起因:在当前我手上的一个项目中需要多个数据源,并且来自于不同类型的数据库... 因为很多历史原因.这个项目的住数据源是MySQL,整个系统的CURD都是操作的这个数据库.
但是还有另外两个用于数据采集的数据库: MSSQL,ACCESS.还好只是用于数据采集,在事务上可以不要跨数据库了,这一点节省了好多的工作量.
环境:我搭建的测试环境是 spring2.5.6+hibernate3.2
思路:动态切换数据源确切的来说是在同一类型数据库的情况下的。意思就是说 , 在系统中的使用的数据库分布在多台数据库服务器或者在同台服务器上的多个数据库. 在运行时期间根据某种标识符来动态的选择当前操作的数据库.
1.数据源是相同类型的数据库: 一个SessionFactory+动态数据源+一个事务管理器
2.数据源是不同类型的数据库: 根据类型 配置多套SessionFactory
模拟:两个mysql数据源+一个Access数据源
实现:
1.切换数据源需要标识符,标识符是Object类型
package lhp.example.context;public enum DBType { dataSource1, dataSource2;}
2.然后创建一个用于切换数据源(设置或者获得上下文)的工具类
package lhp.example.context; public class ContextHolder { private static final ThreadLocal<Object> holder = new ThreadLocal<Object>(); public static void setDbType(DBType dbType) { holder.set(dbType); } public static DBType getDbType() { return (DBType) holder.get(); } public static void clearDbType() { holder.remove(); } }
3.创建动态数据源类,继承org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource这个类.
package lhp.example.context; import java.util.logging.Logger; import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { public static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(DynamicDataSource.class.toString()); @Override protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { DBType key = ContextHolder.getDbType();//获得当前数据源标识符 //logger.info("当前数据源 :" + key); return key; } }
4.然后配置多个数据源
<!-- 数据源1 : mysql --> <bean id="dataSource1" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dec" /> <property name="user" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="" /> </bean> <!-- 数据源2 : mysql --> <bean id="dataSource2" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lms" /> <property name="user" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="" /> </bean> <!-- 数据源3 : access --> <bean id="dataSource3" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:odbc:accessTest" /> <property name="user" value="administrator" /> <property name="password" value="XLZX0309" /> </bean> <!-- mysql 动态数据源设置--> <bean id="mysqlDynamicDataSource" class="lhp.example.context.DynamicDataSource"> <property name="targetDataSources"> <!-- 标识符类型 --> <map key-type="lhp.example.context.DBType"> <entry key="dataSource1" value-ref="dataSource1" /> <entry key="dataSource2" value-ref="dataSource2" /> </map> </property> <property name="defaultTargetDataSource" ref="dataSource1" /> </bean>
5.配置sessionFactory
<!-- mysql sessionFactory --> <bean id="mysqlSessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="mysqlDynamicDataSource" /> <property name="hibernateProperties"> <props> <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</prop> <prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop><!--create validate --> <prop key="hibernate.query.substitutions">true 1, false 0</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <!-- access sessionFactory --> <bean id="aceessSessionFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.LocalSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource3" /> <property name="hibernateProperties"> <props> <!-- access 语法和MSSQL相似 所以用的MSSQL方言,或者可以使用第三方方言 --> <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect</prop> <prop key="hibernate.jdbc.batch_size">30</prop> <prop key="hibernate.jdbc.fetch_size">50</prop> <prop key="hibernate.show_sql">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.format_sql">false</prop> <prop key="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</prop><!--create validate --> <prop key="hibernate.query.substitutions">true 1, false 0</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cglib.use_reflection_optimizer">true</prop> <!-- <prop key="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</prop> --> <!-- <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</prop> --> <!-- <prop key="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</prop> --> <!-- <prop key="hibernate.generate_statistics">true</prop> --> <!-- <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_configuration_file_resource_path">classpath:ehcache.xml</prop> --> </props> </property> </bean>
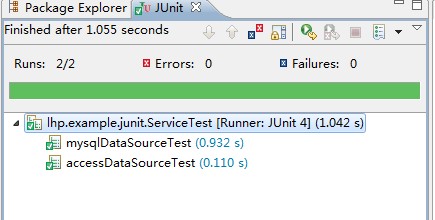
6.测试用例
package lhp.example.junit; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData; import lhp.example.context.ContextHolder; import lhp.example.context.DBType; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.junit.Before; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class ServiceTest { private ApplicationContext context; //三个数据源的URL private String dataSource1_URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/dec"; private String dataSource2_URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lms"; private String dataSource3_URL = "jdbc:odbc:accessTest"; private SessionFactory mysqlSessionFactory; private SessionFactory aceessSessionFactory; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { // 选择数据源初始化spring ContextHolder.setDbType(DBType.dataSource1); // String[] xmlFiles = new String[] { "applicationContext-dataSource.xml", "applicationContext-hibernate.xml", "applicationContext-spring.xml" }; // context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlFiles); // mysqlSessionFactory = (SessionFactory) context.getBean("mysqlSessionFactory"); aceessSessionFactory = (SessionFactory) context.getBean("aceessSessionFactory"); } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Test public void mysqlDataSourceTest() { try { Session mysqlSession = mysqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 获得数据库元数据 DatabaseMetaData meatData = mysqlSession.connection().getMetaData(); // 默认启动数据源 dataSource1 //断言当前数据源URL是否是dataSource1的URL assertEquals(dataSource1_URL, meatData.getURL()); // 切换到数据源 dataSource2 ContextHolder.setDbType(DBType.dataSource2); mysqlSession = mysqlSessionFactory.openSession(); meatData = mysqlSession.connection().getMetaData(); //断言当前数据源URL是否是dataSource2的URL assertEquals(dataSource2_URL, meatData.getURL()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") @Test public void accessDataSourceTest() { try { Session accessSession = aceessSessionFactory.openSession(); // 获得数据库元数据 DatabaseMetaData meatData = accessSession.connection().getMetaData(); //断言当前数据源URL是否是dataSource3的URL assertEquals(dataSource3_URL, meatData.getURL()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
7.测试结果