Java网络编程
1. 获取网络地址ip/domin
InetAddress 获取
package com.fengye.socket.ipaddress; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; /** * @Description: * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 11:30 */ public class TestInetAddress { public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException { InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"); InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); InetAddress deskTopName = InetAddress.getByName("DESKTOP-3POL04N"); // 本机用户名 InetAddress bdAddress = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); byte[] address = new byte[]{(byte) 192, (byte) 168,5,2}; InetAddress byAddress = InetAddress.getByAddress(address); System.out.println(inetAddress); // /127.0.0.1 System.out.println(localhost); // localhost/127.0.0.1 System.out.println(localHost); // DESKTOP-3POL04N/192.168.1.4 System.out.println(deskTopName); // DESKTOP-3POL04N/192.168.1.4 System.out.println(bdAddress); // www.baidu.com/39.156.66.18 System.out.println(byAddress); // /192.168.5.2 System.out.println(localhost.getAddress()); System.out.println(localhost.getCanonicalHostName()); // 获取规范名 System.out.println(localhost.getHostAddress()); // ip System.out.println(localhost.getHostName()); // 域名 主机名 } }
2.Port 端口
-
计算机端口号用于区分不同的进程
-
计算机端口按端口号可分为3大类:
(1)公认端口:从0到1023,它们紧密绑定于一些服务。通常这些端口的通讯明确表明了某种服务的协议。常用的有:http: 80 https: 443 ftp: 21 ssh: 22 telnet: 23
(2)注册端口:从1024到49151。它们松散地绑定于一些服务。也就是说有许多服务绑定于这些端口,这些 端口同样用于许多其它目的。常用的有:TomCat: 8080 MySql: 3306 Oracle:1506
(3)动态和私有端口:从49152到65535。理论上,不应为服务分配这些端口。实际上,机器通常从 1024起分配动态端口。
-
对于不同的传输层传输协议,在进行数据封装时包头信息不一样,即使UDP包和TCP包使用同一个端口,也不会导致端口冲突。
-
查看端口命令
netstat -a # netstat -ano|findstr "7024" #查看指定端口 tasklist|findstr "7024" # 查看指定端口进程
InetSocketAddress
package com.fengye.socket.socketaddress; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * @Description: * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 11:42 */ public class TestInetSocketAddress { public static void main(String[] args) { InetSocketAddress localhost = new InetSocketAddress("192.168.1.4", 8080); // ip/主机+创建端口对象 System.out.println(localhost.getAddress()); // /192.168.1.4 System.out.println(localhost.getHostName()); // DESKTOP-3POL04N System.out.println(localhost.getPort()); // 获得端口号 8080 System.out.println(localhost.getHostString()); // DESKTOP-3POL04N } }
3.通信协议
传输层通信协议
-
TCP:面向连接
-
UDP:非面向连接
4.TCP编程实现
Java语言的基于套接字编程分为服务端编程和客户端编程,其通信模型如图所示:
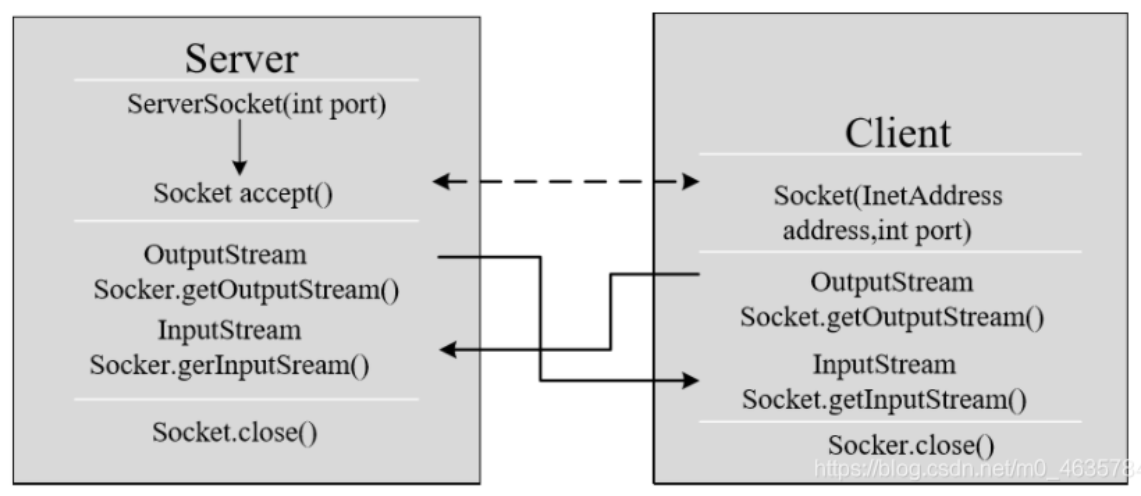
4.1.TCP编程简单C/S通信示例
1、客户端Socket的工作过程包含以下四个基本的步骤:
创建 Socket:根据指定服务端的 IP 地址或端口号构造 Socket 类对象。若服务器端响应,则建立客户端到服务端的通信路线。若连接失败,则会出现异常。
打开连接到 Socket 的输入/出流: 使用 getInputStream()方法获得输入流,使用 getOutputStream()方法获得输出流,进行数据传输
按照一定的协议对 Socket 进行读/写操作:通过输入流读取服务器放入线路的信息(但不能读取自己放入路线的信息),通过输出流将信息写入线程
/** * @Description: * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 11:56 */ public class TestTcpClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8888); OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write("你好,我是机器人小爱,正在为你转接人工服务通信,建立连接中。。。".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); if (outputStream != null) { outputStream.close(); } if (socket != null) { socket.close(); } } }
调用 ServerSocket(int port) :创建一个服务器端套接字,并绑定到指定端口 上。用于监听客户端的请求。
调用 accept():监听连接请求,如果客户端请求连接,则接受连接,返回通信 套接字对象。
调用该Socket类对象的 getOutputStream() 和 getInputStream ():获取输出 流和输入流,开始网络数据的发送和接收。
/** * @Description: * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 12:09 */ public class TestTcpServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8888); System.out.println("连接建立中"); Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept(); System.out.println("与"+clientSocket.getInetAddress()+"成功建立连接"); InputStream inputStream = clientSocket.getInputStream(); ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len=0; while ((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ out.write(buffer,0,len); System.out.println(out.toString()); } if(out!=null) out.close(); if (inputStream!=null) inputStream.close(); if (clientSocket!=null) clientSocket.close(); if (serverSocket!=null) serverSocket.close(); } }
4.2.TCP编程实现C/S文件传输
package com.fengye.socket.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; /** * @Description: 服务端负责接收文件 * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 12:22 */ public class TestTcpFileTransportServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(4396); Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] bufferFile = new byte[1024]; int len; File received = new File("E:\\Workspaces\\Java\\JavaSocket\\src\\com\\fengye\\socket\\tcp\\images\\test.png"); FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(received); while ((len=inputStream.read(bufferFile))!=-1){ output.write(bufferFile,0,len); } // 接受完毕,告知客户断开连接 OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write("接收成功".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)); output.close(); inputStream.close(); socket.close(); serverSocket.close(); } }
Client:
package com.fengye.socket.tcp; import java.io.*; import java.net.Socket; /** * @Description: 客户端向服务端传送文件 * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 12:17 */ public class TestTcpFileTransportClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 创建socket Socket socket = new Socket("localhost",4396); // 创建流 OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream(); // 读取文件 File file = new File("E:\\Workspaces\\Java\\JavaSocket\\src\\com\\fengye\\socket\\tcp\\images\\img.png"); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // 文件输入流 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file); // 写入流 int len; while ((len=fileInputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){ outputStream.write(buffer); } // 文件传输结束,关闭输出 socket.shutdownOutput(); InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte buffer2[] = new byte[20]; ByteArrayOutputStream msg = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); while ((len=inputStream.read(buffer2))!=-1){ msg.write(buffer2,0,len); } System.out.println(msg); msg.close(); inputStream.close(); fileInputStream.close(); outputStream.close(); socket.close(); } }
5.UDP 编程
1、类DatagramSocket 和 DatagramPacket 实现了基于 UDP 协议网络程序。
2、UDP数据报通过数据报套接字 DatagramSocket 发送和接收,系统不保证 UDP数据报一定能够安全送到目的地,也不能确定什么时候可以抵达。
3、DatagramPacket 对象封装了UDP数据报,在数据报中包含了发送端的IP地址和端口号以及接收端的IP地址和端口号。
UDP网络通信流程
1、DatagramSocket与DatagramPacket
2、建立发送端,接收端
3、建立数据包
4、调用Socket的发送、接收方法
5、关闭Socket
接收方:
package com.fengye.socket.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.SocketException; public class TestUdpGet { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //开放端口 DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(2200); while (true){ //接收数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length); socket.receive(packet); //阻塞接收 System.out.println(packet.getAddress().getHostAddress()); String msg = new String(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength()); if (msg.equals("shutdown")){ System.out.println("Connection has been closed"); socket.close(); return; } System.out.println(msg); } } }
发送方
package com.fengye.socket.udp; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.SocketException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.util.Scanner; public class TestUdpSend { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //建立一个socket DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(1111); Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in); while (true){ String data = reader.nextLine(); byte[] msgBytes = data.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); InetAddress localhost = InetAddress.getByName("localhost"); DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(msgBytes, 0, msgBytes.length, localhost, 2200); socket.send(datagramPacket); if (data.equals("shutdown")){ System.out.println("Connection is closed "); reader.close(); socket.close(); return; } } } }
多线程实现聊天功能
package com.fengye.socket.udp.threadchat; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.SocketException; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; /** * @Description: 消息发送方线程 * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 13:14 */ public class MsgSender implements Runnable{ private String destinationAddress; private int destinationPort; DatagramSocket socket = null; BufferedReader reader = null; public MsgSender(int sourcePort, int destinationPort, String destinationAddress) throws SocketException { this.destinationAddress = destinationAddress; this.destinationPort = destinationPort; this.socket = new DatagramSocket(sourcePort); this.reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); } @Override public void run() { while (true){ try { String data = reader.readLine(); byte[] dataByte = data.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(dataByte,0,dataByte.length, new InetSocketAddress(destinationAddress, destinationPort)); socket.send(packet); if(data.equals("shutdown")){ reader.close(); socket.close(); return; } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
package com.fengye.socket.udp.threadchat; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.DatagramPacket; import java.net.DatagramSocket; import java.net.SocketException; /** * @Description: 消息接收方线程 * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 13:23 */ public class MsgReceiver implements Runnable{ private int port; private String msgSeeder; DatagramSocket socket = null; public MsgReceiver(int port, String msgSeeder) throws SocketException { this.port = port; this.msgSeeder = msgSeeder; socket = new DatagramSocket(port); } @Override public void run() { while (true){ try { byte[] msgBuffer = new byte[1024]; DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(msgBuffer,0,msgBuffer.length); socket.receive(packet); byte[] data = packet.getData(); String msg = new String(data,0, packet.getLength()); if (msg.equals("shutdown")) { socket.close(); return; } System.out.println(msgSeeder+": "+msg); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
/** * @Description: 发送目的端口和监听消息端口必须一致 * @Author: huang * @Date: 2021/5/5 13:27 */ public class TestClient01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws SocketException { new Thread(new MsgSender(1233, 8888,"localhost")).start(); new Thread(new MsgReceiver(8888,"T1客户端")).start(); } }
public class TestClient02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws SocketException { new Thread(new MsgSender(1234, 8800,"localhost")).start(); new Thread(new MsgReceiver(8800,"T2客户端")).start(); } }
6.URL 编程
url:统一资源定位符
package com.fengye.socket.url; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; public class TestUrl { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 1.资源地址 URL url = new URL("http://music.163.com/song/media/outer/url?id=1403528956.mp3"); // 2.url解析 System.out.println(url.getProtocol()); // 协议 System.out.println(url.getHost()); // 主机 System.out.println(url.getPort()); // 端口 System.out.println(url.getPath()); System.out.println(url.getFile()); System.out.println(url.getQuery()); // 参数 System.out.println(url.getAuthority()); System.out.println(url.getContent()); // 内容 // 3.连接资源url HttpURLConnection urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); InputStream stream = urlConnection.getInputStream(); // 4. 文件输出流到 test.mp3 FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream("test.mp3"); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len; while ((len=stream.read(bytes))!=-1){ outputStream.write(bytes,0,len); } // 5.下载完毕关闭流和url连接 stream.close(); outputStream.close(); urlConnection.disconnect(); } }
参考博文:
本博客涉及示例代码均已上传至GitHub地址:
