(https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-delegate.html)
1.变量的生命周期与类的实例同步:当方法体执行完毕后,变量随之销毁。
2.常量:①静态常量:const;②动态常量:static readonly(转载博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanglang/p/9003770.html)
-1.const:编译时常量,程序在编译时将对常量值进行解析,并将所有的常量引用替换为相应的值;const默认为静态类型,所以在使用中不再使用static来修饰,否则导致编译报错;必须在声明的同时进行初始化(赋值);const常量只能赋予数字(整数、浮点数)、字符串以及枚举类型;
//错误常量声明 public const DateTime t = DateTime.MaxValue; //使用readonly修改即可 public static readonly DateTime t = DateTime.MaxValue;
-2.(static) readonly:运行时常量,程序运行是进行赋值,赋值完成后便无法更改(只读变量);readonly常量只能声明为类字段,支持实例类型或静态类型,可以在声明的同时初始化或者在构造函数中进行初始化,初始化完成后便无法更改;
-3.可维护性:readonly常量是以引用的方式进行存储工作,莫个常量的值更新后,所有引用了改常量的地方均全部进行更新;const常量由于在声明是就进行了初始化,所以相对用于声明一些不会变动的值(比如一天=24小时),并且const在程序集中夸集使用时,当编译更新其中一个程序集时,另外的程序集不会同步更新
3.ref与out关键字:按地址传递,使用后都将改变原来参数的数值;ref与out在一定程度上解决了C#中的函数只能有一个返回值的问题
① ref:方法定义使用ref关键字时,调用对应的方法也必须带ref返回;

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //初始化 int a = 1; int b = 6; // 调用时带ref关键字,返回多个值 RefFun(ref a,ref b); Console.WriteLine("a:{0},b:{1}", a, b);//输出:7和6说明传入Fun方法是a和b的引用 } //使用ref定义方法 static void RefFun(ref int a, ref int b) { a = a+b; b = 6; } } }
②.使用泛型来使用ref关键字交换两个整数

using System; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; Console.WriteLine("ListNum one:{0},{1}",a, b); //交换两个整型数据 ListNum<int>(ref a, ref b); Console.WriteLine("ListNum two:{0},{1}",a, b); Console.ReadKey(); } //泛型方法 public static void ListNum<T>(ref T a, ref T b) { T t; t = a; a = b; b = t; } } }
-1.ref:有进有出

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int a = 1; int b = 2; Console.WriteLine("交换前:a:{0},a:{1}",a,b); //调用RefFun进行赋值替换 RefFun(ref a, ref b); Console.WriteLine("交换后:a:{0},b:{1}",a,b); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void RefFun(ref int a, ref int b) { int temp = a; a = b; b = temp; Console.WriteLine("RefFun方法体中:a:{0},b:{1}",a,b); } } }
-2.ref参数再传入之前必须先初始化(赋值)

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int b = 5; Console.WriteLine($"输出b:{b}"); Num(ref b); //调用Num(ref b)函数前,必须给传递的参数b赋值 Console.WriteLine($"输出ref的b:{b}"); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void Num(ref int a) { a *= 2; } } }
② out:方法定义使用out关键字时,调用对应的方法也必须带out返回

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int a =100; int b =20; OutFun(out a, out b); //附带奔方法体内的初始化的值进行输出 Console.WriteLine("a:{0},b:{1}",a,b); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void OutFun(out int a, out int b) { // 初始化 int n = 3; int m = 5; a = n*m ; b = 1; } } }
-1.out只出不进
-2.out参数不需要事先进行初始化,只要在传入前声明变量即可

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] list = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 }; int d; // 调用代码可以把已赋值的变量用做out参数,但存储在该变量中的值会在函数执行时丢失 Console.WriteLine($"out输出:{MaxList(list,out d)}"); Console.WriteLine(d); Console.ReadKey(); } static int MaxList(int[] ArrayList, out int v) { int a = ArrayList[0]; v = 0; for (int i = 1; i < ArrayList.Length; i++) { if (ArrayList[i] > a) { a = ArrayList[i]; v = i; } } return a; } } }
③Example:
-1.Person.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_2 { public class Person { public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } } }
-2.Program.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_2 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person p = new Person { Name = "John", Age = 17 }; //调用test前 Console.WriteLine("前:姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}",p.Name,p.Age); //传入 重新初始化的值 Test(p); Console.WriteLine("后:姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}", p.Name, p.Age); //小括号表示要是类的构造函数带有参数的话,必须传参小括号就不可省略 Person ps = new Person (){ Name = "xx", Age = 1 }; Person px = new Person { Name = "tt", Age = 2 }; Test2(ps); Console.WriteLine("test2:姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}",ps.Name,ps.Age); //REF与OUT Person p4 = new Person() { Name="yzz",Age=18}; //调用ref Console.WriteLine("ref前:姓名:{0},年龄:{1}",p4.Name,p4.Age); Test3(ref p4); Console.WriteLine("ref后:姓名:{0},年龄:{1}",p4.Name,p4.Age); //out Person p5 = new Person(){ Name = "jio", Age = 20 }; Console.WriteLine("OUT前:姓名:{0}, 年龄:{1}",p5.Name,p5.Age); Test4(out p5); if (p5!=null) { Console.WriteLine("out:姓名:{0},年龄:{1}",p5.Name,p5.Age); } Console.ReadKey(); } /// <summary> /// 引用Person类 /// </summary> /// <param name="p"></param> static void Test(Person p) { p.Name = "tom"; p.Age = 12; } static void Test2(Person p) { p = new Person { Name = "Chen", Age = 20 }; } static void Test3(ref Person p) { p = new Person(); p.Name = "Boy"; p.Age = 13; } static void Test4(out Person p) { p = new Person(); p.Name = "YY"; p.Age = 17; } } }
4.可选参数要放在参数列表的最后

//string p2="abc"为可选参数 void Dowrok(string p1, string p2="abc") { // 代码块 }
5.Lambda表达式
①用Lambda表达式来声明方法:

//PicName()方法没有参数,返回一个字符串实例 public string PicName() => "tom"; // public int Add(int a, int b) => a+b
②Lambda在委托中的使用

// 匿名方法 delegate int calculator(int x, int y); //委托 static void Main() { calculator cal = delegate(int num1,int num2) { return num1 + num2; }; int he = cal(1, 1); Console.Write(he); } // Lambda实现 delegate int calculator(int x, int y); //委托类型 static void Main() { calculator cal = (x, y) => x + y;//Lambda表达式 int he = cal(1, 1); Console.Write(he); }
③.IEnumerable<>接口中使用Lambda

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { List<string> frits = new List<string> { "apple", "passionfruit", "banana", "mango", "orange", "blueberry", "grape", "strawberry" }; IEnumerable<string> query = frits.Where(fut => fut.Length < 6); foreach (string fut in query) { Console.WriteLine(fut); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
6.析构函数:资源回收

public class Test { // 构造函数 public Test() { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("构造函数被调用"); } //析构函数 ~Test() { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("析构函数被调用"); } } //调用析构函数 static void Main(string[] args) { Test t=new test(); }
7.程序资源释放的方法:
①析构函数
②实现IDisposable接口

public class Test : System.IDisposable { //Dispose方法 public void Dispose() { //带参数的Dispose方法,释放托管和非托管资源 Dispose(true); //手动调用了Dispose释放资源,放弃析构函数,这里阻止了GC调用析构函数 System.GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } //protected的Dispose方法,保证不会被外部调用。 //传入bool值disposing以确定是否释放托管资源 protected void Dispose(bool disposes) { if (disposes) { ///TODO:在这里加入清理"托管资源"的代码,应该是xxx.Dispose(); } ///TODO:在这里加入清理"非托管资源"的代码 } //供GC调用的析构函数 ~TestClass() { Dispose(false);//释放非托管资源 } }
③using函数

using(Test t=new Test()) { // }
8.结构:使用关键字“struct”定义
①在结构中声明字段时不能直接进行赋值

struct Pet { //不能直接进行赋值:public string Name="tom" public string Name; }
②通过new来实现实例

// 1.实现以上的类 Pet p=new pet(); p.Name="tom"; // 2.也可写成 Pet p; p.Name="tom"; // 3.当Pet类中存在方法体时必须使用new来创建实例
9.值类型与引用类型
①类属于引用类型:值随变量的变化而变化(引用实例的内存位置)
②结构属于值类型:值类型属于独立的类型,值之间只存在复制关系,修改一个值,另外一个值不会改变(开辟一个新的内存位置)
10.匿名方法:匿名方法是没有名称只有主体的方法;在匿名方法中不需要指定返回类型,它是从方法主体内的 return 语句推断的。
①匿名方法通过delegate 关键字创建委托实例来声明

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { //定义一个委托 public delegate int SumAdd(int a, int b); static void Main(string[] args) { SumAdd sumAdd = delegate (int a, int b) { return a + b; };//把一个方法赋值给委托,其实这种写法就是匿名方法 int result = sumAdd.Invoke(2, 2); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
②Example

using System; delegate void NumberChanger(int n); namespace DelegateAppl { class TestDelegate { static int num = 10; public static void AddNum(int p) { num += p; Console.WriteLine("Named Method: {0}", num); } public static void MultNum(int q) { num *= q; Console.WriteLine("Named Method: {0}", num); } static void Main(string[] args) { // 使用匿名方法创建委托实例 NumberChanger nc = delegate(int x) { Console.WriteLine("Anonymous Method: {0}", x); }; // 使用匿名方法调用委托 nc(10); // 使用命名方法实例化委托 nc = new NumberChanger(AddNum); // 使用命名方法调用委托 nc(5); // 使用另一个命名方法实例化委托 nc = new NumberChanger(MultNum); // 使用命名方法调用委托 nc(2); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
11.方法重载:在类型内部允许存在相同名字的方法,但不能重复(参数不同)
①具有不同类型的返回值且参数有差异的同名方法阔以重载

public string Dowork(int a){} public int Dowork(){} //第一个返回string类型的带一个int类型参数,第二个返回int类型不带参数,类型参数不同,能构成重载
②参数列表的类型及顺序不同

void Test(string a){} void Test(float a,double b){}
③针对ref与out
-1.一个方法带ref/out,则能构成重载

// ref void Plen(ref short v){} void Plen(short v){} //out void plen(short v){} void plen(out short v){ v = 2 }
-3.ref与out不能构成重载

//编译报错,编译器不区分ref和out参数 void plen(ref short v){} void plen(out short v){ v = 2 }
④构造函数中的重载

public class Test { public Test(){} public Test(string Name){} }
12.方法重写(重写改变父类方法,即调用子类方法):使用关键字virtual修饰的方法,叫虚方法;可以在子类中(继承至虚方法)声明同名的方法,叫重写,重写实现了多态
-1.重写:抽象方法,接口,标记为virtual的方法可以被重写(override),实方法不可以;

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //调用虚方法 C1 c1 = new C1(); Console.WriteLine(c1.GetName()); //调用重写方法 C2 c2 = new C2(); Console.WriteLine(c2.GetName()); //用子类创建父类,new C2开辟新的空间来存放对应调用子类的方法 C1 c3 = new C2(); Console.WriteLine(c3.GetName()); Console.ReadKey(); } public class C1 { public virtual string GetName() { return "实方法"; } } public class C2:C1 { public override string GetName() { return "重写的方法"; } } } }
13.在类中使用new关键字修饰的方法:①实现覆盖
-1.覆盖:仍然调用父类方法;虚方法、实方法都可以被覆盖(new),抽象方法,接口 不可以;

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //调用虚方法 C1 c1 = new C1(); Console.WriteLine(c1.GetName()); //调用覆盖方法 C2 c2 = new C2(); Console.WriteLine(c2.GetName()); //在覆盖创建的基类中用子类创建父类,new C2仍然调用父类C1方法地址 C1 c3 = new C2(); Console.WriteLine(c3.GetName()); Console.ReadKey(); } public class C1 { public virtual string GetName() { return "实方法"; } } public class C2:C1 { public new string GetName() { return "实现覆写的方法"; } } } }
14.静态方法:静态类与静态成员都使用关键字static来定义
①静态类只能定义静态成员

public static class Test() { public static void SoyHelper(){} public static string Message{get; set;} }
15.c#委托:Action、 Action<T>、Func<T>、Predicate<T>
①什么叫委托??(类似c++的指针函数)
定义:委托是一个类,它定义了方法的类型,使得可以将方法当作另一个方法的参数来进行传递,这种将方法动态地赋给参数的做法,可以避免在程序中大量使用If-Else(Switch)语句,同时使得程序具有更好的可扩展性;用于实现事件和回调方法,所有的委托(Delegate)都派生自 System.Delegate 类。
②委托的声明语法:delegate关键字
delegate <return type> <delegate-name> <parameter list>
-1.声明带参的委托方法

/// <summary> /// 委托和事件的应用 /// </summary> /// <param name="name">声明带有一个string参数的方法,并返回一个int类型变量</param> public delegate int MyDelegate(string name);
-2.委托的实例化:使用new关键字来创建

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_Delegate { class Program { /// <summary> /// 委托和事件的应用 /// </summary> /// <param name="args"></param> static void Main(string[] args) { Mydelegate d = new Mydelegate(Name); //使用委托对象调用方法 d("tom"); } //委托 public delegate void Mydelegate(string name); public static void Name(string name) { Console.WriteLine("你好,我的名字叫" + name); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
③.委托的多播(通俗说就是增加附加方法体或减少附加的方法体,即:+ 或 - ;)

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_Delegate { class Program { public delegate int NumAppes(int n); static int a = 10; public static int AddNum(int p) { a += p; return a; } public static int MultNum(int q) { a *= q; return a; } public static int GetNum() { return a; } /// <summary> /// 委托和事件的应用 /// </summary> /// <param name="args"></param> static void Main(string[] args) { //委托的实例 NumAppes nc; NumAppes nc1 = new NumAppes(AddNum); NumAppes nc2 = new NumAppes(MultNum); nc = nc1; nc += nc2; // 调用多播 nc(5); Console.WriteLine("Value of Num: {0}", GetNum()); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
-1.多播的具体实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { //声明一个委托,即命令 public delegate void Icecream(); static void Main(string[] args) { //实现自己买根雪糕 Icecream ic = new Icecream(Brother.Tiket); //实现再给弟弟附带买一根雪糕,同时实现两个买的动作 ic += Brother.MyBrotherTiket; ic(); Console.ReadKey(); } } // 果果类 public class Brother { public static void Tiket() { Console.WriteLine("给我自己买根雪糕!!"); } public static void MyBrotherTiket() { Console.WriteLine("算了,好胸得,给弟弟也带一跟雪糕吧!"); } } }
-2.委托的多播实现

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { //声明一个委托,即命令 public delegate int Icecream(int a, int b); static void Main(string[] args) { Icecream ic; Icecream ic1 = new Icecream(Brother.Multiply); Icecream ic2 = new Icecream(Brother.Sum); Icecream ic3 = new Icecream(Brother.Divide); ic = ic1; ic += ic2; ic += ic3; int ret1 = ic.Invoke(10, 2); Console.WriteLine(ret1); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class Brother { public static int Multiply(int a, int b) { return a * b; } public static int Divide(int a, int b) { return a / b; } public static int Sum(int c, int d) { return c + d; } } }
④Example_3

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.IO; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static FileStream fs; static StreamWriter sw; public delegate void PrintString(string s); static void Main(string[] args) { PrintString p1 = new PrintString(WriteShow); PrintString p2 = new PrintString(WriteToFile); SendString(p1); SendString(p2); Console.ReadKey(); } //打印搭配控制台 public static void WriteShow(string s) { Console.WriteLine("this String is:{0}",s); } //改方法打印到文件 public static void WriteToFile(string s) { fs = new FileStream("D:\\messge.txt", FileMode.Append, FileAccess.Write); sw = new StreamWriter(fs); sw.WriteLine(s); sw.Flush(); sw.Close(); fs.Close(); } //把委托作为参数,并使用他调用方法 public static void SendString(PrintString p) { p("Hello World !!"); } } }
⑤泛型委托(简化委托的定义)
-1.Action:Action委托没有参数,也没有返回值
(1)简单了解:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { // 定义Action委托 public delegate void Action(); static void Main(string[] args) { // 实例化Action委托 Action a = new Action(Alt); a(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void Alt() { Console.WriteLine("hao lo!!"); } } }
(2)Lambd表达式改写以上实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Action t = () => { Console.WriteLine("hao lo"); }; t(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(3)Action的多播

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { public delegate void Action(); static void Main(string[] args) { Action a = new Action(Alt); a += AltS; a(); Console.WriteLine(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void Alt() { Console.WriteLine("hao lo!!"); } public static void AltS() { Console.WriteLine("HO LO!!"); } } }
-2.Aciton<>:Action<>委托可传入<16个参数,无返回值
(1)简单了解:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //实例化Action<>委托 Action<int, int> t = new Action<int, int>(Alt); t(3,3); Console.ReadKey(); } public static void Alt(int a, int b) { Console.WriteLine(a + b); } } }
(2)Lambd表达式改写以上实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Action<int, int> t = (a, b) => { Console.WriteLine(a + b); }; t(3, 4); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
-3.Func<T>:Func<T>委托始终都会有返回值,返回值的类型是参数中最后一个
(1)简单了解:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //1 Func<int, int, int> c1 = (int x, int y) => { return x + y; }; int a = c1(2, 3); //2 Func<int, int, int> c2 = (x, y) => { return x + y; }; int b = c2(2, 2); //3 Func<int, int, int> c3 = (x, y) => x + y; int c = c3(3, 3); Console.WriteLine("输出:{0},{1},{2}", a, b, c); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(2)简单定义:最后一个参数都为返回值类型

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Func<int, int, bool> t = new Func<int, int, bool>(Su); bool result = t(3, 2); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } public static bool Su( int a, int b) { return a > b; } } }
(3)Lambd表达式直接把方法定义在委托中:重新改写以上实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Func<int, int, bool> t = (a, b) => { return a > b; }; bool result = t(3, 4); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
-4.Predicate<T>:Predicate<T>委托表示定义一组条件并确定指定对象是否符合这些条件的方法,返回值始终为bool类型
(1)简单了解:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //委托 Predicate<int> t = new Predicate<int>(Math); int[] arr = { 12, 45, 67, 43, 78, 90, 205 }; int first = Array.Find(arr, t); Console.WriteLine(first); Console.ReadKey(); } public static bool Math(int val) { return val > 60; } } }
(2)Lambd表达式直接把方法定义在委托中:重新改写以上实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //委托 Predicate<int> t = val => { return val>60; }; int[] arr = { 12, 45, 67, 43, 78, 90, 205 }; int first = Array.Find(arr, t); Console.WriteLine(first); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
(3)Predicate<T>实例

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int SetState = 1; int SetType = 1; Double price = 10.00; string[] TypeName = { "蔬菜", "水果" }; List<VegType> t = new List<VegType>() { new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "芹菜", Price = 10.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "大白菜", Price = 3.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "白萝卜", Price = 2.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "花菜", Price = 13.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "韭菜", Price = 8.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "蔬菜", Name = "芹菜", Price = 10.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "水果", Name = "桃子", Price = 16.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "水果", Name = "苹果", Price = 14.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "水果", Name = "车厘子", Price = 25.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "其他", Name = "其他", Price = 28.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "其他", Name = "其他", Price = 14.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "其他", Name = "其他", Price = 25.00 }, new VegType() { VegetablesType = "其他", Name = "其他", Price = 28.00 } }; List<VegType> m = t.FindAll(new Predicate<VegType>(delegate(VegType veg) { bool Result = true; if (SetType==1) { if (veg.Price<price) { Result = false; } } if (SetState==1) { if (veg.VegetablesType != TypeName[0]) { Result = false; } } return Result; })); m.ForEach(x => { Console.WriteLine("类型:{0},名称:{1},价格:{2}", x.VegetablesType, x.Name, x.Price); }); Console.ReadKey(); } public class VegType { public string VegetablesType { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public Double Price { get; set; } } } }
16.Lambda表达式
①Lambda表达式常见写法

using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.IO; namespace Example_3 { class Program { //委托 public delegate int CalAdd(int a, int b); static void Main(string[] args) { //方法一 CalAdd calAdd=(int a, int b) =>{ return a + b; }; int result1 = calAdd.Invoke(2,2); Console.WriteLine(result1); //方法二 CalAdd c = (a, b) => { return a + b; }; int result2 = c(3, 3); Console.WriteLine(result2); //方法三 CalAdd cl = (a, b) => a + b; int result3 = cl(4, 4); Console.WriteLine(result3); Console.ReadKey(); } }
②用Lambda表达式来声明方法:

//PicName()方法没有参数,返回一个字符串实例 public string PicName() => "tom"; // public int Add(int a, int b) => a+b
③Lambda在委托中的使用

// 匿名方法 delegate int calculator(int x, int y); //委托 static void Main() { calculator cal = delegate(int num1,int num2){return num1+num2;}; int he = cal.Invoke(1, 1); Console.Write(he); } // Lambda实现 delegate int calculator(int x, int y); //委托类型 static void Main() { calculator cal = (x, y) => x + y;//Lambda表达式 int he = cal(1, 1); Console.Write(he); }
④Lambda的表达式树:表达式树是存取Lambda表达式的一种数据结构;要使用Lambda表达式的时候,直接从表达式中获取出来,Compile()就可以直接用

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Linq.Expressions; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Example_3 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Expression<Func<int, int, int>> p = (x, y) => x + y; Func<int, int, int> fun = p.Compile(); int result = fun.Invoke(2, 2); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
17.抽象方法和抽象类:使用关键字 abstract 来定义抽象类和抽象方法,同时抽象类不能被初始化,只提供部分实现
18.装箱与拆箱:需要装箱与拆箱的地方就是值类型与引用类型(值转引用为装箱,引用转值类为拆箱),装箱是一种通过将变量存储到System.Object中来显示的将值类型转化为引用类型的机制,当进行装箱操作时,CLR会将新对象分配到堆中,并将值类型的值复制到改实例中。
//装箱: int a = 20; object b = a; //装箱 //拆箱: int c = int(b) ; //拆箱,将引用类型转化为值类型,验证接收数据类型是否与装箱类型一致
19.泛型类:public class Student<T> { }
①.引用命名空间:System.Collection.Generic
②.System.Collection.Generic下核心类类型:
| 泛型类 | 描述 |
| Collection |
泛型集合的基类,可以比较两个泛型是否相等 |
| Dictionary<TKey, TValue> |
键值对的泛型集合 |
| List |
可动态调整列表项的大小 |
| Queue |
队列,先进先出(FIFO)列表的泛型表现 |
| Stack |
堆栈,后进先出(LIFO)列表的泛型表现 |
3.简单了解:
Test.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { class Test { public class Rustul<T> { // 定义一个长度为5的泛型 T[] t = new T[5]; int i = 0; public void Add(T item) { if (i + 1 < 6) { t[i] = item; } i++; } // foreach语句迭代索引 public T this[int index] { get { return t[index]; } set { t[index] = value; } } } } }
Program.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 用整形来实例化泛型类 Test.Rustul<int> Obj = new Test.Rustul<int>(); // 向集合中添加数据 Obj.Add(1); Obj.Add(2); Obj.Add(3); Obj.Add(4); // 没有装箱操作,再泛型中指定了数据类型,在遍历 Obj.Add(5); //泛型集合中时会从编译器动态生成的类中将使用int类型。所以将不会发生装箱和拆箱 // 遍历数据 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Console.WriteLine(Obj[i]); //没有拆箱操作 } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
4.泛型的性能上:在定义范型对象的时候要明确指定传入时的具体类型,所以相同类型之间自然就不用装拆箱之类的操作了,所以泛型的性能是高于其他集合类型的(比如ArrayList)

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ArrayList t = new ArrayList(); t.Add(50); //装箱:值类型转引用 t.Add("tom"); //装箱:值类型转引用 int x = (int)t[0]; // 拆箱 string n = (string)t[1];// 拆箱 //int y = (int)t[1]; // 当使用int类型来接收strin类型时,出现System.InvalidCastException:“指定的转换无效。” //遍历打印 ArrayList foreach (var item in t) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.WriteLine($"拆箱后的值:{n}"); //Console.WriteLine(y); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
20.字典:
作用:允许基于关键字来访问元素的数据结构
特性:快速查询
典型的字典函数:Dictionary <TKey, TValue>, key表示关键字的类型,value表示可以存储的值
①.示例:
示例一:Dictionary 是二叉树式的存储结构,不支持用索引来取值,只能通过遍历

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 定义一个字典集合 Dictionary<int, string> p = new Dictionary<int, string>(5); //向字典中添加类型 p.Add(1, "A"); p.Add(2, "B"); p.Add(3, "C"); p.Add(4, "D"); p.Add(5, "E"); //遍历输出 for (int i = 1; i < p.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine(p[i]); } //获取对应的key与value foreach (var key in p) { Console.WriteLine($"key:{key.Key},value:{key.Value}"); } Console.WriteLine($"查询对应的key,如果不存在则进行创建:"); if (!p.ContainsKey(6)) { p.Add(6, "f"); } Console.WriteLine($"通过key查找元素:"); if (p.ContainsKey(1)) { Console.WriteLine("key:{0},value={1}","1",p[1]); Console.WriteLine(p[1]); } Console.WriteLine($"得到哈希表键的集合:"); Dictionary<int, string>.KeyCollection keyCol = p.Keys; foreach (var item in keyCol) { Console.WriteLine($"key={item}"); } Console.WriteLine($"使用TryGetValue方法获取指定键对应的值:"); string vol = string.Empty; if (p.TryGetValue(1, out vol)) { Console.WriteLine($"找到数据的value:{vol}"); } else { Console.WriteLine($"无数据!"); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
示例二:覆盖Object中的ToString()方法以显示特定员工的名称和奖金
emp.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { public class emp { private string name; private int salary; public emp(string name, int salary) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; } //重写object中ToString方法 public override string ToString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(200); //当指定分配大小之后,性能就会得到提升。如果超过指定大小系统会当前大小倍增 sb.AppendFormat("{0},{1}", name, salary); return sb.ToString(); } } }
Program.cs

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //定义一个字典集合 Dictionary<string, emp> dObj = new Dictionary<string, emp>(2); //向字典中添加元素 emp tom = new emp("tom", 2000); dObj.Add("tom", tom); // 键,值 emp john = new emp("jarr", 1500); dObj.Add("jarr", jarr); //print data foreach (Object str in dObj.Values) { Console.WriteLine(str); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
21.队列 (Queue):队列是一种特殊类型的容器,可确保以FIFO(先进先出)方式访问元素,其次队列集合最适合用来实现消息队列的传递组件
引用命名空间:using System.Collection
|
Queue |
说明 |
| Enqueue() |
将对象添加到队列的末尾(逐一顺序添加队列)
|
| Dequeue() |
从队列的开头删除对象
|
| Peek() |
返回队列开头对象
|
简单示例:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 定义一个队列 Queue q = new Queue(); q.Enqueue("tom"); q.Enqueue(1); q.Enqueue(2); Console.WriteLine($"foreach循环:"); foreach (var item in q) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.WriteLine($"while循环:"); while (q.Count!=0) { Console.WriteLine(q.Dequeue()); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
22.堆栈(Stack):Stack集合是LIFO的抽象(后进先出)
命名引用空间:using System.Collection
Stack函数集:
| Stack |
说明 |
| Contains() |
在集合中查找特定的元素,存在则返回true
|
| Clear() |
删除集合中的元素(清空集合)
|
| Peek() |
预览集合中的最新元素
|
| Push() |
将元素推入堆栈
|
| Pop() |
删除堆栈中的顶部元素并返回
|
简单示例:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //定义一个数组 int[] Arrlist = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 }; //使用result来从小到大排序Arrlist数组 int[] result = Arrlist.OrderByDescending(x => x).ToArray(); //定义一个堆栈,将数组类型对象引用到堆栈集合中 Stack s = new Stack(result); Console.WriteLine($"堆栈数:{s.Count}"); Console.WriteLine($"foreach循环:"); foreach (var item in s) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.WriteLine($"for循环:"); for (int i = 0; i < s.Count; i++) { Console.WriteLine(s.Pop()); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
使用Push()向堆栈集合中添加数据:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Stack s = new Stack(); //向堆栈集合中添加数据 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { s.Push(i+1); } foreach (var item in s) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
23.异步编程:关键字async、await
异步理解:指在执行当前方法的同时,可以异步的去调用其他方法(异步方法),并且不会阻塞当前方法的线程
粗暴理解:同事执行多个方法,等待上一个方法执行完成后执行下一个方法
线程柱塞了解:那就是同步的时候,同步调用会阻塞线程,如果是要调用一项繁重的工作(如大量IO操作),可能会让程序停顿很长时间,造成糟糕的用户体验
委托方法示例:

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Async { public class Program { //委托方法 public delegate int AddSum(int a, int b); public static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("--同步调用--"); AddSum add = new AddSum(Add); //委托的Invoke方法用来进行同步调用。同步调用也可以叫阻塞调用, //它将阻塞当前线程,然后执行调用,调用完毕后再继续向下进行。 int result = add.Invoke(1, 2); Console.WriteLine("其他"); Console.WriteLine(result); Console.ReadKey(); } public static int Add(int a, int b) { Console.WriteLine("开始计算:" + a + "+" + b); Console.WriteLine("计算完成"); return a + b; } } }
①.async三种返回值:void、Task、Task<T>
②.async void:只能直接调用,与调用方法并行执行(同步)
③.async Task:可以直接调用,也可await调用,直接调用是并行执行(同步),await调用会等待执行完成(异步)
④.async Task<T>:只能通过await方式调用,获取T类型的返回值(异步)
示例一:同步下执行

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 使用async关键字 Method(); Setmoder(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static async Task Method() { await Task.Run(() => { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"Method:{i}"); } }); } public static void Setmoder() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"Setmoder:{i}"); } } } }
输出:
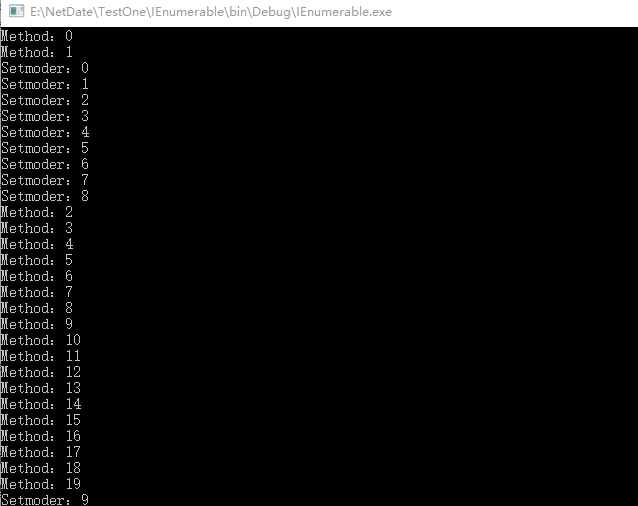
示例二:修改以上的示例,异步(要想异步执行等待,首先两个方法之间得存在依赖)

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { CallHelper(); Console.ReadKey(); } public static async void CallHelper() { Task<int> task = Method(); //await关键字,等待Method执行完成后执行Setmoder方法 int count = await task; Setmoder(count); } public static async Task<int> Method() { int count = 0; await Task.Run(() => { for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) { Console.WriteLine($"Method:{i}"); count += 1; } }); return count ; } //count参数依赖于Method中的count public static void Setmoder(int count) { Console.WriteLine($"Setmoder:循环的总数为{count}"); } } }
输出:
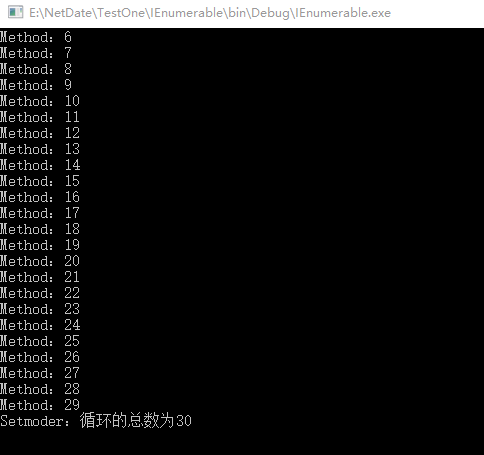
⑤常用的异步方法的Api:
HttpClient, SyndicationClient, StorageFile, StreamWriter, StreamReader, XmlReader, MediaCapture, BitmapEncoder, BitmapDecoder
获取文件字节大小的示例:

using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace IEnumerable { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Task task = new Task(Method); task.Start(); task.Wait(); Console.WriteLine(1); Console.WriteLine(2); Console.WriteLine(3); Console.ReadKey(); } static async void Method() { string FilePath = "C:\\数据处理.txt"; Task<int> task = ReadFile(FilePath); int length = await task; // 使用等待关键字关键字await Console.WriteLine($"Total length:{length}"); Console.WriteLine(1); Console.WriteLine(2); } private static async Task<int> ReadFile(string file) { int length = 0; using (StreamReader read=new StreamReader(file)) { string s =await read.ReadToEndAsync(); length = s.Length; } Console.WriteLine($"读取文件结束:{length}"); return length; } } }
⑥异步执行两个获取文件夹信息的实例

using log4net; using log4net.Config; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Configuration; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace DirPathFile { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 获取文件夹目录下所有文件的完整路径 var strPaths = ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["dirPath"]; List<FileInfo> lst = new List<FileInfo>(); List<FileInfo> lstfiles = GetInfo(strPaths, lst); DirectoryInfo info = new DirectoryInfo(strPaths); foreach (FileInfo item in lstfiles) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.WriteLine($"当前获取到的文件总数:{GetFilesCount(info)}"); Console.WriteLine("--异步--"); Thread.Sleep(3000); Task task = StepFile(); Console.ReadKey(); #endregion #region directoryinfo与directory说明 //1.directory是公开建立、移动和全面列举目录和子目录的静态方法。 //2.directoryinfo是公开建立、移动和全面列举目录和子目录的执行个体(Instance) 方法。 //3.一个是公用的静态类,一个是实例类 #endregion #region 获取指定目录包含的文件和子目录 // 1.DirectoryInfo.GetFiles():获取目录中(不包含子目录)的文件,返回类型为FileInfo[],支持通配符查找; // 2.DirectoryInfo.GetDirectories():获取目录(不包含子目录)的子目录,返回类型为DirectoryInfo[],支持通配符查找; // 3.DirectoryInfo.GetFileSystemInfos():获取指定目录下(不包含子目录)的文件和子目录,返回类型为FileSystemInfo[],支持通配符查找; #endregion #region 获取指定文件的基本信息 //1.FileInfo.Exists:获取指定文件是否存在; //2.FileInfo.Name,FileInfo.Extensioin:获取文件的名称和扩展名; //FileInfo.FullName:获取文件的全限定名称(完整路径); //FileInfo.Directory:获取文件所在目录,返回类型为DirectoryInfo; //FileInfo.DirectoryName:获取文件所在目录的路径(完整路径); //FileInfo.Length:获取文件的大小(字节数); //FileInfo.IsReadOnly:获取文件是否只读; //FileInfo.Attributes:获取或设置指定文件的属性,返回类型为FileAttributes枚举,可以是多个值的组合 //FileInfo.CreationTime、FileInfo.LastAccessTime、FileInfo.LastWriteTime:分别用于获取文件的创建时间、访问时间、修改时间; #endregion } #region 采用异步 public static async Task StepFile() { try { await Task.Run(() => { Console.WriteLine("--获取文件夹下的指定后缀文件--"); string strPath = @"E:\1\"; DirectoryInfo info = new DirectoryInfo(strPath); List<FileInfo> lstfile = GetFile(strPath, ".jpg"); foreach (FileInfo item in lstfile) { Console.WriteLine(item); } Console.WriteLine($"当前获取到的文件总数:{GetFilesCount(info)}"); }); } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } #endregion #region 获取指定文件夹下的指定后缀文件 /// <summary> /// 获取文件夹下的莫个后缀的所有文件 /// </summary> /// <param name="path">文件路劲</param> /// <param name="ExtName">文件后缀</param> /// <returns></returns> public static List<FileInfo> GetFile(string path, string ExtName) { try { List<FileInfo> lst = new List<FileInfo>(); string[] dir = Directory.GetDirectories(path);// 文件夹列表 DirectoryInfo directoryInfo = new DirectoryInfo(path); FileInfo[] files = directoryInfo.GetFiles(); if (files.Length != 0 || dir.Length != 0) // 当前目录文件或文件夹不能为空 { foreach (FileInfo f in files) { if (ExtName.ToLower().IndexOf(f.Extension.ToLower()) >= 0) { lst.Add(f); } } foreach (string d in dir) { GetFile(d, ExtName); } } return lst; } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } #endregion #region 获取文件夹下所有文件的完整路径 /// <summary> /// 获取文件夹下所有文件的完整路径 /// </summary> /// <param name="path">路径</param> /// <param name="lst">返回参数</param> /// <returns></returns> private static List<FileInfo> GetInfo(string path, List<FileInfo> lst) { try { //string[] dirInfo = Directory.GetDirectories(path); string[] fileList = Directory.GetFileSystemEntries(path); foreach (string item in fileList) { FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(item); if (fi.Extension != " ") // 获取路径下的所有文件路径 { lst.Add(fi); } } return lst; } catch (Exception ex) { throw ex; } } #endregion #region 获取当前目录下的文件总数 /// <summary> /// 获取文件夹下的文件总数 /// </summary> /// <param name="dirInfo"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static int GetFilesCount(DirectoryInfo dirInfo) { int totalFile = 0; totalFile += dirInfo.GetFiles().Length; foreach (DirectoryInfo f in dirInfo.GetDirectories()) { totalFile += GetFilesCount(f); } return totalFile; } #endregion } }
24.并行:Parallel






