使用为Centos7创建回收站的方法,可以有效地防止误删文件,并对删除信息进行记录。
实现:
- 每个用户都可以使用回收站功能
- 每个用户具有独立的回收站,用户删除的文件会移动到自己专属的回收站中,不会被未授权的用户看到。
- 回收站内按照天建立文件夹,移入的文件添加时间后缀进行重命名,防止同名文件覆盖。
- 可以记录删除记录,对每个文件的删除时间,源位置,删除到回收站中的位置进行记录。
- 可以手动快速删除3天前移入回收站的文件,快速释放磁盘空间。
- 直接使用rm命令,对使用者无感,即使是其他人来使用这个系统也可以使用回收站功能。
- 如果想直接将文件删除,而不是移动到回收站,可以使用/usr/bin/rm进行删除
步骤:
1、/usr/bin目录创建1个新文件,名字为delete,并赋予可执行权限
#!/bin/bash ######################################### # File Name: delete # Date: 2024-06-18 # Version: v1.0 # Author: jason ######################################### # Records information. Such as when it was "deleted", original location, and location in the recycle bin function log_trash() { file=$1 mark1="." mark2="/" if [ "$file" = ${file/$mark2/} ]; then fullpath="$(pwd)/$file" elif [ "$file" != ${file/$mark1/} ]; then fullpath="$(pwd)${file/$mark1/}" else fullpath="$file" fi # The output format is: ${delete time} \t ${original location} \t ${location in the recycle bin} echo -e "$3\t$fullpath\t$2" >>$HOME/.trash/.log } # The function that actually performs the "delete" operation function move_to_trash() { if [ ! -d $HOME/.trash/ ]; then mkdir -m 777 -p $HOME/.trash touch $HOME/.trash/.log chmod 666 $HOME/.trash/.log fi prefix=$(date +%Y_%m_%d) if [ ! -d $HOME/.trash/$prefix ]; then mkdir -p $HOME/.trash/$prefix fi files=() for arg in "$@"; do # If the input parameter is indeed a file, directory, or link, add it to the array if [[ -e "$arg" || -e "$arg" || -L "$arg" ]]; then files+=("$arg") fi done echo "move files to trash" for file in ${files[@]}; do if [ -f "$file" -o -d "$file" ]; then now=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S_%N) file=${file%/} filename=${file##*/} move_trash_path="${HOME}/.trash/${prefix}/${filename}_${now}" /usr/bin/mv $file $move_trash_path [ $? -eq 0 ] && log_trash $file $move_trash_path $now fi done } # If the number of parameters is 0, display help information if [ $# -eq 0 ]; then echo "Usage: rm file1 [file2 file3....]" exit 128 fi move_to_trash "$@"
chmod +x delete
2、修改/etc/bashrc文件,添加如下内容
alias sudo='sudo' alias rm='delete'
source /etc/bashrc
3、定时清空垃圾箱(每周六零点定时清理删除时间超过3天的文件)
0 0 * * 6 find ~/.trash/* -mtime +3 -name "*" -exec /usr/bin/rm -rf {} \;
之后我们可以使用rm命令进行删除文件,删除的文件会自动移动到回收站中。每个用户都拥有自己的回收站,回收站位于$HOME/.trash,移动到回收站的文件会根据日期按文件夹分类,并且每个删除记录都会写入回收站中的.log文件中
测试:
1、查看当前账户的trash目录
[root@localhost bin]# echo $HOME/.trash /root/.trash
2、测试删除文件和目录
[root@localhost home]# rm -rf test.txt move files to trash [root@localhost jason]# rm -rf dnsub_linux_amd64_v2.0/ move files to trash
3、查看删除的文件和删除日志记录
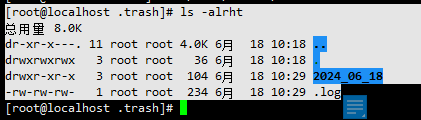

.log文件一共有3列,第一列是删除时间,第二列是文件删除前的位置,第三列是文件位于回收站中的位置
进入具体的日期文件夹,查看删除的文件:
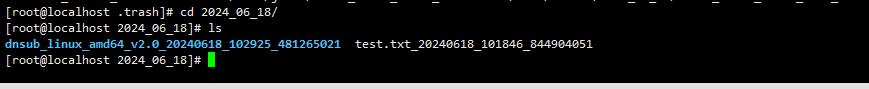
可以看到删除的文件,文件自动被重命名了,可以防止重名文件相互覆盖
参考:
https://blog.uusite.com/system/linux/408.html
https://www.akiraka.net/linux/1101.html
https://note.youdao.com/ynoteshare/index.html?id=974cafdc843fb5fa118e08e2ff538f11&type=note&_time=1719555320627
https://blog.csdn.net/jiandanjinxin/article/details/76686920
标签:
centos






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
2020-06-18 转载:mysql5.7设置不区分大小写