1、内置函数:
什么是内置函数?就是Python内部提供的,拿来可以直接用的函数,比如常用的input(),print()等等,截止到python3.6.2版本,一共为我们提供了68个内置函数,下面表中就是内置的68个函数。
|
内置函数 |
||||
|
abs() |
dict() |
help() |
min() |
setattr() |
|
all() |
dir() |
hex() |
next() |
slice() |
|
any() |
divmod() |
id() |
object() |
sorted() |
|
ascii() |
enumerate() |
input() |
oct() |
staticmethod() |
|
bin() |
eval() |
int() |
open() |
str() |
|
bool() |
exec() |
isinstance() |
ord() |
sum() |
|
bytearray() |
filter() |
issubclass() |
pow() |
super() |
|
bytes() |
float() |
iter() |
print() |
tuple() |
|
callable() |
format() |
len() |
property() |
type() |
|
chr() |
frozenset() |
list() |
range() |
vars() |
|
classmethod() |
getattr() |
locals() |
repe() |
zip() |
|
compile() |
globals() |
map() |
reversed() |
__import__() |
|
complex() |
hasattr() |
max() |
round() |
|
|
delattr() |
hash() |
memoryview() |
set() |
|
1.1作用域相关
globals() 打印全局变量
locals() 打印当前位置的所有变量

1 name = 'alex' 2 age = 19 3 def func1(): 4 sex = 'male' 5 print(sex) 6 7 print(globals()) 8 {'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000000001DBA6D8>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'C:/Users/admin/PycharmProjects/xu/s22day05/05 内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'name': 'alex', 'age': 19, 'func1': <function func1 at 0x00000000005B3E18>} 9 10 print(locals()) 11 {'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000000001DBA6D8>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'C:/Users/admin/PycharmProjects/xu/s22day05/05 内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'name': 'alex', 'age': 19, 'func1': <function func1 at 0x00000000005B3E18>} 12 13 name = 'alex' 14 age = 19 15 def func1(): 16 sex = 'male' 17 print(sex) 18 print(globals()) 19 {'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000000001DBA6D8>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'C:/Users/admin/PycharmProjects/xu/s22day05/05 内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'name': 'alex', 'age': 19, 'func1': <function func1 at 0x00000000005B3E18>} 20 print(locals()) 21 {'sex': 'male'} 22 func1()
1.2 其他相关
1.2.1字符串类型
eval() 将字符串类型左右两边的引号去掉

1 d ='{"name":"alex"}' 现在d表示的是一个字符串,用eval去掉左右两边的引号后 2 print(type(d)) <class 'str'> 3 print(eval(d),type(eval(d))) {'name': 'alex'} <class 'dict'>
exec() 执行字符串类型的代码

1 num = """ 2 l = [] 3 for i in range(1,10): 4 l.append(i) 5 print(l) 6 """ 7 exec(num)
compile() 将字符串类型的代码编译,代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者用eval()来取值
1.2.2输入输出
input()
print()
1.2.3 内存相关
hash() 获取一个对象的哈希值,并且每次执行的值都是不同的,如果遇到数字,是多少值就是多少

1 print(hash('a')) 2 # 7881699691700475916 3 4 print((hash('社会人'))) 5 # -7457837388861874164 6 7 print((hash(20))) 8 # 20
id() 获取对象的内存地址

1 name = 'alex' 2 name1 = name 3 print(id(name)) 4 31369120 5 6 print(id(name1)) 7 31369120
1.2.4 文件操作相关
open() 用于打开一个文件,创建一个文件句柄
1.2.5 模块相关
__import__ 用于动态加载类和函数
1.2.6 帮助信息
help() 用于查看函数或模块的帮助信息

1 help(list) 2 3 class list(object) 4 | list() -> new empty list 5 | list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items 6 | 7 | Methods defined here: 8 | 9 | __add__(self, value, /) 10 | Return self+value. 11 | 12 | __contains__(self, key, /) 13 | Return key in self. 14 | 15 | __delitem__(self, key, /) 16 | Delete self[key]. 17 | 18 | __eq__(self, value, /) 19 | Return self==value. 20 | 21 | __ge__(self, value, /) 22 | Return self>=value. 23 | 24 | __getattribute__(self, name, /) 25 | Return getattr(self, name). 26 | 27 | __getitem__(...) 28 | x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] 29 | 30 | __gt__(self, value, /) 31 | Return self>value. 32 | 33 | __iadd__(self, value, /) 34 | Implement self+=value. 35 | 36 | __imul__(self, value, /) 37 | Implement self*=value. 38 | 39 | __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs) 40 | Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature. 41 | 42 | __iter__(self, /) 43 | Implement iter(self). 44 | 45 | __le__(self, value, /) 46 | Return self<=value. 47 | 48 | __len__(self, /) 49 | Return len(self). 50 | 51 | __lt__(self, value, /) 52 | Return self<value. 53 | 54 | __mul__(self, value, /) 55 | Return self*value.n 56 | 57 | __ne__(self, value, /) 58 | Return self!=value. 59 | 60 | __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type 61 | Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. 62 | 63 | __repr__(self, /) 64 | Return repr(self). 65 | 66 | __reversed__(...) 67 | L.__reversed__() -- return a reverse iterator over the list 68 | 69 | __rmul__(self, value, /) 70 | Return self*value. 71 | 72 | __setitem__(self, key, value, /) 73 | Set self[key] to value. 74 | 75 | __sizeof__(...) 76 | L.__sizeof__() -- size of L in memory, in bytes 77 | 78 | append(...) 79 | L.append(object) -> None -- append object to end 80 | 81 | clear(...) 82 | L.clear() -> None -- remove all items from L 83 | 84 | copy(...) 85 | L.copy() -> list -- a shallow copy of L 86 | 87 | count(...) 88 | L.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value 89 | 90 | extend(...) 91 | L.extend(iterable) -> None -- extend list by appending elements from the iterable 92 | 93 | index(...) 94 | L.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return first index of value. 95 | Raises ValueError if the value is not present. 96 | 97 | insert(...) 98 | L.insert(index, object) -- insert object before index 99 | 100 | pop(...) 101 | L.pop([index]) -> item -- remove and return item at index (default last). 102 | Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range. 103 | 104 | remove(...) 105 | L.remove(value) -> None -- remove first occurrence of value. 106 | Raises ValueError if the value is not present. 107 | 108 | reverse(...) 109 | L.reverse() -- reverse *IN PLACE* 110 | 111 | sort(...) 112 | L.sort(key=None, reverse=False) -> None -- stable sort *IN PLACE* 113 | 114 | ---------------------------------------------------------------------- 115 | Data and other attributes defined here: 116 | 117 | __hash__ = None
1.2.7 调用相关
callable() 检查一个对象是否可被调用,如果可以返回True,不可以返回False

1 name = 'eric' 2 def func(): 3 print(name) 4 5 print(callable(name)) 6 # False 7 8 print(callable(func)) 9 # True
1.2.8 查看内置方法
dir() 查看元素的所有内置方法,以字符串的方式放在列表里面

1 print(dir(str)) 2 ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
1.2.9 迭代器与生成器相关
range() 可创建连续的一段数字

1 for i in range(0,5): 2 print(i) 3 4 # 0 5 # 1 6 # 2 7 # 3 8 # 4
iter() 把可迭代对象变成迭代器

1 from collections import Iterator,Iterable 2 l = [1,2,3,4,5] 3 print(isinstance(l,Iterable)) #判断列表是不是可迭代对象 4 # True 5 6 l1 = iter(l) #将列表转换为迭代器,赋值给l1 7 print(isinstance(l1,Iterator)) 判断l1是不是迭代器 8 # True 9 10 print('__next__' in dir(l1)) 第二种判断l1是不是迭代器的方法 11 True
next() 迭代器的取值方法,每next一次就取一个值

1 l = [1,2,3,4,5] 2 l1 = iter(l) 3 print(next(l1)) 4 print(next(l1)) 5 print(next(l1)) 6 print(next(l1))
1.3 数字相关
int() 将一个字符串类型的数字转换成整数

1 s = '123' 2 print(int(s),type(int(s))) 3 123 <class 'int'> 4 print(int(4.4)) 5 # 4
float() 转换为浮点数

1 print(float(5)) 2 # 5.0 3 4 print(float('3.4')) 5 # 3.4
bool() 将指定参数转换为布尔值类型,没有参数或参数为0则返回false,大于0或是字母则为True

1 print(bool()) 2 # False 3 4 print(bool(1)) 5 # True 6 7 print(bool(10)) 8 # True 9 10 print(bool(0)) 11 # False 12 13 print(bool('a')) 14 # True
complex() 复数的转化
1.3.1 十进制数转换相关,返回值为字符串类型
bin() 将一个十进制数转化为二进制数

1 print(bin(10)) 2 0b1010
oct() 将一个十进制数转化为八进制数

1 print(oct(10)) 2 0o12
hex() 将一个十进制数转化为十六进制数

1 print(hex(10)) 2 0xa
1.3.2 运算相关
sum() 对可迭代对象进行求和运算

1 l = [] 2 for i in range(10): 3 l.append(i) 4 print(sum(l)) 5 # 45
min() 取可迭代对象的最小值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最大值)

1 l = [] 2 for i in range(10): 3 l.append(i) 4 print(min(l)) 5 # 0
max() 取可迭代对象的最大值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最大值)

1 l = [] 2 for i in range(10): 3 l.append(i) 4 print(max(l)) 5 # 9
abs() 返回数字的绝对值

1 print(abs(-10)) 2 # 10 3 4 print(abs(-1.5)) 5 # 1.5 6 7 print(abs(23)) 8 # 23
divmod() 计算除数与被除数的结果,返回有个包含商和余数的元组

1 print(divmod(150,12)) 2 # (12, 6) #第一个数为商,第二个数为余数
round() 保留浮点数的小数位数,默认保留整数部分,有四舍五入的功能

1 print(round(4.56746,2)) 2 # 4.57 3 4 print(round(4.56746)) #小数点后面的一位大于等于5则进一 5 # 5 6 7 print(round(4.36746)) #小数点后面的一位小于5则省略 8 # 4
pow() 求x**y次幂(三个参数为x**y的结果对z取余)

print(pow(3,4)) # 81 #3的4次幂等于81 print(pow(3,4,5)) # 1 #3的4次幂除以5余数是1
1.3.3 数据结构相关
reversed() 将一个序列翻转,而且返回的序列变成了一个迭代器

1 l = [1,4,8,9,3,5,7] 2 l1 = reversed(l) 3 print(l1) # <list_reverseiterator object at 0x00000000021EA7F0> 4 5 print(next(l1)) # 7 6 print(next(l1)) # 5 7 print(next(l1)) # 3
slice() 构造一个切片对象

1 l = [1,4,8,9,3,5,7] 2 l1 = slice(0,4) 3 print(l[l1]) # [1, 4, 8, 9]
1.3.4 数据结构相关
list() 把一个可迭代对象转化为列表

1 s = 'youare' 2 print(list(s)) # ['y', 'o', 'u', 'a', 'r', 'e'] 3 4 t = ('y','o','u','a','r','e') 5 print(list(t)) # ['y', 'o', 'u', 'a', 'r', 'e'] 6 7 s1 = {'y','o','u','a','r','e'} 8 print(list(s1) # ['o', 'r', 'u', 'y', 'e', 'a'] #集合是无序的 9 10 d = {'name':'eric','age':20} 11 print(list(d)) # ['name', 'age'] #字典转换为列表只取字典的key
tuple() 把一个可迭代对象转化为元组

1 s = 'youare' 2 print(tuple(s)) # ('y', 'o', 'u', 'a', 'r', 'e') 3 4 l = ['y','o','u','a','r','e'] 5 print(tuple(l)) # ('y', 'o', 'u', 'a', 'r', 'e') 6 7 s1 = {'y','o','u','a','r','e'} 8 print(tuple(s1)) # ('y', 'r', 'o', 'a', 'e', 'u') 9 10 d = {'name':'eric','age':20} 11 print(tuple(d)) # ('name', 'age')
1.3.5 字符串相关
str() 将数据转化为字符串

1 i = 100 2 print(str(i),type(str(i))) 3 # 100 <class 'str'> 4 5 l = ['y','o','u','a','r','e'] 6 print(str(l),type(str(l))) 7 # ['y', 'o', 'u', 'a', 'r', 'e'] <class 'str'> 8 9 s1 = {'y','o','u','a','r','e'} 10 print(str(s1),type(str(s1))) 11 # {'e', 'a', 'o', 'u', 'y', 'r'} <class 'str'> 12 13 d = {'name':'eric','age':20} 14 print(str(d),type(str(d))) 15 # {'name': 'eric', 'age': 20} <class 'str'> 16 17
format() 用于计算各种小数等
bytes() 将unicode转换成bytes类型

1 s = 'eric' 2 s1 = bytes(s,encoding='utf-8') 3 print(s1) # b'eric' 4 5
bytearry() 返回一个新字节数组,这个数组里面的元素是可变的,并且每个元素值的范围为:0 <= x < 256
memoryview()
ord() 返回字符在unicode中的位置点

1 print(ord('a')) # 97 2 3 print(ord('P')) # 80
chr() 返回数字在uniconde中对应的字符

1 print(chr(101)) # e 2 3 print(chr(345)) # ř
ascii() 返回ascii中对应的值,如果值不存在,返回\u...

1 print(ascii('g')) # 'g' 2 print(ascii('社')) # '\u793e'
repr() 返回一个对象的string类型

1 print(repr("['alex','eric','egon','wusir']")) 2 # "['alex','eric','egon','wusir']"
1.3.6 集合相关
dict() 创建一个字典
set() 创建一个集合
frozenset() 返回一个冻结的集合,冻结后集合不能再做任何操作
len() 返回一个对象中的元素个数,也可以叫对象的长度

1 name = ['alex','eric','egon','wusir'] 2 print(len(name)) # 4
sorted() ***对所有可迭代对象进行排序操作,可以结合key使用

1 l = [1,4,8,9,3,5,7] 2 print(sorted(l)) 3 # [1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9] 4 5 def func(x):return x 6 print(sorted(l,key=func)) 7 # [1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]
enumerate() ***返回一个枚举对象,控制元素的索引

1 name = ['alex','eric','egon','wusir'] 2 3 for i in enumerate(name): #如果接收值是一个的话,则按元组的形式返回 4 print(i) 5 # (0, 'alex') 6 # (1, 'eric') 7 # (2, 'egon') 8 # (3, 'wusir') 9 10 for index,content in enumerate(name): 接收值是两个的话,则分别返回每个值 11 print(index,content) 12 # 0 alex 13 # 1 eric 14 # 2 egon 15 # 3 wusir 16 17 for index,content in enumerate(name,29): 可以指定起始值 18 print(index,content) 19 # 29 alex 20 # 30 eric 21 # 31 egon 22 # 32 wusir
all() 可迭代对象中,全部是True 才是True

1 name = ['alex','eric','egon','wusir',0] 2 print(all(name)) # False 3 4 name = ['alex','eric','egon','wusir',1] 5 print(all(name)) # True
any() 可迭代对象中,有一个是True就是True

1 name = ['alex','',0,(),{}] 2 print(any(name)) # True 3 4 name = [False,'',0,(),{}] 5 print(any(name)) # False
zip() 用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对用的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表,如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一样,则返回列表长 度与最短的对象相同

1 l1 = [1,2,3,4] 2 l2 = ['alex','age','sex'] 3 l3 = ['game','work','kaifa','net_man'] 4 for i in zip(l1,l2,l3): 5 print(i) 6 7 # (1, 'alex', 'game') 8 # (2, 'age', 'work') 9 # (3, 'sex', 'kaifa')
filter() 过滤操作,对不满足条件的值过滤掉

1 l = [i for i in range(1,20) if i % 2 == 0] 2 print(l) 3 # [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18] 4 5 def func1(x): return x % 2 == 0 6 l3 = [] 7 f = filter(func1,l) 8 for i in f: 9 l3.append(i) 10 print(l3) 11 # [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18]
map() 会根据提供的函数对指定序列做映射,相当于列表的循环模式

1 l1 = [1,4,7,9,10] 2 def func3(x): 3 return x**2 4 5 m = map(func3,l1) #返回一个生成器 6 for i in m: 7 print(i) 8 # [1, 16, 49, 81, 100] 9 10 11 m1 = map(lambda x:x**2, l1) 12 l2 = [] 13 for i in m1: 14 l2.append(i) 15 print(l2) 16 # [1, 16, 49, 81, 100]
***** min(),max(),filter(),sorted(),zip(),map(),enumerate()
2、匿名函数:
匿名函数就是为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数。
def calculation(n):
return n ** n
print(calculation(5))
换成匿名函数:
calculation = lambda n:n ** n print(calculation(5))
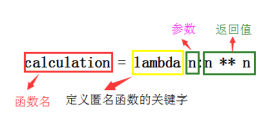
使用匿名函数和内置函数:
sorted()结合lambda排序:

1 l = [1,5,9,88,100,3,7,8,0,4,23,87,6,435,233,2,10,56,96] 2 func = sorted(l,key=lambda n:n) 3 print(func) 4 # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 23, 56, 87, 88, 96, 100, 233, 435]
min()和max()结合lambda获取最大值和最小值:

1 func2 = max(l,key=lambda x:x) 2 print(func2) 3 # 435 4 5 func3 = min(l,key=lambda x:x) 6 print(func3) 7 # 0
map()结合lambda对序列做映射,然后生成一个生成器:

1 l = [1,5,9,88,100,3,7,8,0,4,23,87] 2 l1 = [] 3 func4 = map(lambda x : x * 2,l) 4 for num in func4: 5 l1.append(num) 6 print(l1) 7 # [2, 10, 18, 176, 200, 6, 14, 16, 0, 8, 46, 174]
filter()结合lambda对数据做过滤:

1 l = [1,5,9,88,100,3,7,8,0,4,23,87] 2 l2 = [] 3 func5 = filter(lambda x : x > 22,l) 4 for num in func5: 5 l2.append(num) 6 print(l2) 7 # [88, 100, 23, 87]




