第四章 委托与事件
目标
本章学习目标:
1.使用Delegate类控制组件间的交互
2.使用Event语句、EventHandler委托和EventArgs类控制组件间的交互
委托的定义:
- 委托实现了函数回调功能
- 委托确保了回调方法是类型安全的
- 委托集成了连续调用多个方法的功能
- 委托是引用类型,这与类和接口相似
namespace DelegateDemo
{
public static class A
{
public static void disp()
{
B b1 = new B();
//b1.dh = new DemoHandler(f1); //第一种使用方法,初始化DemoHandler(),
//并提供方法名作为参数
//b1.test();
//b1.dh =delegate{ Console.WriteLine("test");};//第二种使用方法,使用匿名方法作为参数
//b1.test();
}
//第一种使用方法对应的无参无返回值方法
public static void f1()
{
Console.WriteLine("f1 function");
}
public static void Main()
{
disp();
}
}
//使用委托,实现在调用该类时的相同返回值类型及参数的方法
public class B
{
public DemoHandler dh;
public void test()
{
dh();
}
}
public delegate void DemoHandler(); //申明委托
}
增加委托行为:
C# 2.0对委托的语言进行了某些增加,引入了匿名方法,协变和逆变.
1. 匿名方法
2. 协变:当委托方法的返回类型具有派生程序比委托签名更大的时候
3. 逆变:当委托方法的签名具有一个或者多个参数,并且这些参数的类型派生自方法参数的类型时.
示例:使用委托来传值:
匿名方法:
namespace Demo
{
public delegate string ConsoleDelegate(string str);
public class RW
{
public ConsoleDelegate dg;
public RW()
{
//dg = new ConsoleDelegate(Read);
dg = delegate(string str) //此为使用匿名方法代替方面的方式,
{ //当只有委托使用该方法时,使用匿名方法.
Console.WriteLine("Please Input{0}:", str);
return Console.ReadLine();
};
}
/*public string Read(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please Input{0}:",str);
return Console.ReadLine();
}*/
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
RW c1 = new RW();
if (c1.dg("Password:") != "2005")
{
Console.WriteLine("error");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("pass");
}
}
}
}
协变: 当委托方法的返回类型具有派生程序比委托签名更大的时候(委托的类型返回值是它所指向函数的返回值得基类.)
namespace XieBian
{
public class Animal
{
}
public class Dogs : Animal { }
public delegate Animal HandlerDemo();
public class Program
{
public Animal f1()
{
return null;
}
public Dogs f2()
{
return null;
}
public void test()
{
HandlerDemo hd1 = new HandlerDemo(f1);
HandlerDemo hd2 = new HandlerDemo(f2);
}
}
}
逆变: 委托的类型参数是它所指向函数的参数的派生类.
namespace DemoNiBian
{
public class Animal
{
}
public class Dogs : Animal { }
public delegate void HandlerDemo(Dogs dog);
public class Program
{
public void f1(Animal animal)
{
}
public void f2(Dogs tom)
{
}
public void test()
{
HandlerDemo hd1 = new HandlerDemo(f1);
HandlerDemo hd2 = new HandlerDemo(f2);
}
}
}
事件
1. 使用事件的好处
2. 事件的工作方式
3. EventHandler委托的实现方法
4. 自定义事件参数类
5. 事件和委托的关系
4.2.1 使用事件的好处:
.NET Framework通常会在对象发生某些情况时自动引预构建的事件作为响应.
当用户在UI中单击自定义事件时,该控件就会触发Click事件.
4.2.2 事件的工作方式
在程序中创建并使用自定义事件包含三个步骤:
1. 首先,必须在类中声明事件并确定将要使用的委托和参数.
2. 其次,必须定义在触发事件时要调用的委托.
3. 最后,必须设计事件参数类,该参数类的实例会将信息传递给被调用的方法.
namespace EventDemo
{
static class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new mywin());
}
public class mywin : Form
{
private Button btn;
public mywin()
{
btn = new Button();
btn.Text = "Click Me";
btn.Click += new EventHandler(btnClick); //事件使用+=赋值,
//并且是将一个委托赋值给Click事件
//EventHandler为系统内置的事件
this.Controls.Add(btn);
}
public void btnClick(object o, EventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("This is windows!");
}
}
/*Button 按钮原型*/
//public delegate void EventHandler(object o, EventArgs e);
//public class Button
//{
// public event EventHandler Click;//按钮的Click事件是一种委托类型
//}
}
}
4.2.3 使用Event语句创建事件
.NET Framework提供Event语句,可以在需要创建自定义事件时使用该语句.
1. 使用VB.NET实现
在VB.NET中,可以使用默认的委托或具有特定签名的自定义委托将一个事件声明为简单事件
2. 使用C#实现
在C#中,始终使用委托命名声明事件,但是也可使用诸如EventHandler等预定义的委托或具有特定签名的自定义委托.
声明事件
1. 为事件声明一个委托类型
2. 声明事件:
语法和声明一个委托类型的字段类似,但字段的前面加event关键字
//声明MouseClicked委托
public delegate void MouseClickedEventHandler();
public class Mouse
{
//声明MouseClieked事件
public static event MouseCliekedEventHandler MouseClicked;
//…
}
3. 连接事件
1. 通过添加委托来连接到事件
2. 通过移除委托来断开到事件的连接
//处理MouseClick事件的客户端方法
private void MouseClicked()
{
//…
}
//连接到MouseClick事件的客户端代码
Mouse.MouseClicked += new MouseClickedEventHandler(MouseClicked);
//断开连接到MouseClick事件的代码
Mouse.MouseClicked -= new MouseClickedEventHandler(MouseClicked);
4. 激发事件
1. 检查是否客户端已连接事件
如果事件字段是null,则表明没有客户端
2. 通过调用事件的委托来引发事件
if (MouseClicked != null)
{
MouseClicked();
}
示例:
namespace EventDemo//用户登入控件
{
public delegate void LoginHandler(); //声明委托
public partial class LoginDialog : UserControl
{
public event LoginHandler login; //声明事件(如果此处不加event,则为定义一个委托对象,
//引用时就不需要用+=,直接用=
public LoginDialog()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "abc" && textBox2.Text == "123")
{
if (login != null) //激发事件,并在不为空时激发
{
login();
}
}
}
}
}
namespace EventDemo //引用用户登入控件的窗体
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
loginDialog1.login += new LoginHandler(disp);//连接事件(使用+=),
//如果login只是委托,则直接用=
}
public void disp()
{
MessageBox.Show("This is a login");
}
}
static class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
}
4.2.4 EventHandler委托的实现
3. VB.NET
在VB.NET中有两种向EventHandler添加方法的途径.可以在设计时对方法使用Handles关键字,也可以在运行时使用AddHandler语句.
4. C#
C#中没有与VB.NET中的Handles语句等价的语句.要在C#中预订事件处理程序,可使用Addition Assignment 运算符(+=) 将方法添加到分配给事件的EventHandler委托中.
namespace DemoEventHandler
{
public partial class LoginDialog : UserControl
{
public event EventHandler login;//使用系统内置的委托EventHandler来定义事件
public LoginDialog()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "abc" && textBox2.Text == "123")
{
if (login != null)
{
login(this, e);//内置的委托有两个参数,所以此处传两个参数
}
}
}
}
}
namespace DemoEventHandler
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
loginDialog1.login += new EventHandler(loginDialog1_login);//连接委托
}
void loginDialog1_login(object sender, EventArgs e) //带有两个参数的方法
{
MessageBox.Show("This is a login");
}
}
static class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
}
4.2.5 自定义事件参数类
可以使用继承自EventArgs的类将参数传递给处理事件的方法.
1. 每当想要将来自事件发布者的特定数据传递给预定者方法时,就必须使用继承自EventArgs基类的自定义类.
2. 如果想要允许来自事件处理程序的反馈,可以提供一个可读/写的属性.
namespace DemoUDefineEventAgrs
{
public delegate void LoginHandler(object o, LoginEvent e);//声明自定义参数类的委托
public partial class LoginDialog : UserControl
{
public event LoginHandler login; //声明事件
public LoginDialog()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (textBox1.Text == "abc" && textBox2.Text == "123")
{
if (login != null)
{
LoginEvent le = new LoginEvent(this.textBox1.Text, this.textBox2.Text);
login(this, le); //激发
}
}
}
}
//自定义参数类
public class LoginEvent : EventArgs //需要继承自EventArgs类
{
private string userName;
private string passWord;
public LoginEvent(string uname, string upwd)
{
this.userName = uname;
this.passWord = upwd;
}
public string UserName
{
get { return this.userName; }
}
public string PassWrod
{
get { return this.passWord; }
}
}
}
//调用
namespace DemoUDefineEventAgrs
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
loginDialog1.login +=new LoginHandler(loginDialog1_login);
}
void loginDialog1_login(object sender, LoginEvent e)
{
MessageBox.Show(e.UserName + e.PassWrod);
}
}
static class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Application.Run(new Form1());
}
}
}
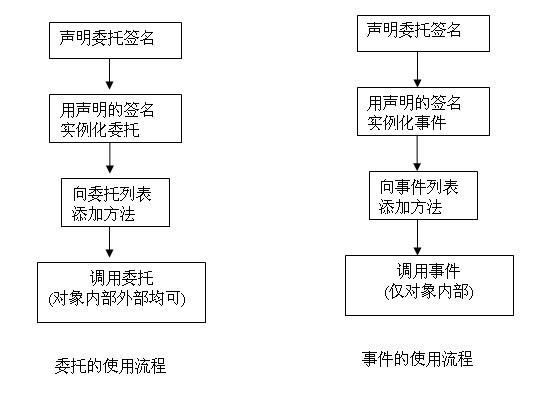
4.2.6 事件和委托的关系
事件和委托的使用流程



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号