#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int girl = 19;
int boy = 21;
int const* p1 = &girl; //不能修改指向变量的值,其中int const * p1 = &girl等同于const int * p1 = &girl;
//*p1 = 22; //这些有注释的都是不能被正常运行的
girl = 26;
//p1 = 28;
p1 = &boy;
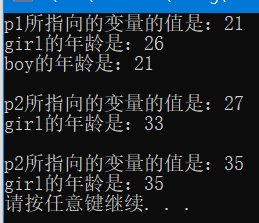
printf("p1所指向的变量的值是:%d\n", *p1);
printf("girl的年龄是:%d\n", girl);
printf("boy的年龄是:%d\n\n", boy);
int* const p2 = &girl; //不允许指向别的地址
*p2 = 27;
printf("p2所指向的变量的值是:%d\n", *p2);
girl = 33;
//p2 = &boy;
printf("girl的年龄是:%d\n\n", girl);
const int* const p3 = &girl; //不允许指向别的地址,也不能修改指向变量的值
//*p3 = 27;
girl = 35;
//p3 = &boy;
printf("p2所指向的变量的值是:%d\n", *p3);
printf("girl的年龄是:%d\n", girl);
system("pause");
return 0;
} //总结:const离谁越近,谁就不能被修改
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号