给定两个增序的链表,试将其合并成一个增序的链表。
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int x) :val(x), next(nullptr) {}
};
void printList(ListNode* head) {
while (head) {
std::cout << head->val << " ";
head = head->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) {
ListNode* head3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = head3;
while (head1 && head2) {
if (head1->val <= head2->val) {
tail->next = head1;
head1 = head1->next;
}
else {
tail->next = head2;
head2 = head2->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = head1 ? head1 : head2;
return head3->next;
/*
head3被初始化为一个新的ListNode对象,这个对象并不包含任何实际的数据值(通常为0或某个哨兵值),它的主要作用是作为合并后链表的头部。
在释放内存时,我们也需要从head3->next开始释放,跳过哨兵节点。这是因为在某些实现中,哨兵节点可能不会被释放,因为它可能在其他地方还有用途,
或者它可能被用作一个永久的头部节点。
*/
}
int main() {
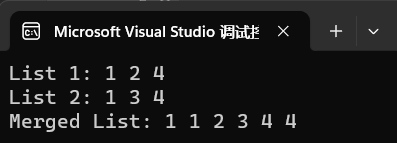
// 创建链表1: 1 -> 2 -> 4
ListNode* head1 = new ListNode(1);
head1->next = new ListNode(2);
head1->next->next = new ListNode(4);
// 创建链表2: 1 -> 3 -> 4
ListNode* head2 = new ListNode(1);
head2->next = new ListNode(3);
head2->next->next = new ListNode(4);
std::cout << "List 1: ";
printList(head1);
std::cout << "List 2: ";
printList(head2);
ListNode* mergedHead = mergeTwoLists(head1, head2);
std::cout << "Merged List: ";
printList(mergedHead);
// 释放内存
ListNode* current = mergedHead;
while (current) {
ListNode* next = current->next;
delete current;
current = next;
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号