项目总结63:使用Spring AOP和BindingResult实现对接口的请求数据校验,并用@ExceptionHandler返回校验结果
问题
合格的接口,应该在接口的内部对请求参数进行校验,但是在接口内部通过业务代码进行校验,显得十分冗余,参数越多,代码就越混乱;
思考:可以将接口请求参数的校验封装成一个全局的方法,进行统一处理。
目的
使用Spring AOP 和 @ExceptionHandler 对接口的数据校验进行全局封装,从而做到只要在请求数据的实体类中进行注解说明,就可以进行数据校验;
具体可以:
1- 避免在接口内部,通过代码方式进行冗余的数据校验;比如:if(data is empty){retur ...}
2- 可以在请求数据的实体类中进行注解说明,比如:@NotEmpty(message = "手机号不能为空");就可以进行数据校验;
3- 可以将具体的校验结果直接返回给前端;比如: {...,"msg": "手机号不能为空",...}
解决思路
1- 用@Valid 和 BindingResult分析请求参数校验情况
2- 用AOP对BindingResult中的校验结果进行处理,如果校验出问题,抛出异常;
3- 使用@ExceptionHandler注解捕获校验异常,并返回给前端
具体实现方案(源码示例)(以修改登陆密码接口为例)
第一步:用@Valid 和 BindingResult分析请求参数校验
具体逻辑:被@Validated的实体类,会自动根据实体类中的参数的@NotEmpty注解,进行数据校验;并将数据校验结果封装到BindingResult类中;如果检验有问题,BindingResult数据如下
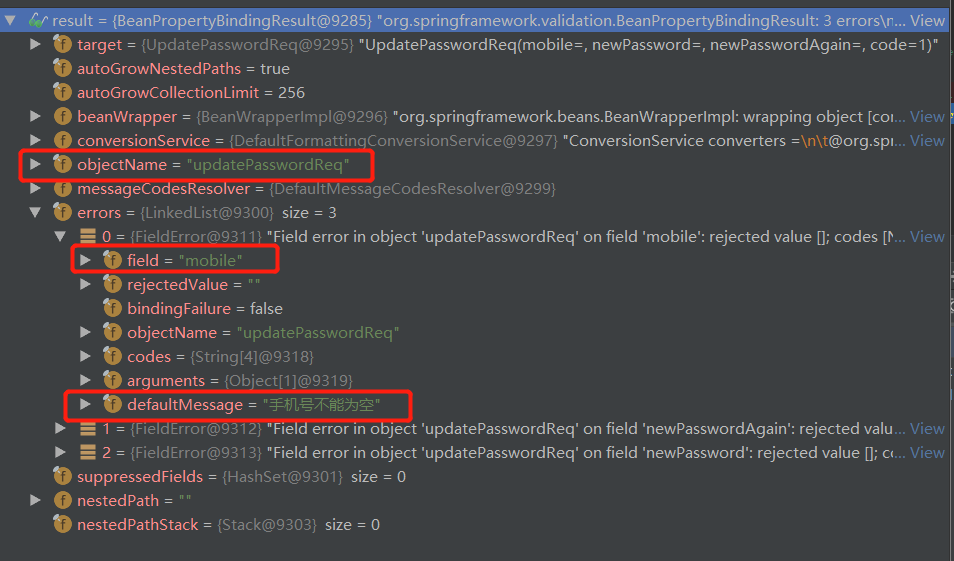
源码如下:
1- controller层接口
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController @RequestMapping(value="/api") public class ApiLoginController extends ApiBaseController { @ValidAnn //AOP切入点 @PostMapping(value="/password/update") public ResultModel<Object> updatePassword(@Valid @RequestBody UpdatePasswordReq updatePasswordReq, BindingResult bindingResult){ //1-校验验证码 //2-更新密码 return ResultUtil.success(); } }
2- 请求数据实体类
//使用了lombok @Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class UpdatePasswordReq { @NotEmpty(message = "手机号不能为空") private String mobile; @NotEmpty(message = "新密码1不能为空") private String newPassword; @NotEmpty(message = "新密码2不能为空") private String newPasswordAgain; @NotEmpty(message = "验证码不能为空") private String code; }
3- 返回参数实体类
@Data public class ResultModel<T> { // Http网络码 private Integer code; // 提示消息 private String msg; // 数据 private T data; }
4- 返回结果通用类和异常枚举
/** * 工具类 * * @author cjm * @date 2018/2/1 */ public class ResultUtil { /** * 返回异常信息 */ public static ResultModel exception(ResultEnum enums) { ResultModel model = new ResultModel(); model.setCode(enums.getCode()); model.setMsg(enums.getMessage()); return model; } /** * 返回成功信息(只包含提示语) */ public static ResultModel success() { ResultModel model = new ResultModel(); model.setCode(ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode()); model.setMsg(ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getMessage()); return model; } } public enum ResultEnum { SUCCESS(200, "success"), FAIL(400, "fail"), VISIT_NOT_AUTHORIZED(401, "未授权"), ARGUMENT_ERROR(402,"参数错误"), ARGUMENT_EXCEPTION(407, "参数存在异常"), ARGUMENT_TOKEN_EMPTY(409, "Token为空"), ARGUMENT_TOKEN_INVALID(410, "Token无效"), SERVER_ERROR(501, "服务端异常"), SERVER_SQL_ERROR(503,"数据库操作出现异常"), SERVER_DATA_REPEAT(504, "服务器数据已存在"), SERVER_DATA_NOTEXIST(505,"数据不存在"), SERVER_DATA_STATUS_ERROR(506, "数据状态错误"), SERVER_SMS_SEND_FAIL(701, "短信发送失败"), ; private int code; private String message; private ResultEnum(int code, String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } public int getCode() { return code; } public String getMessage() { return message; } }
第二步:用AOP对BindingResult中的校验结果进行处理,如果校验出问题,抛出异常;
具体实现:AOP根据@ValidAnn定位到每一个需要数据校验的接口,使用环绕通知,处理BindingResult类的结果,如果数据校验有问题,将校验结果交给ServerException,并且抛出ServerException异常
源码如下
1- ValidAnn 注解,用户AOP定位
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface ValidAnn { }
2- 环绕AOP类,处理判断并处理校验结果,如果校验出问题,则抛出ServerException;
@Aspect @Component @Order(1) public class ValidAop { /** * 所有controller方法都会执行此切面 * 用于检验参数 */ @Pointcut("@annotation(com.hs.annotation.ValidAnn)") public void validAop() { } /** * 对切面进行字段验证 * * @param joinPoint 切点 * @return Object * @throws Throwable */ @Around("validAop()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); List<String> errorList = new ArrayList<>(); if (args != null) { Arrays.stream(args) .forEach(arg -> { if (arg instanceof BindingResult) { BindingResult result = (BindingResult) arg; if (result.hasErrors()) { result.getAllErrors() .forEach(err -> { errorList.add(err.getDefaultMessage()); }); throw new ServerException(Joiner.on(" || ").join(errorList)); } } }); } return joinPoint.proceed(); } }
3- ServerException,当校验出问题时,抛出当前异常
public class ServerException extends RuntimeException { private Integer code; private Object Data; public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } public Object getData() { return Data; } public void setData(Object data) { Data = data; } public ServerException() { super(); } public ServerException(Integer code, String message, Object data) { super(message); this.code = code; this.Data = data; } public ServerException(Integer code, String message) { super(message); this.code = code; } public ServerException(String message) { super(message); this.code = ResultEnum.ARGUMENT_ERROR.getCode(); } public ServerException(String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); } public ServerException(Throwable cause) { super(cause); } protected ServerException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) { super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace); } }
第三步:使用@ExceptionHandler注解捕获校验异常,并返回给前端
具体实现:@ControllerAdvice和@ExceptionHandler拦截异常并统一处理。在GlobalExceptionHandler 类中使用@ExceptionHandler(value = ServerException.class)专门捕获ServerException异常,并且将结果封装到返回类中,返回给前端
源码如下:
1- GlobalExceptionHandler 类,用于捕获异常,并作相关处理
@ControllerAdvice //使用 @ControllerAdvice 实现全局异常处理 @ResponseBody public class GlobalExceptionHandler { protected Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(this.getClass()); /** * 自定义异常捕获 * * @param exception 捕获的异常 * @return 返回信息 */ @ExceptionHandler(value = ServerException.class) public ResultModel exceptionHandler(ServerException exception) { logger.warn(exception); ResultModel model = new ResultModel(); model.setCode(exception.getCode()); model.setMsg(exception.getMessage()); model.setData(exception.getData()); //3-以Json格式返回数据 return model; } }
测试结果
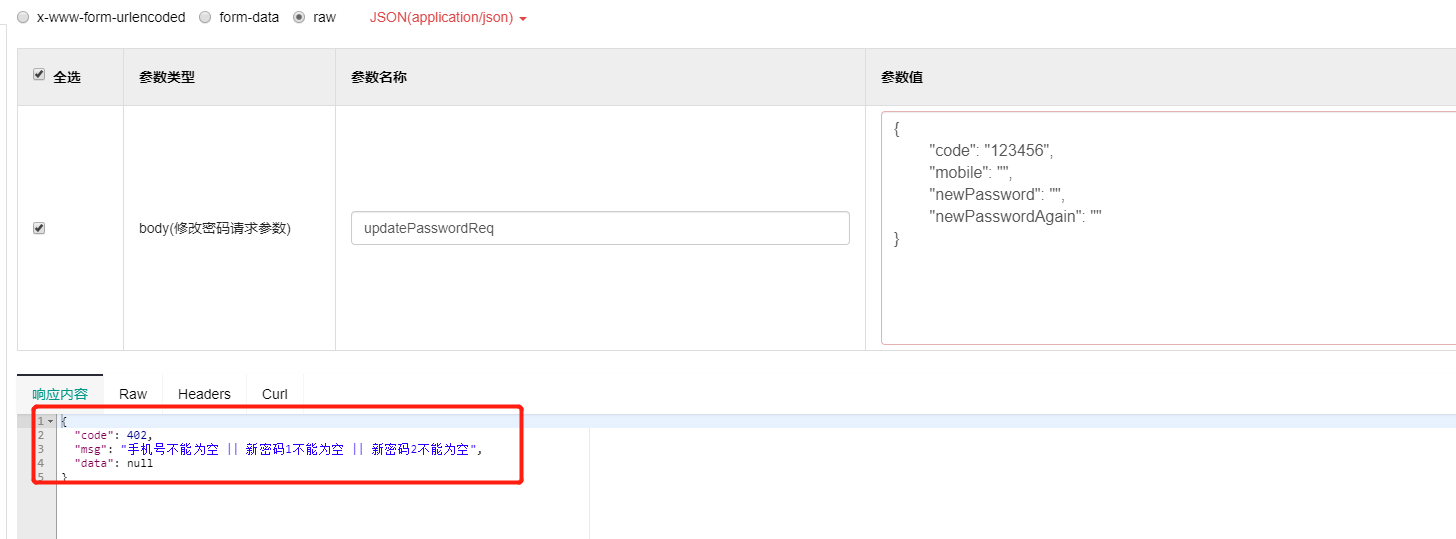
END



