关于异步的好处我在这里就不多说了,自从servlet3.1规范发布以来,控制层的异步处理也越来越多的被人提及。而Spring5的webflux诞生也意味着Spring全方位对异步提供了支持。其实早在SpringMVC3.2版本就开始支持异步了,那么这篇文章我们就来探讨一下SpringMVC使用异步的方式。
一、DeferredResult
DeferredResult这个类代表延迟结果,我们先看一看spring的API文档给我们的解释:
{@code DeferredResult} provides an alternative to using a {@link Callable} for asynchronous request processing. While a {@code Callable} is executed concurrently on behalf of the application, with a {@code DeferredResult} the application can produce the result from a thread of its choice.
根据文档说明DeferredResult可以替代Callable来进行异步的请求处理。只不过这个类可以从其他线程里拿到对应的结果。当使用DeferredResult,我们可以将DefferedResult的类型并将其保存到可以获取到该对象的地方,比如说队列或者集合当中,这样方便其它线程能够取到并设置DefferedResult的值。
1.1、示例
我们先定义一个Controller,代码内容如下:
package com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.web.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.DeferredResult;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
/**
* 异步任务的控制器
*
* @author chen.nie
* @date 2018/8/2
**/
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
private BlockingQueue<DeferredResult<String>> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(1024);
/**
* 返回值是DeferredResult类型,如果没有结果请求阻塞
*
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/quotes")
public DeferredResult<String> quotes() {
//指定超时时间,及出错时返回的值
DeferredResult<String> result = new DeferredResult(3000L,"error");
blockingQueue.add(result);
return result;
}
/**
* 另外一个请求(新的线程)设置值
*
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@GetMapping("take")
public void take() throws InterruptedException {
DeferredResult<String> result = blockingQueue.take();
result.setResult("route");
}
@GetMapping
public Callable<String> callable() {
return () -> "callable";
}
}
控制器可以从不同的线程异步生成返回值,例如响应外部事件(JMS消息)、计划任务等,那么在这里我先使用另外一个请求来模拟这个过程
此时我们启动tomcat,先访问地址http://localhost:8080/quotes ,此时我们会看到发送的请求由于等待响应遭到了阻塞:
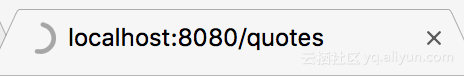
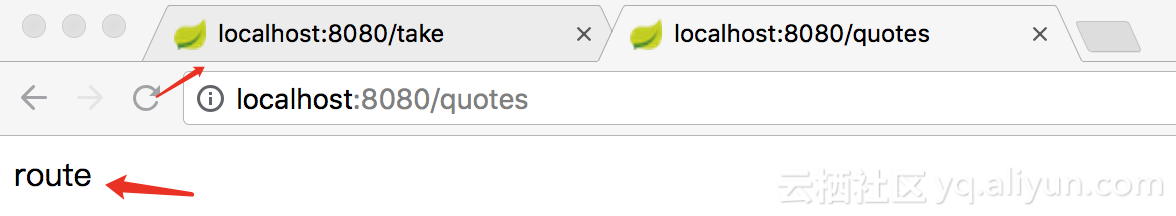
当在规定时间内访问http://localhost:8080/take 时,则能成功显示结果:
1.2、DeferredResult处理流程
根据官网描述:
DeferredResult processing:
- Controller returns a DeferredResult and saves it in some in-memory queue or list where it can be accessed.
- Spring MVC calls request.startAsync().
- Meanwhile the DispatcherServlet and all configured Filter’s exit the request processing thread but the response remains open.
- The application sets the DeferredResult from some thread and Spring MVC dispatches the request back to the Servlet container.
- The DispatcherServlet is invoked again and processing resumes with the asynchronously produced return value.
将Controller返回的DeferredResult值保存到内存队列或集合当中,紧接着SpringMVC调用HttpServletRequest的startAsync()方法,与此同时DispatcherServlet和所有配置的Filter退出当前的请求线程(不过响应时开放的),当其他线程里设置DeferredResult的值时将重新发送请求,此时DispatcherServlet使用异步生成的返回值继续处理。
在这里一切的一切还需要通过源代码来解释:
- 当一个请求被
DispatcherServlet处理时,会试着获取一个WebAsyncManager对象
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
// ......省略部分代码
// 执行子控制器的方法
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
//如果当前的请求需要异步处理,则终止当前请求,但是响应是开放的
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//....省略部分代码
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
- 对于每一个子控制器的方法返回值,都是
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler接口处理的,其中有一个实现类是DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler,关键代码如下:
package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletionStage;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.lang.UsesJava8;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.DeferredResult;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.WebAsyncUtils;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.ModelAndViewContainer;
/**
* Handler for return values of type {@link DeferredResult}, {@link ListenableFuture},
* {@link CompletionStage} and any other async type with a {@link #getAdapterMap()
* registered adapter}.
*
* @author Rossen Stoyanchev
* @since 3.2
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler implements AsyncHandlerMethodReturnValueHandler {
//存放DeferredResult的适配集合
private final Map<Class<?>, DeferredResultAdapter> adapterMap;
public DeferredResultMethodReturnValueHandler() {
this.adapterMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, DeferredResultAdapter>(5);
this.adapterMap.put(DeferredResult.class, new SimpleDeferredResultAdapter());
this.adapterMap.put(ListenableFuture.class, new ListenableFutureAdapter());
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("java.util.concurrent.CompletionStage", getClass().getClassLoader())) {
this.adapterMap.put(CompletionStage.class, new CompletionStageAdapter());
}
}
/**
* Return the map with {@code DeferredResult} adapters.
* <p>By default the map contains adapters for {@code DeferredResult}, which
* simply downcasts, {@link ListenableFuture}, and {@link CompletionStage}.
* @return the map of adapters
* @deprecated in 4.3.8, see comments on {@link DeferredResultAdapter}
*/
@Deprecated
public Map<Class<?>, DeferredResultAdapter> getAdapterMap() {
return this.adapterMap;
}
private DeferredResultAdapter getAdapterFor(Class<?> type) {
for (Class<?> adapteeType : getAdapterMap().keySet()) {
if (adapteeType.isAssignableFrom(type)) {
return getAdapterMap().get(adapteeType);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean supportsReturnType(MethodParameter returnType) {
return (getAdapterFor(returnType.getParameterType()) != null);
}
@Override
public boolean isAsyncReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType) {
return (returnValue != null && (getAdapterFor(returnValue.getClass()) != null));
}
@Override
public void handleReturnValue(Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
if (returnValue == null) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
//根据返回值的类型获取对应的DeferredResult适配器
DeferredResultAdapter adapter = getAdapterFor(returnValue.getClass());
if (adapter == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not find DeferredResultAdapter for return value type: " + returnValue.getClass());
}
DeferredResult<?> result = adapter.adaptToDeferredResult(returnValue);
//开启异步请求
WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(webRequest).startDeferredResultProcessing(result, mavContainer);
}
}
在这里我们关注handleReturnValue的方法,在经过适配包装后获取DeferredResult开启了异步之旅
- 紧接着我们关注一下
WebAsyncManager的startDeferredResultProcessing方法
/**
* Start concurrent request processing and initialize the given
* {@link DeferredResult} with a {@link DeferredResultHandler} that saves
* the result and dispatches the request to resume processing of that
* result. The {@code AsyncWebRequest} is also updated with a completion
* handler that expires the {@code DeferredResult} and a timeout handler
* assuming the {@code DeferredResult} has a default timeout result.
* @param deferredResult the DeferredResult instance to initialize
* @param processingContext additional context to save that can be accessed
* via {@link #getConcurrentResultContext()}
* @throws Exception if concurrent processing failed to start
* @see #getConcurrentResult()
* @see #getConcurrentResultContext()
*/
public void startDeferredResultProcessing(
final DeferredResult<?> deferredResult, Object... processingContext) throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(deferredResult, "DeferredResult must not be null");
Assert.state(this.asyncWebRequest != null, "AsyncWebRequest must not be null");
//设置超时时间
Long timeout = deferredResult.getTimeoutValue();
if (timeout != null) {
this.asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(timeout);
}
//获取所有的延迟结果拦截器
List<DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor>();
interceptors.add(deferredResult.getInterceptor());
interceptors.addAll(this.deferredResultInterceptors.values());
interceptors.add(timeoutDeferredResultInterceptor);
final DeferredResultInterceptorChain interceptorChain = new DeferredResultInterceptorChain(interceptors);
this.asyncWebRequest.addTimeoutHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
interceptorChain.triggerAfterTimeout(asyncWebRequest, deferredResult);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(ex);
}
}
});
this.asyncWebRequest.addCompletionHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
interceptorChain.triggerAfterCompletion(asyncWebRequest, deferredResult);
}
});
interceptorChain.applyBeforeConcurrentHandling(this.asyncWebRequest, deferredResult);
//开始异步处理
startAsyncProcessing(processingContext);
try {
interceptorChain.applyPreProcess(this.asyncWebRequest, deferredResult);
deferredResult.setResultHandler(new DeferredResultHandler() {
@Override
public void handleResult(Object result) {
result = interceptorChain.applyPostProcess(asyncWebRequest, deferredResult, result);
//设置结果并转发
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(result);
}
});
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(ex);
}
}
private void startAsyncProcessing(Object[] processingContext) {
clearConcurrentResult();
this.concurrentResultContext = processingContext;
//实际上是执行的是HttpServletRequest对应方法
this.asyncWebRequest.startAsync();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
HttpServletRequest request = this.asyncWebRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
String requestUri = urlPathHelper.getRequestUri(request);
logger.debug("Concurrent handling starting for " + request.getMethod() + " [" + requestUri + "]");
}
}
在这里首先收集所有配置好的DeferredResultProcessingInterceptor ,然后设置asyncRequest的超时处理,完成时的处理等,同时会分阶段执行拦截器中的各个方法。在这里真的佩服Spring框架的扩展机制做的实在是太好了。最后我们关注一下如下代码:
deferredResult.setResultHandler(new DeferredResultHandler() {
@Override
public void handleResult(Object result) {
result = interceptorChain.applyPostProcess(asyncWebRequest, deferredResult, result);
//设置结果并转发
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(result);
}
});
其最终还是要调用AsyncWebRequest接口中的dispatch方法进行转发,让DispatcherServlet重新处理异步结果:
/**
* Dispatch the request to the container in order to resume processing after
* concurrent execution in an application thread.
*/
void dispatch();
其实在这里都是封装自HttpServletRequest的异步操作,我们可以看一下StandardServletAsyncWebRequest的类结构图: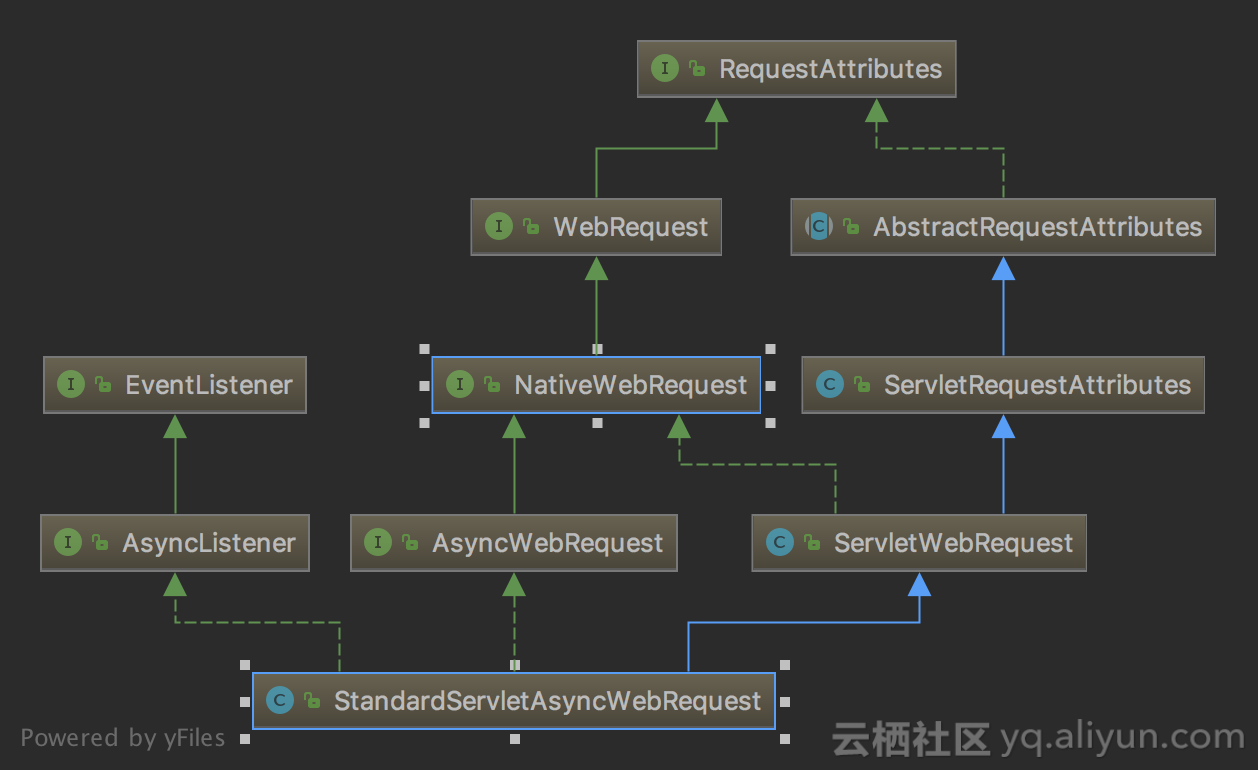
我们可以在其父类ServletRequestAttributes里找到对应的实现:
private final HttpServletRequest request;
/**
* Exposes the native {@link HttpServletRequest} that we're wrapping.
*/
public final HttpServletRequest getRequest() {
return this.request;
}
最后我在贴出一段StandardServletAsyncWebRequest 代码,大家就应该知道整个异步是怎么执行的了:
//java.servlet.AsnycContext
private AsyncContext asyncContext;
@Override
public void startAsync() {
Assert.state(getRequest().isAsyncSupported(),
"Async support must be enabled on a servlet and for all filters involved " +
"in async request processing. This is done in Java code using the Servlet API " +
"or by adding \"<async-supported>true</async-supported>\" to servlet and " +
"filter declarations in web.xml.");
Assert.state(!isAsyncComplete(), "Async processing has already completed");
if (isAsyncStarted()) {
return;
}
this.asyncContext = getRequest().startAsync(getRequest(), getResponse());
this.asyncContext.addListener(this);
if (this.timeout != null) {
this.asyncContext.setTimeout(this.timeout);
}
}
@Override
public void dispatch() {
Assert.notNull(this.asyncContext, "Cannot dispatch without an AsyncContext");
this.asyncContext.dispatch();
}
二、使用Callable作为返回值
使用Callable作为返回值来实现异步与DeferredResult类似,我们先看一看官网描述的具体流程:
Callable processing:
- Controller returns a Callable.
- Spring MVC calls request.startAsync() and submits the Callable to a TaskExecutor for processing in a separate thread.
- Meanwhile the DispatcherServlet and all Filter’s exit the Servlet container thread but the response remains open.
- Eventually the Callable produces a result and Spring MVC dispatches the request back to the Servlet container to complete processing.
- The DispatcherServlet is invoked again and processing resumes with the asynchronously produced return value from the Callable.
流程上大体与DeferredResult类似,只不过Callable是由TaskExecutor来处理的,而TaskExecutor继承自java.util.concurrent.Executor。我们来看一下它的源代码,它也是在WebAysncManager中处理的:
/**
* Use the given {@link WebAsyncTask} to configure the task executor as well as
* the timeout value of the {@code AsyncWebRequest} before delegating to
* {@link #startCallableProcessing(Callable, Object...)}.
* @param webAsyncTask a WebAsyncTask containing the target {@code Callable}
* @param processingContext additional context to save that can be accessed
* via {@link #getConcurrentResultContext()}
* @throws Exception if concurrent processing failed to start
*/
public void startCallableProcessing(final WebAsyncTask<?> webAsyncTask, Object... processingContext) throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(webAsyncTask, "WebAsyncTask must not be null");
Assert.state(this.asyncWebRequest != null, "AsyncWebRequest must not be null");
Long timeout = webAsyncTask.getTimeout();
if (timeout != null) {
this.asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(timeout);
}
AsyncTaskExecutor executor = webAsyncTask.getExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
this.taskExecutor = executor;
}
List<CallableProcessingInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<CallableProcessingInterceptor>();
interceptors.add(webAsyncTask.getInterceptor());
interceptors.addAll(this.callableInterceptors.values());
interceptors.add(timeoutCallableInterceptor);
final Callable<?> callable = webAsyncTask.getCallable();
final CallableInterceptorChain interceptorChain = new CallableInterceptorChain(interceptors);
this.asyncWebRequest.addTimeoutHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
logger.debug("Processing timeout");
Object result = interceptorChain.triggerAfterTimeout(asyncWebRequest, callable);
if (result != CallableProcessingInterceptor.RESULT_NONE) {
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(result);
}
}
});
this.asyncWebRequest.addCompletionHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
interceptorChain.triggerAfterCompletion(asyncWebRequest, callable);
}
});
interceptorChain.applyBeforeConcurrentHandling(this.asyncWebRequest, callable);
startAsyncProcessing(processingContext);
//启动线程池的异步处理
try {
this.taskExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Object result = null;
try {
interceptorChain.applyPreProcess(asyncWebRequest, callable);
result = callable.call();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
result = ex;
}
finally {
result = interceptorChain.applyPostProcess(asyncWebRequest, callable, result);
}
//设置当前的结果并转发
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(result);
}
});
}
catch (RejectedExecutionException ex) {
Object result = interceptorChain.applyPostProcess(this.asyncWebRequest, callable, ex);
setConcurrentResultAndDispatch(result);
throw ex;
}
}
对比DeferredResult,在这里刚开始也是添加拦截器,只不过拦截器的名称是CallableProcessingInterceptor ,同时也需要设置WebAsyncRequest的超时处理,完成时处理的响应操作。这其中最大的区别就是使用TaskExecutor来对Callable进行异步处理


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号