1、学习任务
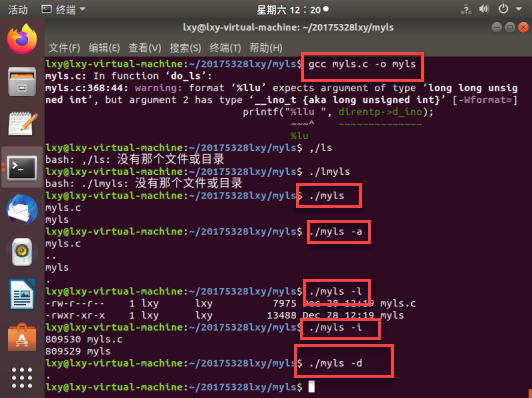
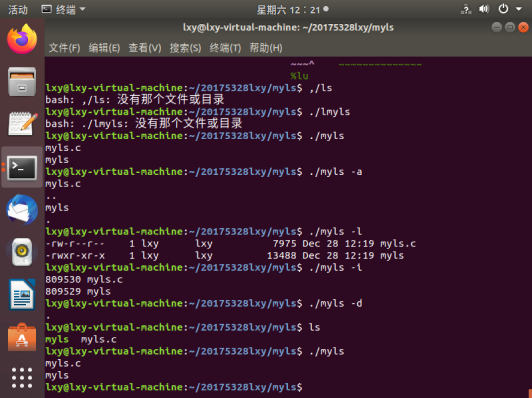
参考伪代码实现ls的功能,提交代码的编译,运行结果截图,码云代码链接
打开目录文件
针对目录文件
读取目录条目
显示文件名
关闭文件目录文件
2、ls功能
ls:显示文件目录列表
- -a:显示所有的文件,包括隐藏文件
- -l:列出长数据串,显示出文件的属性与权限等数据信息(常用)
- -i:结合-l参数列出每个文件的inode
- -d:仅列出目录本身,而不是列出目录里的内容列表
3、代码
include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#define LS_NONE 0
#define LS_L 101
#define LS_R 102
#define LS_D 103
#define LS_I 104
#define LS_A 200
#define LS_AL (LS_A+LS_L)
#define LS_AI (LS_A+LS_I)
// 展示单个文件的详细信息
void show_file_info(char* filename, struct stat* info_p)
{
char* uid_to_name(), *ctime(), *gid_to_name(), *filemode();
void mode_to_letters();
char modestr[11];
mode_to_letters(info_p->st_mode, modestr);
printf("%s", modestr);
printf(" %4d", (int) info_p->st_nlink);
printf(" %-8s", uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid));
printf(" %-8s", gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid));
printf(" %8ld", (long) info_p->st_size);
printf(" %.12s", 4 + ctime(&info_p->st_mtime));
printf(" %s\n", filename);
}
void mode_to_letters(int mode, char str[])
{
strcpy(str, "----------");
if (S_ISDIR(mode))
{
str[0] = 'd';
}
if (S_ISCHR(mode))
{
str[0] = 'c';
}
if (S_ISBLK(mode))
{
str[0] = 'b';
}
if ((mode & S_IRUSR))
{
str[1] = 'r';
}
if ((mode & S_IWUSR))
{
str[2] = 'w';
}
if ((mode & S_IXUSR))
{
str[3] = 'x';
}
if ((mode & S_IRGRP))
{
str[4] = 'r';
}
if ((mode & S_IWGRP))
{
str[5] = 'w';
}
if ((mode & S_IXGRP))
{
str[6] = 'x';
}
if ((mode & S_IROTH))
{
str[7] = 'r';
}
if ((mode & S_IWOTH))
{
str[8] = 'w';
}
if ((mode & S_IXOTH))
{
str[9] = 'x';
}
}
char* uid_to_name(uid_t uid)
{
struct passwd* getpwuid(),* pw_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if((pw_ptr = getpwuid(uid)) == NULL)
{
sprintf(numstr,"%d",uid);
return numstr;
}
else
{
return pw_ptr->pw_name;
}
}
char* gid_to_name(gid_t gid)
{
struct group* getgrgid(),* grp_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if(( grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid)) == NULL)
{
sprintf(numstr,"%d",gid);
return numstr;
}
else
{
return grp_ptr->gr_name;
}
}
void do_ls(char dirname[],int mode)
{
DIR* dir_ptr;
struct dirent* direntp;
if ((dir_ptr = opendir(dirname)) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "ls2: cannot open %s \n", dirname);
}
else
{
if(mode==LS_D)
{
printf("%s\n", dirname);
}
else
{
char dirs[20][100];
int dir_count = 0;
while ((direntp = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
{
if(mode < 200 && direntp->d_name[0]=='.')
{
continue;
}
char complete_d_name[200]; // 文件的完整路径
strcpy (complete_d_name,dirname);
strcat (complete_d_name,"/");
strcat (complete_d_name,direntp->d_name);
struct stat info;
if (stat(complete_d_name, &info) == -1)
{
perror(complete_d_name);
}
else
{
if(mode == LS_L||mode == LS_AL)
{
show_file_info(direntp->d_name, &info);
}
else if(mode == LS_A||mode == LS_NONE||mode == LS_I||mode == LS_AI)
{
if(mode == LS_I||mode == LS_AI)
{
printf("%llu ", direntp->d_ino);
}
printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name);
}
else if(mode == LS_R)
{
if(S_ISDIR(info.st_mode))
{
printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name);
strcpy (dirs[dir_count],complete_d_name);
dir_count++;
}
else
{
printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name);
}
}
}
}
if(mode == LS_R)
{
int i=0;
printf("\n");
for(;i<dir_count;i++){
printf("%s:\n", dirs[i]);
do_ls(dirs[i],LS_R);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
closedir(dir_ptr);
}
}
// 解析一个单词参数,如-l,-i
int analyzeParam(char* input){
if(strlen(input)==2)
{
if(input[1]=='l') return LS_L;
if(input[1]=='a') return LS_A;
if(input[1]=='d') return LS_D;
if(input[1]=='R') return LS_R;
if(input[1]=='i') return LS_I;
}
else if(strlen(input)==3)
{
if(input[1]=='a'&& input[2]=='l') return LS_AL;
if(input[1]=='a'&& input[2]=='i') return LS_AI;
}
return -1;
}
int main(int ac,char* av[])
{
if(ac == 1)
{
do_ls(".",LS_NONE);
}
else
{
int mode = LS_NONE; // 默认为无参数ls
int have_file_param = 0; // 是否有输入文件参数
while(ac>1)
{
ac--;
av++;
int calMode = analyzeParam(*av);
if(calMode!=-1)
{
mode+=calMode;
}
else
{
have_file_param = 1;
do
{
printf("%s:\n", *av);
do_ls(*av,mode);
printf("\n");
ac--;
av++;
}while(ac>=1);
}
}
if (!have_file_param)
{
do_ls(".",mode);
}
}
}
4、测试实现mystat