Design and implement a TwoSum class. It should support the following operations: add and find.
add - Add the number to an internal data structure.find - Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value.
Example 1:
add(1); add(3); add(5); find(4) -> true find(7) -> false
Example 2:
add(3); add(1); add(2); find(3) -> true find(6) -> false
题目
设计一个数据结构,能像其中添加数,能查找其中是否存在两数相加等于某值。
Solution1: HashMap
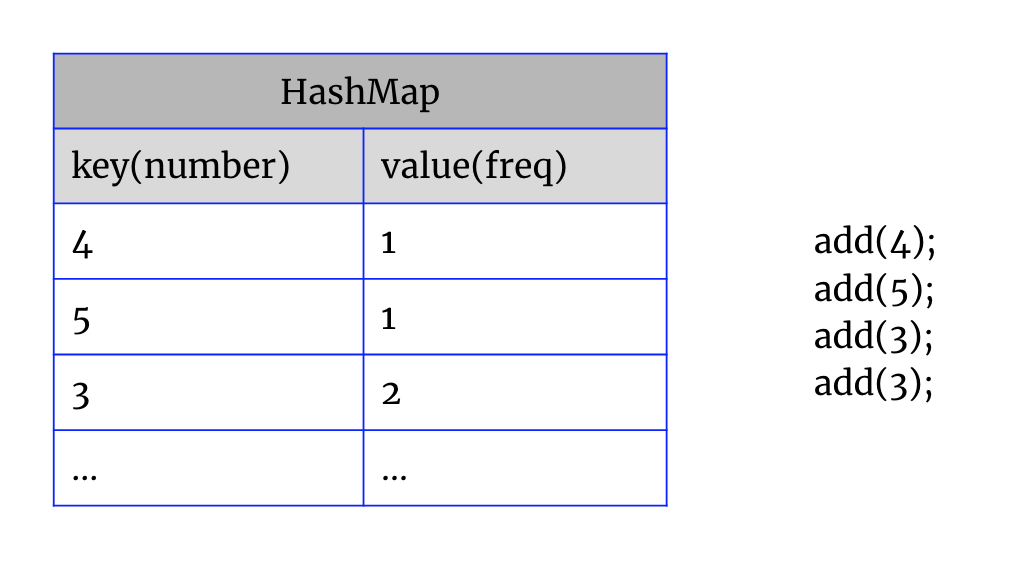
重头戏在find()的实现, 类似two sum的思想:遍历所有的key,同时算出remain = sum - key, 我们的任务是查找
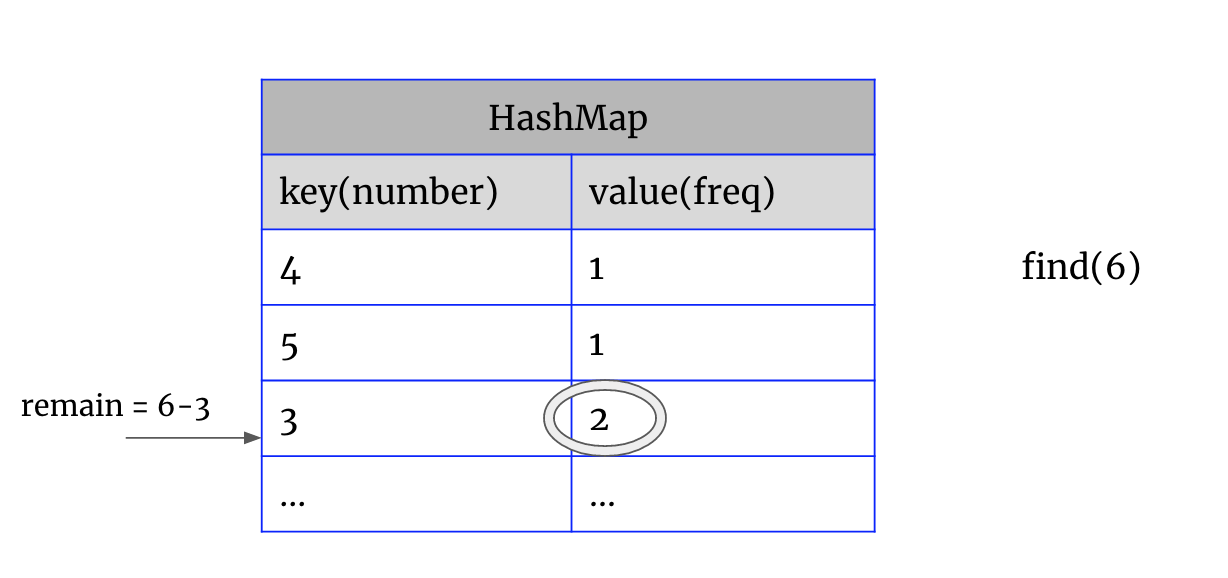
1. key 等于 remain时, 要组成一对pair的条件是map.get(key) >1
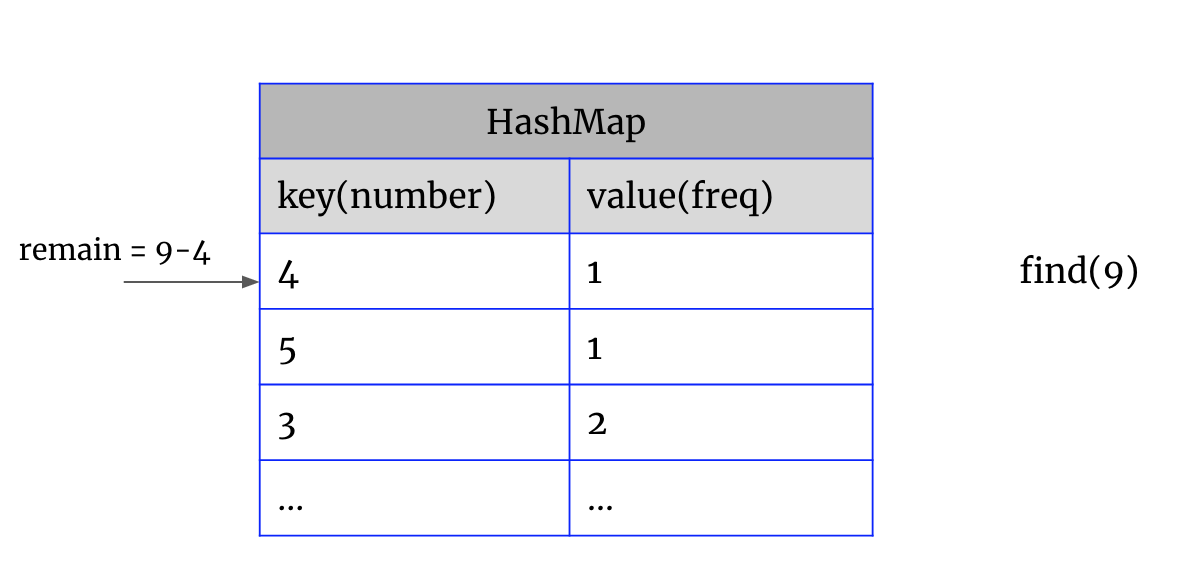
2. key不等于remain, 要组成一对pair的条件是,remain也在map中
code
1 class TwoSum { // O(1) add, O(n)find 2 3 private Map<Integer, Integer> map; 4 5 /** Initialize your data structure here. */ 6 public TwoSum() { 7 map = new HashMap<>(); 8 } 9 10 /** Add the number to an internal data structure.. */ 11 public void add(int number) { 12 if(!map.containsKey(number)){ 13 map.put(number, 1); 14 }else{ 15 map.put(number, map.get(number)+1); 16 } 17 } 18 19 /** Find if there exists any pair of numbers which sum is equal to the value. */ 20 public boolean find(int value) { 21 for (Integer num : map.keySet()){ 22 int remain = value - num; 23 if (( num == remain && map.get(num) > 1) || num != remain && map.containsKey(remain)){ 24 return true; 25 } 26 } 27 return false; 28 } 29 }
注意:
我之前写成
if(remaining != n){ return map.containsKey(remaining); }else{ if(map.get(n) > 1){ return true; } }
一直想不通逻辑上有什么区别。
比如
add(3), add(2), add(1), find(5)
而此时遍历的key是1, 对应remaining = 4
如果按照错误的思路,程序会直接return map.containsKey(4) -> false
而程序并没有尝试key是3, 对应remaining = 2, rreturn true 的情况
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Followup1:
要求O(1) find
思路
1. 在add()操作的时候,就用set做了pre-computation, 来记录 sum for any pair of numbers
2. 如此,在find()操作是,只需要check一下set.contains() 即可
代码
1 // O(n) add, O(1) find 2 public class TwoSumIII { 3 Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); 4 Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); 5 6 public void add(int number) { 7 // record sum for any pair of numbers 8 for (Integer n : map.keySet()){ 9 set.add(number + n); 10 } 11 // key: each item, value: its frequency 12 if(!map.containsKey(number)){ 13 map.put(number, 1); 14 }else{ 15 map.put(number, map.get(number) + 1); 16 } 17 } 18 // set.contains() using O(1) time 19 public boolean find(int value) { 20 return set.contains(value); 21 } 22 }




