A.
/* 发现每次反转或者消除都会减少一段0 当0只有一段时只能消除 这样判断一下就行 */ #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<set> #include<map> #define M 300010 #define ll long long using namespace std; int read() { int nm = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar(); for(; !isdigit(c); c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1; for(; isdigit(c); c = getchar()) nm = nm * 10 + c - '0'; return nm * f; } ll n,x,y; char s[M]; int main() { n = read(), x = read(), y = read(); scanf("%s", s + 1); int len = strlen(s + 1); s[0] = '?'; ll tot = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= len; i++) if(s[i] != s[i - 1] && s[i] == '0') tot++; if(tot == 0) return puts("0"); cout << min(tot * y, tot * x - x + y); return 0; }
B.
/* 可能这种题是打表克星 小数据部分没有规律 数据大了有规律 //一个显然的结论 ,如果数字总数确定的话我们求 1, 5, 10, 50 加起来的不同和的个数相当于求0, 4, 9, 49 的 好吧打打表就出来了 对于前12的数据 直接暴力 ,后面的线性增加 */ #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<set> #include<map> #define M 30 #define ll long long using namespace std; int read() { int nm = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar(); for(; !isdigit(c); c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1; for(; isdigit(c); c = getchar()) nm = nm * 10 + c - '0'; return nm * f; } const ll dx[]={0,4,10,20,35,56,83,116,155,198,244,292,341,390,439,488}; int main() { ll n = read(); if(n <= 12) cout << dx[n]; else cout << dx[12] + (n - 12) * 49; return 0; }
C.
显然同色的一行在哪一行对答案贡献是一样的,于是我们可以直接得出容斥的式子
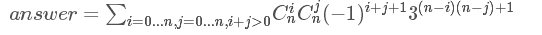
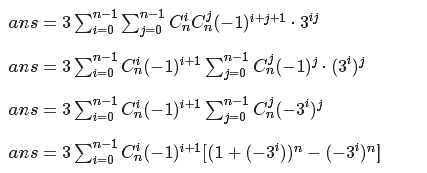
/* difficult 看题解啦 */ #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<set> #include<map> #define M 1231231 #define ll long long const int mod = 998244353; using namespace std; int read() { int nm = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar(); for(; !isdigit(c); c = getchar()) if(c == '-') f = -1; for(; isdigit(c); c = getchar()) nm = nm * 10 + c - '0'; return nm * f; } ll poww(ll a, ll b) { ll as = 1, tmp = a; for(; b; b >>= 1, tmp = tmp * tmp % mod) if(b & 1) as = as * tmp % mod; return as; } ll c[M]; inline ll ni(ll a) { return poww(a, mod - 2); } void shai(ll n) { c[0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) c[i] = c[i - 1] * (n - i + 1) % mod * ni(i) % mod; } int main() { ll n = read(); ll ans = 0; shai(n); for(int i = 1, j = 1; i <= n; i++, j = -j) ans += j * c[i] % mod * poww(3, (n - i) * n + i) % mod, ans %= mod; ans = ans * 2 % mod; for(int i = 0, j = -1; i < n; i++, j = -j) ans += 3ll * c[i] * j % mod * (poww(1ll - poww(3, i), n) - poww(-1ll * poww(3ll, i), n)) % mod, ans %= mod; cout << (ans + mod) % mod; return 0; }
