将具有多表关联的Excel数据,通过sql语句脚本的形式,导入到数据库
写在前面:本文用的语言是java;数据库是MySql;
需求:在实际项目中,经常会被客户要求,做批量导入数据;一般的简单的单表数据,可以直接通过Navicat的导入功能,将Excel表格信息直接导入;单实际情况是——需要导入的数据要分别保存在对应的多张表中,其中一张主表,多张关联副表,这个时候再用Navicat的导入功能,无法满足需求! 本文总结一种方法处理这种批量录入多表数据;如下。
核心思路:将Excel数据表中的数据,保存到TXT中;通过脚本读取TXT中的数据,写成对应的sql语句;在Navicat运行sql语句,实现保存目的;
为了展示完整的操作步骤,我准备了一个简单的业务需求:保存学生基本信息和学生选课信息;原始EXCEL数据在一张表里;需要将数据分别保存在student_info和select_class两张数据表中
具体操作步骤:
1.准备Excel原始数据:Excel原始数据有一定的格式要求,要求每列信息必须明确(1表示选课0表示没选),如下图:
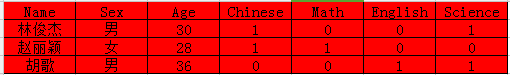
将Excel数据复制到TXT中,如下;
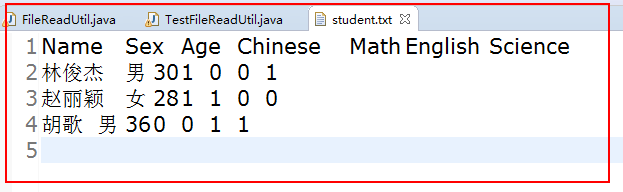
2.准备初始化数据表;
CREATE TABLE `student_info` (
`student_id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学生id',
`name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(1) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(2) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`student_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `select_class` (
`id` int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id',
`student_id` int(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生id',
`class_name` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '课程名称',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
初始化的数据表数据表,如下:
3.编写脚本(核心步骤),代码如下:
package com.fh.readfile;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestFileReadUtil {
private static int Number = 0;
/**
* 功能:Java读取txt文件的内容 步骤:1:先获得文件句柄 2:获得文件句柄当做是输入一个字节码流,需要对这个输入流进行读取
* 3:读取到输入流后,需要读取生成字节流 4:一行一行的输出。readline()。 备注:需要考虑的是异常情况
* @param filePath
* 文件路径[到达文件:如: D:\aa.txt]
* @return 将这个文件按照每一行切割成数组存放到list中。
*/
public static List<String> readTxtFileIntoStringArrList(String filePath) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (file.isFile() && file.exists()) { // 判断文件是否存在
InputStreamReader read = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file));// 考虑到编码格式
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(read);
String lineTxt = null;
while ((lineTxt = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(lineTxt);
}
bufferedReader.close();
read.close();
} else {
System.out.println("找不到指定的文件");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("读取文件内容出错");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
//学生基本信息sql语句模板
private static String studentMainInfoSql = "insert into student_info(student_id,name,sex,age)value(${student_id},'${name}','${sex}',${age});";//注意'${name}'需要单引号,表示是字符串,否则生成的sql语句会出错
//学生选课信息sql语句模板
private static String selectClassInfoSql= "insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(${id},${student_id},'${class_name}');";
//Excel数据表头
private static final String[] HEAD_ARRAY = new String[]{"Name","Sex","Age","Chinese","Math","English","Science"};
//根据表头名称获取列索引索引"Name","Sex","Age","Chinese","Math","English","Science"分别是0 1 2 3 4 5 6
private static int getIndex(String headName){
for(int i=0;i<HEAD_ARRAY.length;i++){
String head = HEAD_ARRAY[i];
if(head.equals(headName)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//生成学生基本信息sql语句方法
private static void createStudentInfo(List<String>lineList){
int student_id =Number;//定义student_id的起始值
for(String line:lineList){//遍历每一行数据
student_id++;
String[] array = line.split("\t");//将每一行数据根据空格拆分成数组
//将sql模板中的value值是用真实数据替换(使用replace()方法)
String studentInfoSql = studentMainInfoSql.replace("${student_id}", student_id+"").
replace("${name}", array[getIndex("Name")]).
replace("${sex}", array[getIndex("Sex")]).
replace("${age}", array[getIndex("Age")]);
//打印sql语句
System.out.println(studentInfoSql);
}
}
//生成学生选课信息sql语句
private static void createSelectClassInfo(List<String>lineList){
int student_id =Number;//定义student_id的起始值
int select_class_id =Number;//定义select_class_id的起始值
int startIndex = getIndex("Chinese");//获取选课信息列的首列索引
int endIndex = getIndex("Science");//获取选课信息列的末列索引
for(String line:lineList){//遍历每一行数据
student_id++;
String[] array = line.split("\t");//将每一行数据根据空格拆分成数组
for(int i=startIndex;i< (endIndex+1);i++){//遍历每一行数据中每个课程的选择情况
if(array[i].equals("1")){//如果是1,表示选择该课程,要生成对应的sql语句
select_class_id++;
String className =HEAD_ARRAY[i];
//生成学生选课信息sql语句
String selectClassSql = selectClassInfoSql.replace("${id}", select_class_id+"").
replace("${student_id}", student_id+"").
replace("${class_name}", className);
//打印 语句
System.out.println(selectClassSql);
}
}
}
}
//main方法,打印最终sql语句
public static void main(String[] args) {
//读取txt文件中的数据,格式是list集合
List<String> lineList = readTxtFileIntoStringArrList("txt/student.txt");
//去掉第一行数据,因为第一行数据是表头
lineList.remove(0);
//打印学生基本信息sql语句
createStudentInfo(lineList);
//打印学生选课数据sql语句
createSelectClassInfo(lineList);
}
}
4.运行脚本,得到sql语句;如下:
insert into student_info(student_id,name,sex,age)value(1,'林俊杰','男',30);
insert into student_info(student_id,name,sex,age)value(2,'赵丽颖','女',28);
insert into student_info(student_id,name,sex,age)value(3,'胡歌','男',36);
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(1,1,'Chinese');
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(2,1,'Science');
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(3,2,'Chinese');
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(4,2,'Math');
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(5,3,'English');
insert into select_class(id,student_id,class_name) value(6,3,'Science');
在navicat中运行sql语句,最终结果,如下;

5.总结:本案例是多表数据导入案例中最简单的一张,但是基本思路已经表达完整;再多的关联表,沿用select_class即可;


