Django之DRF源码分析(二)---数据校验部分
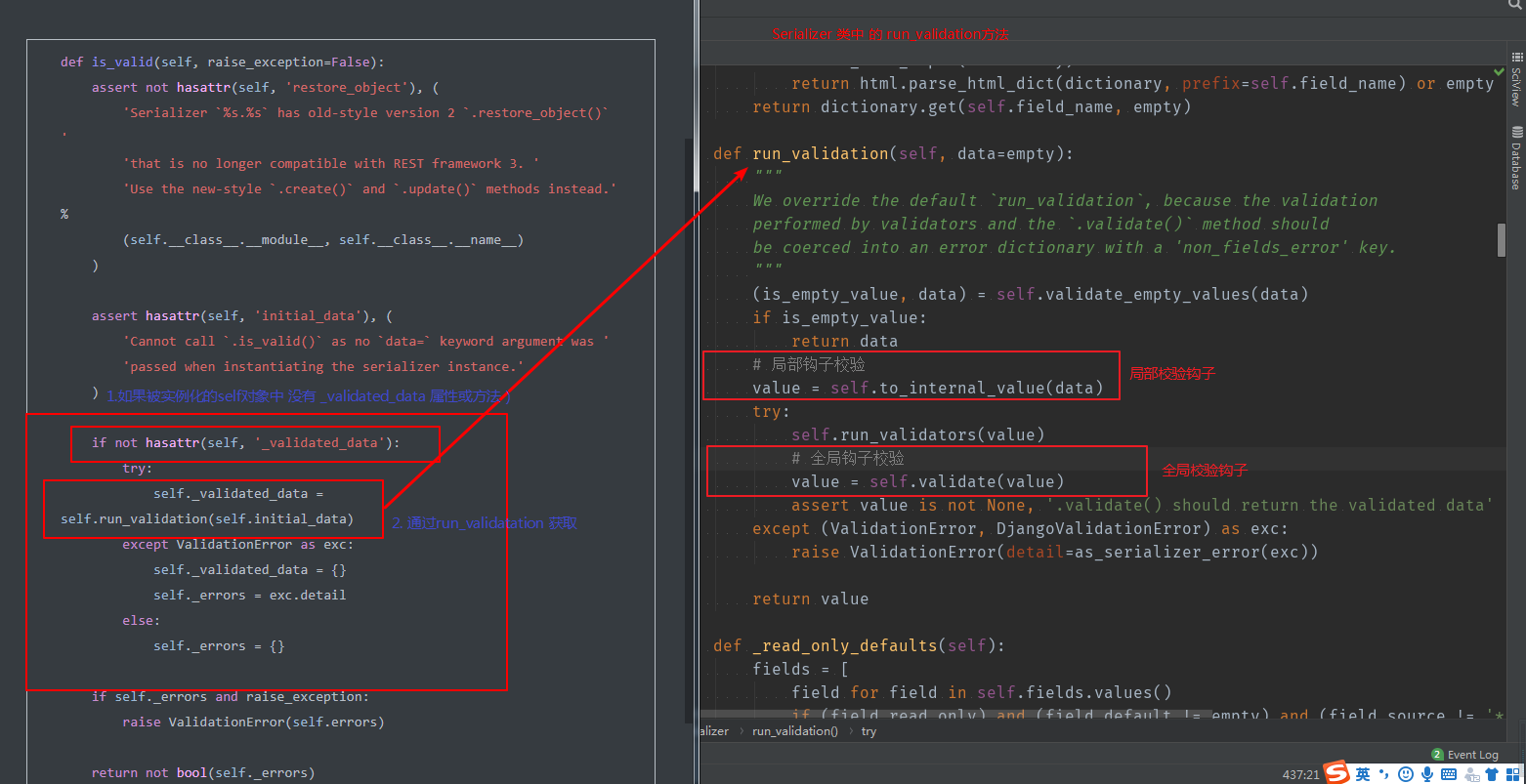
is_valid() 源码
def is_valid(self, raise_exception=False):
assert not hasattr(self, 'restore_object'), (
'Serializer `%s.%s` has old-style version 2 `.restore_object()` '
'that is no longer compatible with REST framework 3. '
'Use the new-style `.create()` and `.update()` methods instead.' %
(self.__class__.__module__, self.__class__.__name__)
)
assert hasattr(self, 'initial_data'), (
'Cannot call `.is_valid()` as no `data=` keyword argument was '
'passed when instantiating the serializer instance.'
)
if not hasattr(self, '_validated_data'):
try:
self._validated_data = self.run_validation(self.initial_data)
except ValidationError as exc:
self._validated_data = {}
self._errors = exc.detail
else:
self._errors = {}
if self._errors and raise_exception:
raise ValidationError(self.errors)
return not bool(self._errors)
serializers.py
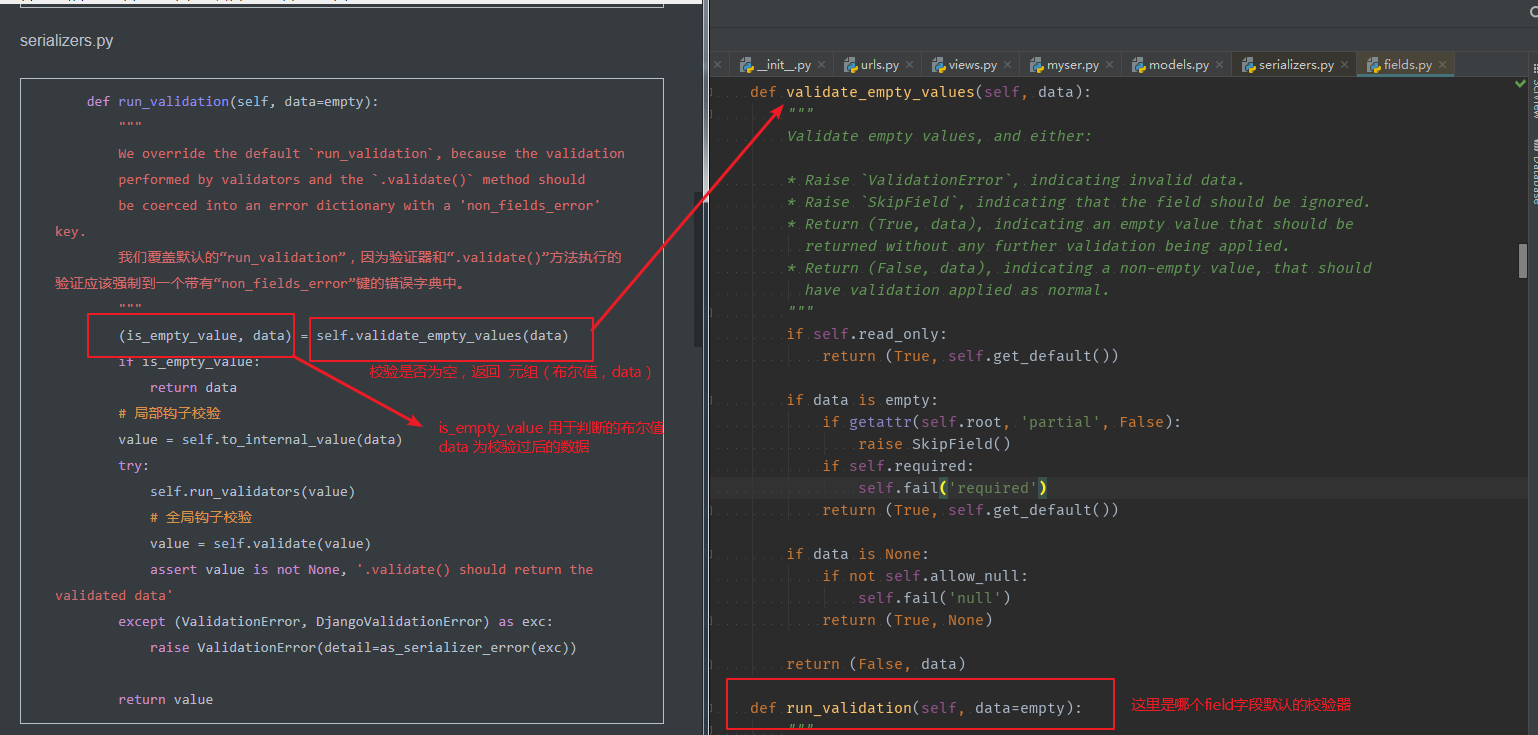
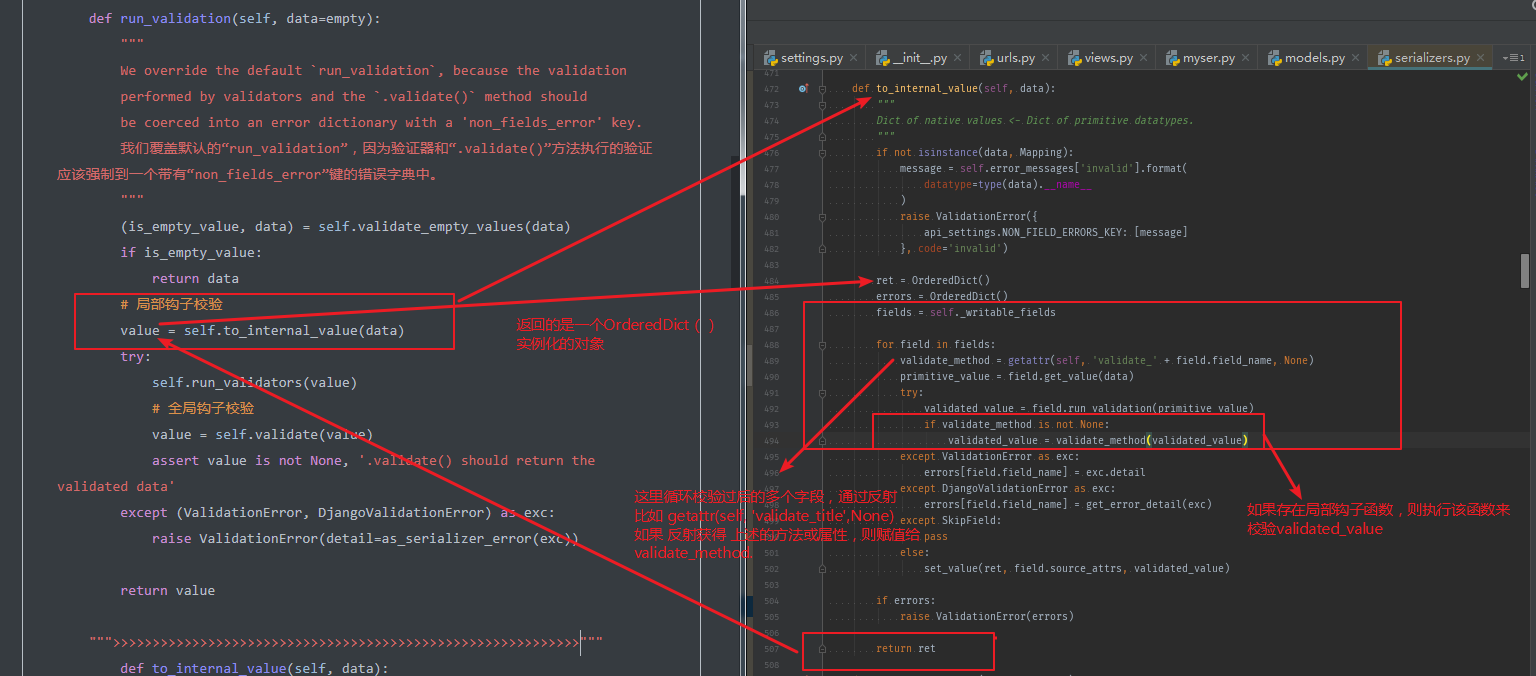
def run_validation(self, data=empty):
"""
We override the default `run_validation`, because the validation
performed by validators and the `.validate()` method should
be coerced into an error dictionary with a 'non_fields_error' key.
我们覆盖默认的“run_validation”,因为验证器和“.validate()”方法执行的验证应该强制到一个带有“non_fields_error”键的错误字典中。
"""
(is_empty_value, data) = self.validate_empty_values(data)
if is_empty_value:
return data
# 局部钩子校验
value = self.to_internal_value(data)
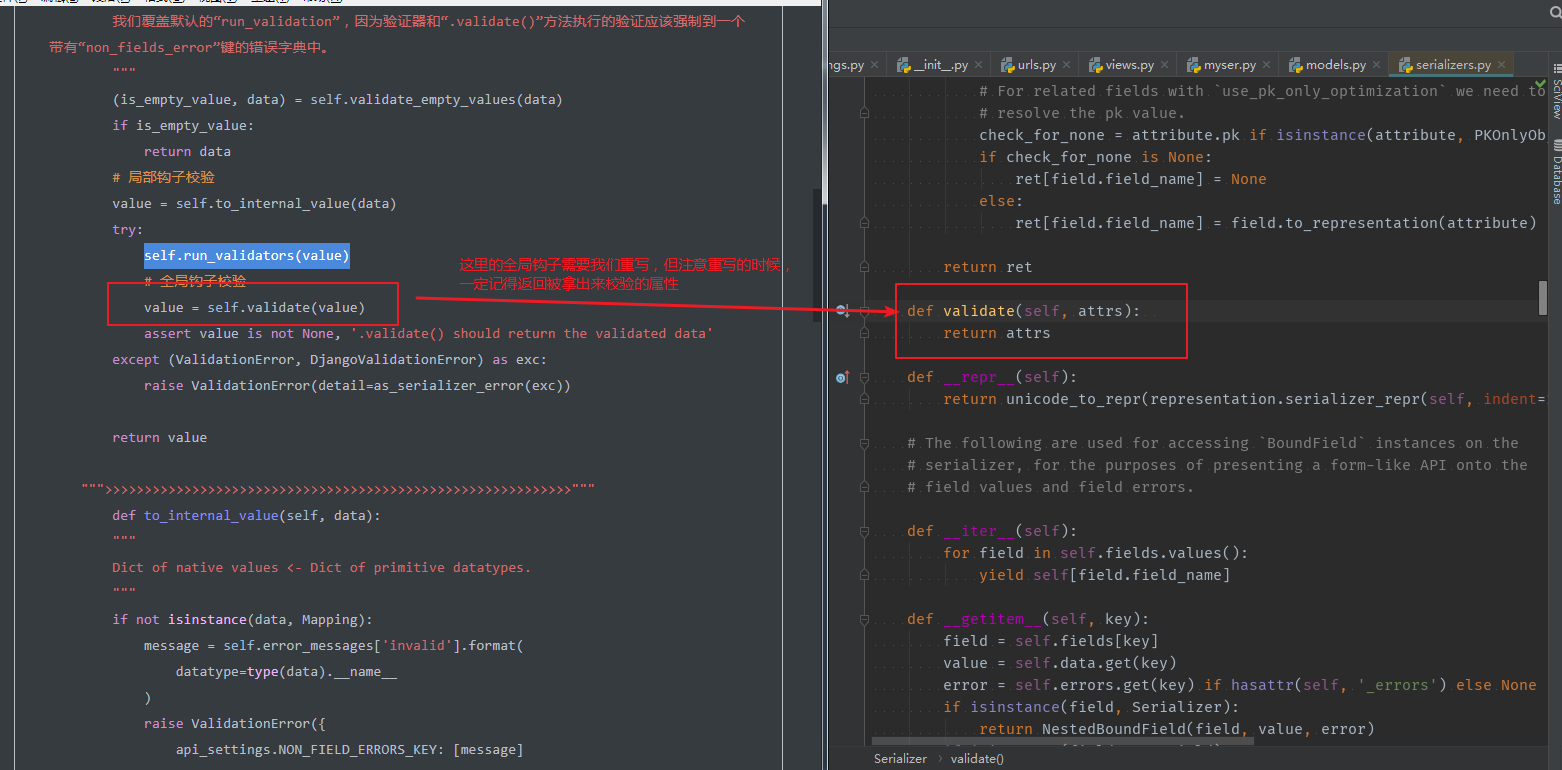
try:
self.run_validators(value)
# 全局钩子校验
value = self.validate(value)
assert value is not None, '.validate() should return the validated data'
except (ValidationError, DjangoValidationError) as exc:
raise ValidationError(detail=as_serializer_error(exc))
return value
""">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"""
def to_internal_value(self, data):
"""
Dict of native values <- Dict of primitive datatypes.
"""
if not isinstance(data, Mapping):
message = self.error_messages['invalid'].format(
datatype=type(data).__name__
)
raise ValidationError({
api_settings.NON_FIELD_ERRORS_KEY: [message]
}, code='invalid')
ret = OrderedDict()
errors = OrderedDict()
fields = self._writable_fields
for field in fields:
validate_method = getattr(self, 'validate_' + field.field_name, None)
primitive_value = field.get_value(data)
try:
validated_value = field.run_validation(primitive_value)
if validate_method is not None:
validated_value = validate_method(validated_value)
except ValidationError as exc:
errors[field.field_name] = exc.detail
except DjangoValidationError as exc:
errors[field.field_name] = get_error_detail(exc)
except SkipField:
pass
else:
set_value(ret, field.source_attrs, validated_value)
if errors:
raise ValidationError(errors)
return ret
""">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"""
def validate(self, attrs):
return attrs
fileds.py
def validate_empty_values(self, data):
"""
Validate empty values, and either:
* Raise `ValidationError`, indicating invalid data.
* Raise `SkipField`, indicating that the field should be ignored.
* Return (True, data), indicating an empty value that should be
returned without any further validation being applied.
* Return (False, data), indicating a non-empty value, that should
have validation applied as normal.
"""
if self.read_only:
return (True, self.get_default())
if data is empty:
if getattr(self.root, 'partial', False):
raise SkipField()
if self.required:
self.fail('required')
return (True, self.get_default())
if data is None:
if not self.allow_null:
self.fail('null')
return (True, None)
return (False, data)
def run_validation(self, data=empty):
"""
Validate a simple representation and return the internal value.
The provided data may be `empty` if no representation was included
in the input.
May raise `SkipField` if the field should not be included in the
validated data.
"""
(is_empty_value, data) = self.validate_empty_values(data)
if is_empty_value:
return data
value = self.to_internal_value(data)
self.run_validators(value)
return value
def run_validators(self, value):
"""
Test the given value against all the validators on the field,
and either raise a `ValidationError` or simply return.
"""
errors = []
for validator in self.validators:
if hasattr(validator, 'set_context'):
validator.set_context(self)
try:
validator(value)
except ValidationError as exc:
# If the validation error contains a mapping of fields to
# errors then simply raise it immediately rather than
# attempting to accumulate a list of errors.
if isinstance(exc.detail, dict):
raise
errors.extend(exc.detail)
except DjangoValidationError as exc:
errors.extend(get_error_detail(exc))
if errors:
raise ValidationError(errors)
def to_internal_value(self, data):
"""
Transform the *incoming* primitive data into a native value.
"""
raise NotImplementedError(
'{cls}.to_internal_value() must be implemented.'.format(
cls=self.__class__.__name__
)
)
def to_representation(self, value):
"""
Transform the *outgoing* native value into primitive data.
"""
raise NotImplementedError(
'{cls}.to_representation() must be implemented for field '
'{field_name}. If you do not need to support write operations '
'you probably want to subclass `ReadOnlyField` instead.'.format(
cls=self.__class__.__name__,
field_name=self.field_name,
)
)