| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 班级链接 | 19级信计班 |
| 作业要求链接 | Java第十一周作业 |
| 博客名称: | 1903021133-杨媛媛-Java十一周作业-继承,多态和抽象类使用 |
| *要求: | 每道题要有题目,代码(使用插入代码,不会插入代码的自己查资料解决,不要直接截图代码!!),截图(只截运行结果)。 |
题目1:
-
类Person定义了姓名name,出生年份birthYear,其子类Graduate在继承父类的基础上新增定义了成绩gpa、毕业年份graduateYear。编写测试类,输出毕业生的姓名、年龄、毕业年份、成绩。
- 提示:父类要有构造方法,子类通过super调用父类构造方法。
代码:
package xjweek11;
public class Person {
String name;
int birthYear;
public Person(String name,int birthYear ) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.birthYear = birthYear;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int birthYear(){
return birthYear;
}
}
子类:
package xjweek11;
public class Graduate extends Person {
int gpa;
int graguateYear;
int nowYear;
public Graduate(String name, int birthYear, int gpa, int graguateYear,
int nowYear) {
super(name, birthYear);
this.gpa = gpa;
this.graguateYear = graguateYear;
this.nowYear = nowYear;
}
public int getGpa() {
return gpa;
}
public int getGraguateYear() {
return graguateYear;
}
public int getNowYear() {
return nowYear;
}
public int age(){
return nowYear-birthYear;
}
}
测试类:
package xjweek11;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
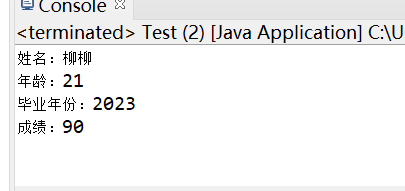
Graduate s=new Graduate("柳柳",2001,90,2023,2022);
System.out.println("姓名:"+s.name+"\n年龄:"+s.age()+"\n毕业年份:"+s.getGraguateYear()+"\n成绩:"+s.gpa);
}
}
截图:
 题目2:
题目2:
- 定义一个基本类Shape,有一个draw方法,定义三个类Circle(圆)、Triangle(三角形)、Square(正方形)都继承于Shape。在测试类中定义一个方法doStuff,传入基本类shape为参数,并调用draw方法。使用父类Shape创建三个类Circle、 Triangle、Square的实例对象并分别作为参数传入draw方法中。
- 提示:多态
-
代码:
-
package xjweek11; public class Shape { void draw(){ } } package xjweek11; Circle类: public class Circle extends Shape { void draw(){ System.out.println("Circle.draw()"); } } Triangle类 package xjweek11; public class Triangle extends Shape { void draw(){ System.out.println("Triangle.draw()"); } } Square类 package xjweek11; public class Square extends Shape { void draw(){ System.out.println("Square.draw()"); } } 测试类: package xjweek11; public class Test2 { static void doStuff(Shape s){ s.draw(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Shape c=new Circle(); Shape s=new Square(); Shape t=new Triangle(); doStuff(c); doStuff(s); doStuff(t); // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
截图:

题目3:
-
所有的动物都有一个父类Animal,再定义两个子类Bird(鸟)和Dog(狗)继承自Animal,并实现父类中的bark(叫唤)方法。
- 提示:抽象
-
代码:
-
package xjweek11; public class Animal { void bark(){ } } Bird类 package xjweek11; public class Bird extends Animal { void bark(){ System.out.println("鸟的叫声是:布谷布谷~"); } } Dog类: package xjweek11; public class Dog extends Animal { void bark(){ System.out.println("狗的叫声是:汪汪汪~"); } } 测试类: package xjweek11; public class Tsst3{ public static void main(String[] args) { Dog d=new Dog(); Bird b=new Bird(); d.bark(); b.bark(); // TODO Auto-generated method stub } } -
截图:

题目4:
-
不同几何图形的面积计算公式是不一样的,可是,它们具有的特性是一样的,都具有长和宽这两个属性,也都具有面积计算的方法。根据抽象的概念计算长方形的面积和三角形的面积。
- 提示:抽象
-
代码:
-
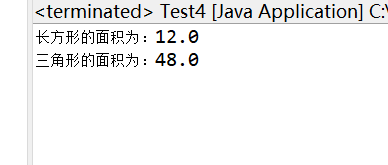
package xjweek11; public abstract class Area { int width; int height; public Area(int width, int height) { super(); this.width = width; this.height = height; } public abstract double area(); } Trigon类: package xjweek11; public class Trigon extends Area { public Trigon(int width, int height) { super(width, height); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public double area(){ return width*height; } } package xjweek11; Rectangle public class Rectangle extends Area { public Rectangle(int width, int height) { super(width, height); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public double area(){ return width*height; } } 测试类: package xjweek11; public class Test4 { public static void main(String[] args) { Rectangle r=new Rectangle(3,4); System.out.println("长方形的面积为:"+r.area()); Trigon t=new Trigon(6,8); System.out.println("三角形的面积为:"+t.area()); // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
截图:
心得体会:
1.java中的每一个类都有一个父类,有的显性的表示,有的则隐性表示,但都是继承一Objec,他是所有java类的父类。
2.Object类------java中万物之祖
3.多态的分类
(1)对象的多态。(父对象引用指向子类实例)
(2)方法的多态。(分为方法的重载和重写或者覆盖)
4.重写的函数只能抛出比之前更小的异常。访问权限只能比之前的更大。
5.对象的多态里面,父类对象指向子类实例,只能调用父类和子类中相同的方法,子类中新添加的方法并不能调用,若要调用就要有强制类型转换。



