图论--Kruskal算法求最小生成树 稀疏图
给定一个 n 个点 m 条边的无向图,图中可能存在重边和自环,边权可能为负数。
求最小生成树的树边权重之和,如果最小生成树不存在则输出 impossible。
给定一张边带权的无向图 G=(V,E),其中 V 表示图中点的集合,E 表示图中边的集合,n=|V|,m=|E|。
由 V 中的全部 n 个顶点和 E 中 n−1 条边构成的无向连通子图被称为 G 的一棵生成树,其中边的权值之和最小的生成树被称为无向图 G 的最小生成树。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 n 和 m。
接下来 m 行,每行包含三个整数 u,v,w,表示点 u 和点 v 之间存在一条权值为 w 的边。
输出格式
共一行,若存在最小生成树,则输出一个整数,表示最小生成树的树边权重之和,如果最小生成树不存在则输出 impossible。
数据范围
1≤n≤105,
1≤m≤2∗105,
图中涉及边的边权的绝对值均不超过 1000。
输入样例:
4 5
1 2 1
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 2
3 4 4
输出样例:
6
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/861/
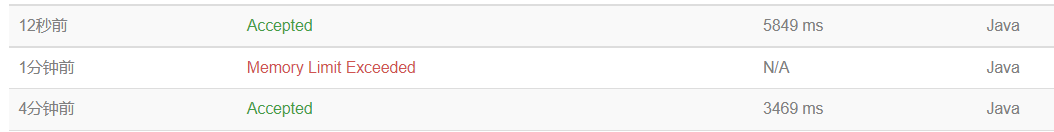
20万条数据下:java快读和非快读的时间对比。。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int N=100005,M=200005,n,m,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
static int f[]=new int [N];
static class edge
{
int a,b,w;
public edge(int x,int y,int z)
{
a=x;b=y;w=z;
}
}
static edge es[]=new edge[M];
static class mcomp implements Comparator<edge>
{
public int compare(edge o1,edge o2)
{
return o1.w-o2.w;
}
}
static int find(int x)
{
return (x==f[x])?x:(f[x]=find(f[x]));
}
static int kruskal()
{
Arrays.sort(es,0,m,new mcomp());
int res=0,cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
int a=es[i].a;
int b=es[i].b;
int w=es[i].w;
a=find(a);b=find(b);
if(a!=b)
{
f[a]=b;
res+=w;
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt<n-1)return INF;
else return res;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out)));
String ss[]=in.readLine().split(" ");
n=Integer.parseInt(ss[0]);
m=Integer.parseInt(ss[1]);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
int a,b,c;
ss=in.readLine().split(" ");
a=Integer.parseInt(ss[0]);
b=Integer.parseInt(ss[1]);
c=Integer.parseInt(ss[2]);
es[i]=new edge(a,b,c);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i)f[i]=i;
int ans=kruskal();
if(ans==INF)out.print("impossible");
else out.print(ans);
out.flush();
}
}

