题目:

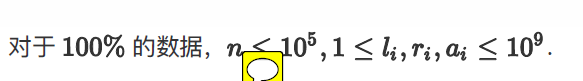
分析:
对于许多给出无序区间的问题,通常有将区间按照左or右端点排序的思路。
在这道题中,通过排序区间与采矿点,我们可以由前一个采矿点占有的区间推到当前采矿点有的区间。
而考虑一个采矿点如果拥有x个种矿,那么贡献就是:C(x,1)+C(x,2)+……C(x,x) ,也就等于2^x-1
而如果两个点间有重复计算的部分y,就应该-(2^y-1)(多计算了一次)。
所以我们只需要在推导下一个点的矿石种类的时候记录一下重复了多少,然后减去即可。
而前面通过排序,只需要移动指针统计下一个点。
优先队列的作用:
区间是按照l从小到大来排序的,每一次统计一个点新的贡献的时候,要知道它已经不包含哪些区间,就应该用r来移动,将不包含的区间弹出。
为了使r从小到大有序,用优先队列来维护。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define N 100005 #define ri register int #define ll long long const ll mod=998244353; int pos[N],n,m; ll ans=0,mul[N]; int read() { int x=0,fl=1; char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9') { if(ch=='-') fl=-1; ch=getchar(); } while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0') x=x*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return x*fl; } struct node { int l,r; }a[N]; priority_queue<node> q; bool operator < (const node &a,const node &b) { return a.r>b.r; } bool cmp(const node &a,const node &b) { return a.l<b.l; } int main() { freopen("A.in","r",stdin); freopen("A.out","w",stdout); n=read(); m=read(); for(ri i=1;i<=n;++i) a[i].l=read(),a[i].r=read(); for(ri i=1;i<=m;++i) pos[i]=read(); sort(a+1,a+1+n,cmp); sort(pos+1,pos+1+m); mul[0]=1; for(ri i=1;i<=n;++i) mul[i]=mul[i-1]*2%mod; for(ri i=0;i<=n;++i) mul[i]--; int now=1; for(ri i=1;i<=m;++i){ while(!q.empty()){ if(q.top().r<pos[i]) q.pop(); else break; } ll x2=q.size(); while(a[now].l<=pos[i] && now<=n){ if(a[now].r>=pos[i]) q.push(a[now]); now++; } ll x3=q.size(); ans=(ans + mul[x3]-mul[x2] )%mod; } ans=(ans+mod)%mod; printf("%lld\n",ans); } /* 3 2 7 11 1 5 3 8 4 7 */




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号