各位童鞋大家好,向来简单粗暴的铁柱兄给大家来玩一手套娃模式来组Json数据,不说别的,无脑套。
当然,这一手比较适合临场用一下,若长期用的话建议搞一套适用的框架,只管set就好了。话不多说开始上课。
套娃模式这个顾名思义啊,就是一层一层的往里面套就好了,特舒服。先上一手代码:
发送https请求的代码我是随便搜的,这一套如果对你适用的话就直接复制过去了,套娃这套代码对发什么请求都无所谓,只要对方要求的是json格式的。
package test;
import org.apache.http.conn.ClientConnectionManager;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.Scheme;
import org.apache.http.conn.scheme.SchemeRegistry;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.TrustManager;
import javax.net.ssl.X509TrustManager;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import net.sf.json.JSONObject;
public class SSLClient extends DefaultHttpClient {
public SSLClient() throws Exception {//网上搜的发https的方法
super();
//传输协议需要根据自己的判断
SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
X509TrustManager tm = new X509TrustManager() {
@Override
public void checkClientTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
@Override
public void checkServerTrusted(X509Certificate[] chain,
String authType) throws CertificateException {
}
@Override
public X509Certificate[] getAcceptedIssuers() {
return null;
}
};
ctx.init(null, new TrustManager[]{tm}, null);
SSLSocketFactory ssf = new SSLSocketFactory(ctx, SSLSocketFactory.ALLOW_ALL_HOSTNAME_VERIFIER);
ClientConnectionManager ccm = this.getConnectionManager();
SchemeRegistry sr = ccm.getSchemeRegistry();
sr.register(new Scheme("https", 443, ssf));
}
public static String doPost(String url, String map, String charset) {
org.apache.http.client.HttpClient httpClient = null;
HttpPost httpPost = null;
String result = null;
try {
httpClient = new SSLClient();
httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
//设置参数
httpPost.addHeader("Accept", "application/json");
httpPost.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
StringEntity stringEntity = new StringEntity(map);
stringEntity.setContentEncoding("UTF-8");
stringEntity.setContentType("application/json");
httpPost.setEntity(stringEntity);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
if (response != null) {
HttpEntity resEntity = response.getEntity();
if (resEntity != null) {
result = EntityUtils.toString(resEntity, charset);
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
private static String url = "https://xx.xx.xx.xxx:xxxx/xxxx/xxxx";//填写需要发送请求的地址 https后面跟ip跟端口跟地址
private static String charset = "utf-8";
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* new几个JSONObject出来作为套筒
* 需要几层就new几个
*/
JSONObject json=new JSONObject();//最大的套筒
JSONObject json1=new JSONObject();
JSONObject json2=new JSONObject();
//json1、json2作为第二层套筒 这些数据放自己需要的即可
json1.put("txnCode", "GWS00004");
json1.put("reqDate", "20201102");
json1.put("reqTime", "101532");
json1.put("channelId", " stockapp");
json1.put("traceNo", "9e4124f5b1c145c18b698fb7d5628002");
json.put("header", json1);
json2.put("ciNo", "8000001397");
json.put("body",json2 );
String encryptStr = json.toString();
System.out.println("encryptStr:" + encryptStr);
String httpOrgCreateTestRtn = doPost(url, encryptStr, charset);//丢去发送刚组的数据
System.out.println("result:" + httpOrgCreateTestRtn);//返回数据
}
}
组起来其实是很容易的,有了思路随便套,随便多少层,随意套。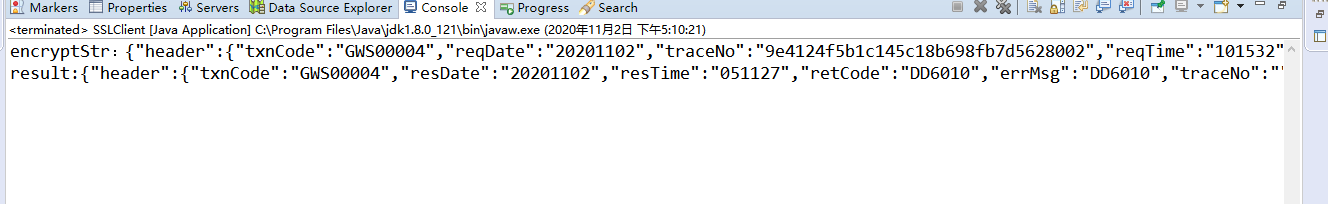
encryptStr:{"header":{"txnCode":"GWS00004","reqDate":"20201102","traceNo":"9e4124f5b1c145c18b698fb7d5628002","reqTime":"101532","channelId":" stockapp"},"body":{"ciNo":"8000001397"}}
result:{"header":{"txnCode":"GWS00004","resDate":"20201102","resTime":"051127","retCode":"DD6010","errMsg":"DD6010","traceNo":""}}
这套方法也适用Map,解释啥的我一如既往的丢注释里了,有不明白的地方欢迎提问。谢谢




