我们知道自动装配是SpringBoot微服务化的核心,它会把META-INF/spring.factoires里配置的EnableAutoConfiguration注册到IOC容器里。但是,请大家考虑一个问题,根据需求我们要配置一个tomcat的内嵌容器,可是当前的运行环境里都没有servlet的相关API或者说当前的ApplicationContext不是一个WebApplicationContext,如果这样的话,那么创建tomcat的内嵌容器还有什么意义上呢?如果根据需求我们想自动装配一个Mybatis的SqlSessionFactory,可是运行环境里连DataSource都没有,恐怕要自动装配Mybatis的愿望也会落空吧!针对这种问题,SpringBoot早都考虑到了,下面我们来看看SpringBoot是怎么解决的。
一、关于@Conditional
conditional中文的意思为条件,其本身是Springframework提供的核心注解,通常情况下该注解可以加在类上或者方法上与@Configuration或者@Bean配合使用,当和@Configuration配合使用时,那么该类下所有@Bean方法 或者@Import 或者 @ComponentScan都会受到其配置条件的影响,我们先看一下其源码:

/* * Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.context.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * Indicates that a component is only eligible for registration when all * {@linkplain #value specified conditions} match. * * <p>A <em>condition</em> is any state that can be determined programmatically * before the bean definition is due to be registered (see {@link Condition} for details). * * <p>The {@code @Conditional} annotation may be used in any of the following ways: * <ul> * <li>as a type-level annotation on any class directly or indirectly annotated with * {@code @Component}, including {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes</li> * <li>as a meta-annotation, for the purpose of composing custom stereotype * annotations</li> * <li>as a method-level annotation on any {@link Bean @Bean} method</li> * </ul> * * <p>If a {@code @Configuration} class is marked with {@code @Conditional}, * all of the {@code @Bean} methods, {@link Import @Import} annotations, and * {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} annotations associated with that * class will be subject to the conditions. * * <p><strong>NOTE</strong>: Inheritance of {@code @Conditional} annotations * is not supported; any conditions from superclasses or from overridden * methods will not be considered. In order to enforce these semantics, * {@code @Conditional} itself is not declared as * {@link java.lang.annotation.Inherited @Inherited}; furthermore, any * custom <em>composed annotation</em> that is meta-annotated with * {@code @Conditional} must not be declared as {@code @Inherited}. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Sam Brannen * @since 4.0 * @see Condition */ @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Conditional { /** * All {@link Condition}s that must {@linkplain Condition#matches match} * in order for the component to be registered. */ Class<? extends Condition>[] value(); }
在这里文档注释提醒我们去看Condition接口:

/* * Copyright 2002-2013 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.context.annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; /** * A single {@code condition} that must be {@linkplain #matches matched} in order * for a component to be registered. * * <p>Conditions are checked immediately before the bean-definition is due to be * registered and are free to veto registration based on any criteria that can * be determined at that point. * * <p>Conditions must follow the same restrictions as {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} * and take care to never interact with bean instances. For more fine-grained control * of conditions that interact with {@code @Configuration} beans consider the * {@link ConfigurationCondition} interface. * * @author Phillip Webb * @since 4.0 * @see ConfigurationCondition * @see Conditional * @see ConditionContext */ public interface Condition { /** * Determine if the condition matches. * @param context the condition context * @param metadata metadata of the {@link org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata class} * or {@link org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata method} being checked. * @return {@code true} if the condition matches and the component can be registered * or {@code false} to veto registration. */ boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata); }
该接口就有一个方法:matches方法。它定义了最基本的匹配规则,该方法传入两个参数一个是ConditionContext ,该接口定义了若干个方法来获取spring核心接口的方法:

/* * Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.context.annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; /** * Context information for use by {@link Condition}s. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 4.0 */ public interface ConditionContext { /** * Return the {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry} that will hold the bean definition * should the condition match, or {@code null} if the registry is not available. */ BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry(); /** * Return the {@link ConfigurableListableBeanFactory} that will hold the bean * definition should the condition match, or {@code null} if the bean factory * is not available. */ ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory(); /** * Return the {@link Environment} for which the current application is running, * or {@code null} if no environment is available. */ Environment getEnvironment(); /** * Return the {@link ResourceLoader} currently being used, or {@code null} if * the resource loader cannot be obtained. */ ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(); /** * Return the {@link ClassLoader} that should be used to load additional classes, * or {@code null} if the default classloader should be used. */ ClassLoader getClassLoader(); }
在这里我们能获取到BeanFactory,ResourceLoader,Enviroment等。而另外一个参数是AnnotatedTypeMetadata接口,该接口主要获取该类上标记的注解。在这里我先写一个简单的例子,来试验一下:
MyTestConditional:
package com.hzgj.lyrk.autoconfigure; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationCondition; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; import java.util.Map; public class MyTestConditional implements ConfigurationCondition { @Override public ConfigurationPhase getConfigurationPhase() { return ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN; } @Override public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { Map<String, Object> map = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes("org.springframework.context.annotation.Description"); System.out.println(map); return false; } }
这个是自定义的Conditional,该类实现了ConfigurationCondition接口,该接口继承了Condition,只不过它多添加了一个用于设置解析Condition阶段的方法,在这里有两个阶段进行解析:
1)PARSE_CONFIGURATION:会在解析@Configuration时进行condition的解析
2)REGISTER_BEAN:会在注册Bean的时候进行condition的解析
ServerAutoConfiguration:
package com.hzgj.lyrk.autoconfigure; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Description; @Configuration public class ServerAutoConfiguration { @Configuration @Conditional(MyTestConditional.class) @Description(value = "student") public static class StudentAutoConfiguration { @Bean public Student student() { System.out.println("student create...."); return new Student(); } } @Configuration @Conditional(MyTestConditional.class) @Description(value = "teacher") public static class TeacherAutoConfiguration { @Bean public Teacher teacher() { System.out.println("teacher create....."); return new Teacher(); } } }
此时由于自定义的Conditional的match方法返回值是false,因此不能注册@Bean配置的对象:

当值改为true时,则能注册@Bean配置的对象:
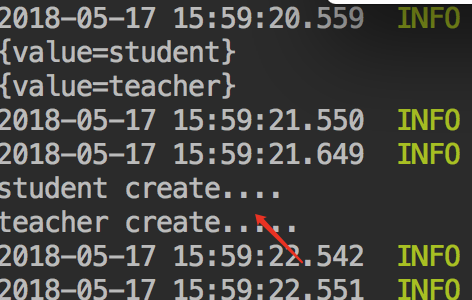
二、SpringBoot中对Conditional的扩展
在SpringBoot中定义了一个SpringBootCondition类对Condition进行了扩展,该类源代码如下:

/* * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata; import org.springframework.core.type.ClassMetadata; import org.springframework.core.type.MethodMetadata; import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * Base of all {@link Condition} implementations used with Spring Boot. Provides sensible * logging to help the user diagnose what classes are loaded. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Greg Turnquist */ public abstract class SpringBootCondition implements Condition { private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); @Override public final boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { String classOrMethodName = getClassOrMethodName(metadata); try { ConditionOutcome outcome = getMatchOutcome(context, metadata); logOutcome(classOrMethodName, outcome); recordEvaluation(context, classOrMethodName, outcome); return outcome.isMatch(); } catch (NoClassDefFoundError ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Could not evaluate condition on " + classOrMethodName + " due to " + ex.getMessage() + " not " + "found. Make sure your own configuration does not rely on " + "that class. This can also happen if you are " + "@ComponentScanning a springframework package (e.g. if you " + "put a @ComponentScan in the default package by mistake)", ex); } catch (RuntimeException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Error processing condition on " + getName(metadata), ex); } } private String getName(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata) { return ((AnnotationMetadata) metadata).getClassName(); } if (metadata instanceof MethodMetadata) { MethodMetadata methodMetadata = (MethodMetadata) metadata; return methodMetadata.getDeclaringClassName() + "." + methodMetadata.getMethodName(); } return metadata.toString(); } private static String getClassOrMethodName(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { if (metadata instanceof ClassMetadata) { ClassMetadata classMetadata = (ClassMetadata) metadata; return classMetadata.getClassName(); } MethodMetadata methodMetadata = (MethodMetadata) metadata; return methodMetadata.getDeclaringClassName() + "#" + methodMetadata.getMethodName(); } protected final void logOutcome(String classOrMethodName, ConditionOutcome outcome) { if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this.logger.trace(getLogMessage(classOrMethodName, outcome)); } } private StringBuilder getLogMessage(String classOrMethodName, ConditionOutcome outcome) { StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder(); message.append("Condition "); message.append(ClassUtils.getShortName(getClass())); message.append(" on "); message.append(classOrMethodName); message.append(outcome.isMatch() ? " matched" : " did not match"); if (StringUtils.hasLength(outcome.getMessage())) { message.append(" due to "); message.append(outcome.getMessage()); } return message; } private void recordEvaluation(ConditionContext context, String classOrMethodName, ConditionOutcome outcome) { if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) { ConditionEvaluationReport.get(context.getBeanFactory()) .recordConditionEvaluation(classOrMethodName, this, outcome); } } /** * Determine the outcome of the match along with suitable log output. * @param context the condition context * @param metadata the annotation metadata * @return the condition outcome */ public abstract ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata); /** * Return true if any of the specified conditions match. * @param context the context * @param metadata the annotation meta-data * @param conditions conditions to test * @return {@code true} if any condition matches. */ protected final boolean anyMatches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Condition... conditions) { for (Condition condition : conditions) { if (matches(context, metadata, condition)) { return true; } } return false; } /** * Return true if any of the specified condition matches. * @param context the context * @param metadata the annotation meta-data * @param condition condition to test * @return {@code true} if the condition matches. */ protected final boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, Condition condition) { if (condition instanceof SpringBootCondition) { return ((SpringBootCondition) condition).getMatchOutcome(context, metadata) .isMatch(); } return condition.matches(context, metadata); } }
在这里,我们需要重写getMatchOutcome方法来进行,匹配结果的过滤,下面我们列举一下常见的Conditional:
2.1、Class Conditions
常见的有ConditionalOnClass,ConditionalOnMissingClass
ConditionalOnClass:表明当前classpath有对应指定的类型才去创建Bean,我们来看一下源代码:

/* * Copyright 2012-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional; /** * {@link Conditional} that only matches when the specified classes are on the classpath. * * @author Phillip Webb */ @Target({ ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD }) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Conditional(OnClassCondition.class) public @interface ConditionalOnClass { /** * The classes that must be present. Since this annotation is parsed by loading class * bytecode, it is safe to specify classes here that may ultimately not be on the * classpath, only if this annotation is directly on the affected component and * <b>not</b> if this annotation is used as a composed, meta-annotation. In order to * use this annotation as a meta-annotation, only use the {@link #name} attribute. * @return the classes that must be present */ Class<?>[] value() default {}; /** * The classes names that must be present. * @return the class names that must be present. */ String[] name() default {}; }
根据注释我们去寻找一下:OnClassCondition这个类,我贴出部分代码:
@Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader(); ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty(); List<String> onClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnClass.class); if (onClasses != null) { List<String> missing = getMatches(onClasses, MatchType.MISSING, classLoader); if (!missing.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome .noMatch(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class) .didNotFind("required class", "required classes") .items(Style.QUOTE, missing)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnClass.class) .found("required class", "required classes").items(Style.QUOTE, getMatches(onClasses, MatchType.PRESENT, classLoader)); } List<String> onMissingClasses = getCandidates(metadata, ConditionalOnMissingClass.class); if (onMissingClasses != null) { List<String> present = getMatches(onMissingClasses, MatchType.PRESENT, classLoader); if (!present.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch( ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class) .found("unwanted class", "unwanted classes") .items(Style.QUOTE, present)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingClass.class) .didNotFind("unwanted class", "unwanted classes").items(Style.QUOTE, getMatches(onMissingClasses, MatchType.MISSING, classLoader)); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage); }
在这里我们关注一下getMatches方法:
private List<String> getMatches(Collection<String> candidates, MatchType matchType, ClassLoader classLoader) { List<String> matches = new ArrayList<String>(candidates.size()); for (String candidate : candidates) { if (matchType.matches(candidate, classLoader)) { matches.add(candidate); } } return matches; } //..... private enum MatchType { PRESENT { @Override public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { return isPresent(className, classLoader); } }, MISSING { @Override public boolean matches(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { return !isPresent(className, classLoader); } }; private static boolean isPresent(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) { if (classLoader == null) { classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader(); } try { forName(className, classLoader); return true; } catch (Throwable ex) { return false; } } private static Class<?> forName(String className, ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException { if (classLoader != null) { return classLoader.loadClass(className); } return Class.forName(className); }
我们可以看到这里是通过ClassLoader或者Class.forName来加载类的
2.2、Bean Conditionals
在这里常见的是ConditionalOnBean和ConditionalOnMissingBean,只有当BeanFactory里(不)包含指定的Bean时,才能通过匹配。注意:官网建议我们在AutoConfiguration里使用此注解,因为受到bean装配顺序影响,很有可能不能达到我们的预期效果。
package com.hzgj.lyrk.autoconfigure; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Description; @Configuration public class ServerAutoConfiguration { @Configuration @ConditionalOnBean(Teacher.class) public static class StudentAutoConfiguration { @Bean public Student student() { System.out.println("student create...."); return new Student(); } } @Configuration public static class TeacherAutoConfiguration { @Bean public Teacher teacher() { System.out.println("teacher create....."); return new Teacher(); } } }
比如说如上代码,运行后将得到如下结果:
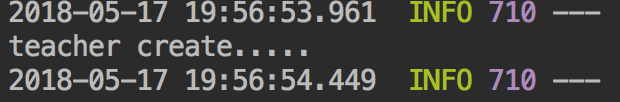
我们可以看到此时Student并未创建。因为受其顺序影响当注册Student时,IOC容器里并没有Teacher,我在这里贴出OnBeanCondition的关键代码:
@Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { ConditionMessage matchMessage = ConditionMessage.empty(); if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnBean.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnBean.class); List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (matching.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch( ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll()); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnBean.class, spec) .found("bean", "beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching); } if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new SingleCandidateBeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class); List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (matching.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll()); } else if (!hasSingleAutowireCandidate(context.getBeanFactory(), matching, spec.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ALL)) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .didNotFind("a primary bean from beans") .items(Style.QUOTE, matching)); } matchMessage = matchMessage .andCondition(ConditionalOnSingleCandidate.class, spec) .found("a primary bean from beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching); } if (metadata.isAnnotated(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class.getName())) { BeanSearchSpec spec = new BeanSearchSpec(context, metadata, ConditionalOnMissingBean.class); List<String> matching = getMatchingBeans(context, spec); if (!matching.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .found("bean", "beans").items(Style.QUOTE, matching)); } matchMessage = matchMessage.andCondition(ConditionalOnMissingBean.class, spec) .didNotFind("any beans").atAll(); } return ConditionOutcome.match(matchMessage); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") private List<String> getMatchingBeans(ConditionContext context, BeanSearchSpec beans) { ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); if (beans.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.PARENTS || beans.getStrategy() == SearchStrategy.ANCESTORS) { BeanFactory parent = beanFactory.getParentBeanFactory(); Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.class, parent, "Unable to use SearchStrategy.PARENTS"); beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) parent; } if (beanFactory == null) { return Collections.emptyList(); } List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(); boolean considerHierarchy = beans.getStrategy() != SearchStrategy.CURRENT; for (String type : beans.getTypes()) { beanNames.addAll(getBeanNamesForType(beanFactory, type, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy)); } for (String ignoredType : beans.getIgnoredTypes()) { beanNames.removeAll(getBeanNamesForType(beanFactory, ignoredType, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy)); } for (String annotation : beans.getAnnotations()) { beanNames.addAll(Arrays.asList(getBeanNamesForAnnotation(beanFactory, annotation, context.getClassLoader(), considerHierarchy))); } for (String beanName : beans.getNames()) { if (containsBean(beanFactory, beanName, considerHierarchy)) { beanNames.add(beanName); } } return beanNames; }
在这里我们关注getMatchingBeans方法,此方法从当前的BeanFactory找所需要的Bean。由于BeanFactory层次化的关系,因此在ConditionalOn(Missing)Bean里有相关属性来配置寻找策略:
/** * Strategy to decide if the application context hierarchy (parent contexts) should be * considered. * @return the search strategy */ SearchStrategy search() default SearchStrategy.ALL;
/* * Copyright 2012-2018 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition; /** * Some named search strategies for beans in the bean factory hierarchy. * * @author Dave Syer */ public enum SearchStrategy { /** * Search only the current context. */ CURRENT, /** * Search all parents and ancestors, but not the current context. * @deprecated as of 1.5 in favor of {@link SearchStrategy#ANCESTORS} */ @Deprecated PARENTS, /** * Search all ancestors, but not the current context. */ ANCESTORS, /** * Search the entire hierarchy. */ ALL }
2.3、Property Conditions
常见的注解为@ConditionalOnProperty,该注解会在Spring的Environment里面找对应的PropertySource,如果存在对应的属性值并且对应的值不为false时则匹配,我贴出关键代码部分:
@Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { //..... for (AnnotationAttributes annotationAttributes : allAnnotationAttributes) { ConditionOutcome outcome = determineOutcome(annotationAttributes, context.getEnvironment()); (outcome.isMatch() ? match : noMatch).add(outcome.getConditionMessage()); } //..... } private static class Spec { // ..... private void collectProperties(PropertyResolver resolver, List<String> missing, List<String> nonMatching) { if (this.relaxedNames) { resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(resolver, this.prefix); } for (String name : this.names) { String key = (this.relaxedNames ? name : this.prefix + name); if (resolver.containsProperty(key)) { if (!isMatch(resolver.getProperty(key), this.havingValue)) { nonMatching.add(name); } } else { if (!this.matchIfMissing) { missing.add(name); } } } } private boolean isMatch(String value, String requiredValue) { if (StringUtils.hasLength(requiredValue)) { return requiredValue.equalsIgnoreCase(value); } return !"false".equalsIgnoreCase(value); } //..... }
在这里通过ConditionContext拿到当前的Environment对象,在通过PropertyResover获取其配置的值。isMatch方法表明如果值存在且不等于false的情况下条件才生效
2.4、Resource Conditions
常见的注解为:@ConditionalOnResource,只有存在指定的资源文件时才生效,默认情况下是classpath,当然我们也可以指定其绝对路径,例如:file:/home/user/test.dat,源代码如下:

package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionMessage.Style; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Condition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConditionContext; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotatedTypeMetadata; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap; /** * {@link Condition} that checks for specific resources. * * @author Dave Syer * @see ConditionalOnResource */ @Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 20) class OnResourceCondition extends SpringBootCondition { private final ResourceLoader defaultResourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(); @Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) { MultiValueMap<String, Object> attributes = metadata .getAllAnnotationAttributes(ConditionalOnResource.class.getName(), true); ResourceLoader loader = context.getResourceLoader() == null ? this.defaultResourceLoader : context.getResourceLoader(); List<String> locations = new ArrayList<String>(); collectValues(locations, attributes.get("resources")); Assert.isTrue(!locations.isEmpty(), "@ConditionalOnResource annotations must specify at " + "least one resource location"); List<String> missing = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String location : locations) { String resource = context.getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(location); if (!loader.getResource(resource).exists()) { missing.add(location); } } if (!missing.isEmpty()) { return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(ConditionMessage .forCondition(ConditionalOnResource.class) .didNotFind("resource", "resources").items(Style.QUOTE, missing)); } return ConditionOutcome .match(ConditionMessage.forCondition(ConditionalOnResource.class) .found("location", "locations").items(locations)); } private void collectValues(List<String> names, List<Object> values) { for (Object value : values) { for (Object item : (Object[]) value) { names.add((String) item); } } } }
在这里我们可以看到,它是用DefaultResourceLoader来加载资源文件的,它会根据路径前缀来判断根据classpath加载或是url加载,其相关代码如下:
@Override public Resource getResource(String location) { Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null"); for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) { Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this); if (resource != null) { return resource; } } if (location.startsWith("/")) { return getResourceByPath(location); } else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) { return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader()); } else { try { // Try to parse the location as a URL... URL url = new URL(location); return new UrlResource(url); } catch (MalformedURLException ex) { // No URL -> resolve as resource path. return getResourceByPath(location); } } }
2.5、WebApplication Conditions
最常见的是@ConditionalOnWebApplication或者@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication,此注解的含义为:判断当前的ApplicationContext是否为WebApplicationContext。其关键代码如下:
private ConditionOutcome isWebApplication(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, boolean required) { ConditionMessage.Builder message = ConditionMessage.forCondition( ConditionalOnWebApplication.class, required ? "(required)" : ""); if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS, context.getClassLoader())) { return ConditionOutcome .noMatch(message.didNotFind("web application classes").atAll()); } if (context.getBeanFactory() != null) { String[] scopes = context.getBeanFactory().getRegisteredScopeNames(); if (ObjectUtils.containsElement(scopes, "session")) { return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("'session' scope")); } } if (context.getEnvironment() instanceof StandardServletEnvironment) { return ConditionOutcome .match(message.foundExactly("StandardServletEnvironment")); } if (context.getResourceLoader() instanceof WebApplicationContext) { return ConditionOutcome.match(message.foundExactly("WebApplicationContext")); } return ConditionOutcome.noMatch(message.because("not a web application")); }
在此我们可以看到它的判断依据有如下几个方面:
1)是否为WebApplicationContext
2) 是否包含session的scope
3) 当前的Environment是否为StandardServletEnvironment
三、基于@Configuration注册Bean分析
我们知道解析@Configuration的最主要的类是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,这个类下有一个属性叫ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader,与接口BeanDefiinitiaonReader类似,一看这个类我们就能联想到它的loadBeanDefinitions,其方法会调用loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass,我们来看一看这个方法:
/** * Read a particular {@link ConfigurationClass}, registering bean definitions * for the class itself and all of its {@link Bean} methods. */ private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) { if (trackedConditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass)) { String beanName = configClass.getBeanName(); if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.registry.containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) { this.registry.removeBeanDefinition(beanName); } this.importRegistry.removeImportingClass(configClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); return; } if (configClass.isImported()) { registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass); } for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) { loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod); } loadBeanDefinitionsFromImportedResources(configClass.getImportedResources()); loadBeanDefinitionsFromRegistrars(configClass.getImportBeanDefinitionRegistrars()); }
在这里大家关注一下loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod,此方法是加载@Bean注解所配置的Bean,我们来看一下其源码,我贴出关键部分:
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) { ConfigurationClass configClass = beanMethod.getConfigurationClass(); MethodMetadata metadata = beanMethod.getMetadata(); String methodName = metadata.getMethodName(); // Do we need to mark the bean as skipped by its condition? if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { configClass.skippedBeanMethods.add(methodName); return; } if (configClass.skippedBeanMethods.contains(methodName)) { return; } //.....省略后续代码 }
在这里会调用conditionEvaluator的shouldSkip方法 如果为true,则return,那么shuoldSkip方法又是怎么样的呢?我们来追踪一下:
/** * Determine if an item should be skipped based on {@code @Conditional} annotations. * @param metadata the meta data * @param phase the phase of the call * @return if the item should be skipped */ public boolean shouldSkip(AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata, ConfigurationPhase phase) { if (metadata == null || !metadata.isAnnotated(Conditional.class.getName())) { return false; } if (phase == null) { if (metadata instanceof AnnotationMetadata && ConfigurationClassUtils.isConfigurationCandidate((AnnotationMetadata) metadata)) { return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION); } return shouldSkip(metadata, ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN); } List<Condition> conditions = new ArrayList<Condition>(); for (String[] conditionClasses : getConditionClasses(metadata)) { for (String conditionClass : conditionClasses) { Condition condition = getCondition(conditionClass, this.context.getClassLoader()); conditions.add(condition); } } AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(conditions); for (Condition condition : conditions) { ConfigurationPhase requiredPhase = null; if (condition instanceof ConfigurationCondition) { requiredPhase = ((ConfigurationCondition) condition).getConfigurationPhase(); } if (requiredPhase == null || requiredPhase == phase) { if (!condition.matches(this.context, metadata)) { return true; } } } return false; }
那么至此,终于和先前的Condition所关联了。
四、总结
SpringBoot通过扩展Conditional来设置装配Bean的条件,通过Condition接口的matches方法的返回值来判断是否向IOC容器里注册Bean



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号