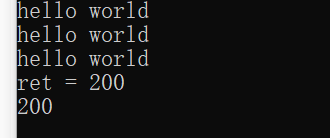
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 //函数调用运算符重载 5 //打印出类 6 class myprint 7 { 8 public: 9 //重载函数调用运算符 10 void operator()(string test) 11 { 12 cout << test << endl; 13 } 14 }; 15 void myprint02(string test) 16 { 17 cout << test << endl; 18 } 19 void test01() 20 { 21 myprint mprint; 22 mprint("hello world"); 23 } 24 void test02() 25 { 26 myprint mprint; 27 mprint("hello world");//由于使用起来非常类似于函数调用,因此称之为仿函数 28 myprint02("hello world");//函数调用 29 } 30 ////仿函数非常灵活,没有固定写法 31 ////加法类 32 class myadd 33 { 34 public: 35 int operator()(int num1, int num2) 36 { 37 return num1 + num2; 38 } 39 }; 40 void test03() 41 { 42 myadd myad; 43 int ret = myad(100, 100); 44 cout <<"ret = " << ret << endl; 45 //匿名函数对象 46 cout << myadd()(100, 100) << endl;//当前行执行完了立马释放 47 } 48 int main() 49 { 50 test01(); 51 test02(); 52 test03(); 53 }





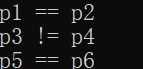


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结