题:
二维数组表示迷宫(格子组成),0不能走,1能走。求走出路径。
指导思想:
一步步尝试出所有可能,输出成功结果。
尝试过程保存在栈里,一旦走出,栈里保存的就是正确路径。
编程思路:
从某个格子开始找:
{
如果该格子是出口,成功!
某个格子入栈
{
某个格子上可用,某个格子上开始找
某个格子右可用,某个格子右开始找
某个格子下可用,某个格子下开始找
某个格子左可用,某个格子左开始找
}
某个格子出栈
}
编程:
1、先准备数组,并测试:
public class App { static int[][] a; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { a = getArray(); showArray(); } public static int[][] getArray() { int[][] x = { { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 } }; return x; } public static void showArray() { for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } } }
测试结果:

目测有正确解,通过。
2、写一个简单的栈,用于保存走过的路径:
public class MyStack { public static int[][] n = new int[150][2]; public static int p = 150; public static void push(int x, int y) { p--; n[p][0] = x; n[p][1] = y; } public static int[] pop() { int[] x = new int[2]; if (p == 150)//栈空 { x[0] = -1; x[1] = -1; } else { x[0] = n[p][0]; x[1] = n[p][1]; p++; } return x; } }
3、按之前的思路,搭好“走迷宫”方法的架子
//从(x,y)位置开始走迷宫 public static void goMiGong(int x,int y) { //如果这个格子是出口,则程序结束 if(x==7&&y==12) { //当前格子设置为2 //输出数组 //退出程序 } else { //当前格子设置为2,入栈 //*按上、右、下、左顺序依次走其他格子 //出栈(且还原为1)(栈空则无解) } }
4、回头阅读上面的程序,打星号的部分稍微有一点复杂,希望有一个方法,辅助判断某个格子是否可以走。代码如下:
public static boolean nengZou(int x,int y) { boolean b=false; if(x>=0&&y>=0) { if(a[x][y]==1) { b=true; } } return b; }
5、一切准备完毕,用上面的东西拼装起整个程序。调试后代码如下:
主程序(app.java)
public class App { static int[][] a; // 存放出栈元素的位置,如(3,2) static int[] p = new int[2]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { a = getArray(); System.out.println("原始迷宫:"); showArray(); System.out.println("-----------------------------------"); goMiGong(0, 0); } public static int[][] getArray() { int[][] x = { { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 } }; return x; } public static void showArray() { for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } } // 从(x,y)位置开始走迷宫 public static void goMiGong(int x, int y) { // 如果这个格子是出口,则程序结束 if (x == 7 && y == 12) { // 当前格子设置为2 a[x][y] = 2; // 输出数组 System.out.println("迷宫有解:"); showArray(); // 退出程序 System.exit(0); } else { // 当前格子设置为2,入栈 a[x][y] = 2; MyStack.push(x, y); // 按上、右、下、左顺序依次走其他格子 if (nengZou(x - 1, y)) { goMiGong(x - 1, y); } if (nengZou(x, y + 1)) { goMiGong(x, y + 1); } if (nengZou(x + 1, y)) { goMiGong(x + 1, y); } if (nengZou(x, y - 1)) { goMiGong(x, y - 1); } // 出栈(且还原为1)(栈空则无解) p = MyStack.pop(); if (p[0] == -1) { System.out.println("迷宫无解"); } else { a[p[0]][p[1]] = 1; } } } // 判断(x,y)是否可以走。判断方法: // 1、超出数组不能走;2、在栈内(为2)不能走;3、为0不能走 // 即:都大于等于0,且对应数组值为1,就可以走。 public static boolean nengZou(int x, int y) { boolean b = false; if (x >= 0 && y >= 0&&x<8&&y<13) { if (a[x][y] == 1) { b = true; } } return b; } }
辅助栈(myStack.java)
public class MyStack { public static int[][] n = new int[150][2]; public static int p = 150; public static void push(int x, int y) { p--; n[p][0] = x; n[p][1] = y; } public static int[] pop() { int[] x = new int[2]; if (p == 150)//栈空 { x[0] = -1; x[1] = -1; } else { x[0] = n[p][0]; x[1] = n[p][1]; p++; } return x; } }
程序运行结果:
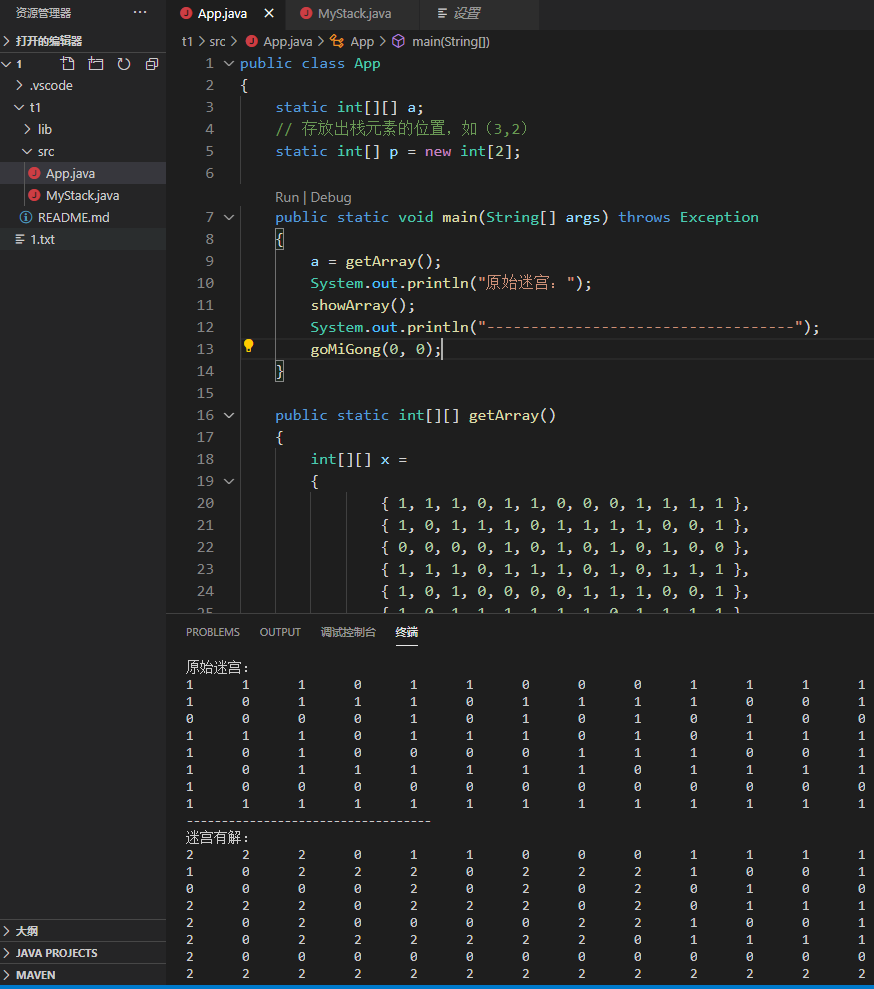
人为修改最后一行第一个元素的值为0,发现并未输出正确结果。
请检查程序,修改它,得出正确的程序。
提示:判断“迷宫无解”的条件。什么情况下迷宫无解?当弹出迷宫入口的时候,即可判定无解。
思考:1、在这道题目中,栈是必须的吗?2、看看下面的图,猜猜是什么?
纯栈版。思路类似,用栈实现。
位置类:
public class MyPoint { public int x,y; public MyPoint() { } public MyPoint(int _x,int _y) { x=_x; y=_y; } }
主类:
import java.util.Stack; //程序中状态说明: //0、不可通过,原始状态 //1、可通过,原始状态 //2、已入栈,尚未尝试 //3、正在尝试 //4、已尝试,无法通过 public class c1 { static int[][] a; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Stack<MyPoint> mystack=new Stack<MyPoint>(); MyPoint mp,t; boolean b=false; a = getArray(); System.out.println("原始迷宫:"); showArray(); System.out.println("-----------------------------------"); mystack.push(new MyPoint(0,0)); a[0][0]=2; while(!mystack.empty()) { b=false; //peek方法,获取栈顶值,但不出栈。 mp=mystack.peek(); a[mp.x][mp.y]=3; if(mp.x==7&&mp.y==12) { System.out.println("有解"); b=true; showArray(); break; } t=new MyPoint(mp.x-1, mp.y); if(nengZou1(t)) { b=true; mystack.push(t); a[t.x][t.y]=2; } t=new MyPoint(mp.x, mp.y+1); if(nengZou1(t)) { b=true; mystack.push(t); a[t.x][t.y]=2; } t=new MyPoint(mp.x+1, mp.y); if(nengZou1(t)) { b=true; mystack.push(t); a[t.x][t.y]=2; } t=new MyPoint(mp.x, mp.y-1); if(nengZou1(t)) { b=true; mystack.push(t); a[t.x][t.y]=2; } if(!b) { mystack.pop(); a[mp.x][mp.y]=4; } } if(!b) { System.out.println("无解"); } } public static int[][] getArray() { int[][] x = { { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 } }; return x; } public static void showArray() { for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j] + "\t"); } System.out.println(); } } public static boolean nengZou1(MyPoint x) { boolean b = false; if (x.x >= 0 && x.y >= 0&&x.x<8&&x.y<13) { if (a[x.x][x.y] == 1) { b = true; } } return b; } }
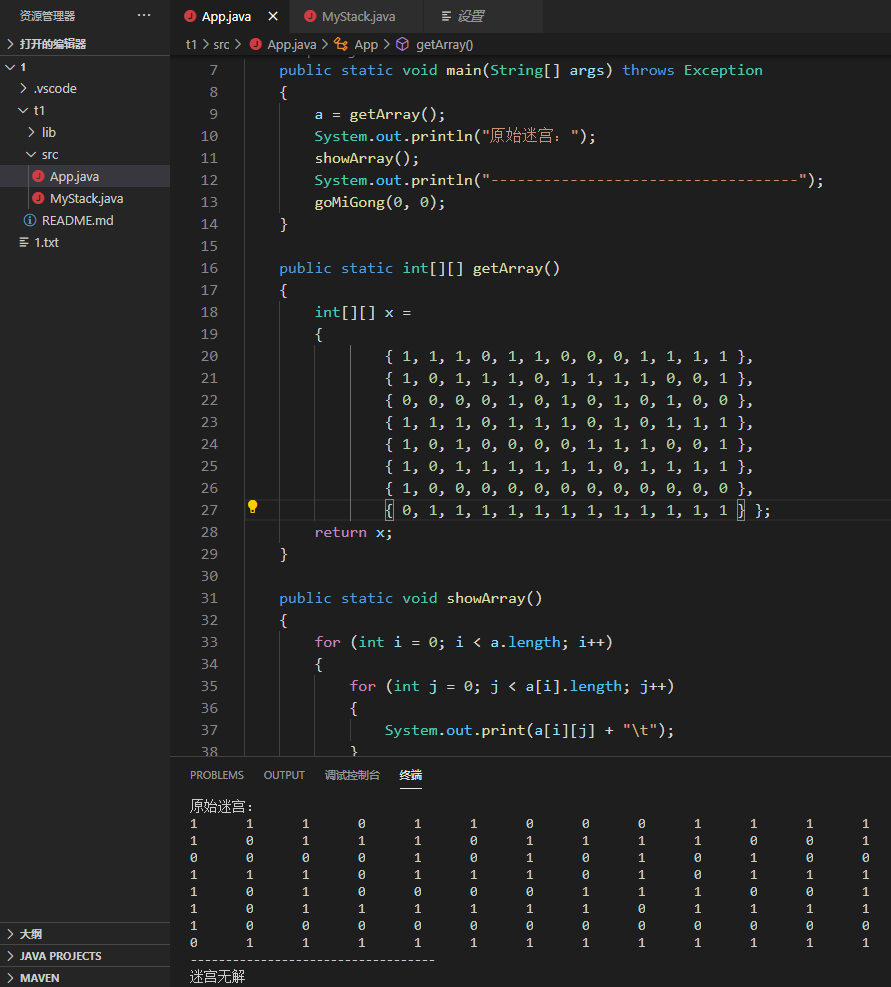
运行效果(其中3为尝试后的通路,2为尚未尝试的点,4为尝试失败的点)
原始迷宫: 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ----------------------------------- 有解 3 3 3 0 2 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 4 0 3 3 3 0 3 3 3 2 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 3 0 3 0 3 0 1 0 0 3 3 3 0 3 3 3 0 3 0 1 1 1 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 3 3 2 0 0 1 3 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 0 1 1 1 1 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现