MATLAB程序:ELM极速学习机
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
来源:Extreme Learning Machines
http://www.ntu.edu.sg/home/egbhuang/elm_codes.html
更新:只做科普,别做学术。
2004年南洋理工大学黄广斌提出了ELM算法。极限学习机(ELM Extreme Learning Machine)是一种快速的的单隐层神经网络(SLFN)训练算法。该算法的特点是在网络参数的确定过程中,隐层节点参数随机选取,在训练过程中无需调节,只需要设置隐含层神经元的个数,便可以获得唯一的最优解;而网络的外权(即输出权值)是通过最小化平方损失函数得到的最小二乘解(最终化归成求解一个矩阵的 Moore-Penrose 广义逆问题).这样网络参数的确定过程中无需任何迭代步骤,从而大大降低了网络参数的调节时间。与传统的训练方法相比,该方法具有学习速度快、泛化性能好等优点。
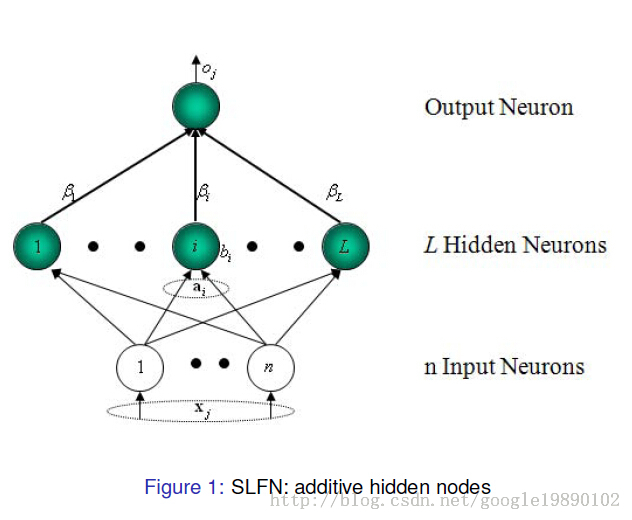

ELM的MATLAB算法:

1 function [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction) 2 3 % Usage: elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction) 4 % OR: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm(TrainingData_File, TestingData_File, Elm_Type, NumberofHiddenNeurons, ActivationFunction) 5 % 6 % Input: 7 % TrainingData_File - Filename of training data set 8 % TestingData_File - Filename of testing data set 9 % Elm_Type - 0 for regression; 1 for (both binary and multi-classes) classification 10 % NumberofHiddenNeurons - Number of hidden neurons assigned to the ELM 11 % ActivationFunction - Type of activation function: 12 % 'sig' for Sigmoidal function 13 % 'sin' for Sine function 14 % 'hardlim' for Hardlim function 15 % 'tribas' for Triangular basis function 16 % 'radbas' for Radial basis function (for additive type of SLFNs instead of RBF type of SLFNs) 17 % 18 % Output: 19 % TrainingTime - Time (seconds) spent on training ELM 20 % TestingTime - Time (seconds) spent on predicting ALL testing data 21 % TrainingAccuracy - Training accuracy: 22 % RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification 23 % TestingAccuracy - Testing accuracy: 24 % RMSE for regression or correct classification rate for classification 25 % 26 % MULTI-CLASSE CLASSIFICATION: NUMBER OF OUTPUT NEURONS WILL BE AUTOMATICALLY SET EQUAL TO NUMBER OF CLASSES 27 % FOR EXAMPLE, if there are 7 classes in all, there will have 7 output 28 % neurons; neuron 5 has the highest output means input belongs to 5-th class 29 % 30 % Sample1 regression: [TrainingTime, TestingTime, TrainingAccuracy, TestingAccuracy] = elm('sinc_train', 'sinc_test', 0, 20, 'sig') 31 % Sample2 classification: elm('diabetes_train', 'diabetes_test', 1, 20, 'sig') 32 % 33 %%%% Authors: MR QIN-YU ZHU AND DR GUANG-BIN HUANG 34 %%%% NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY, SINGAPORE 35 %%%% EMAIL: EGBHUANG@NTU.EDU.SG; GBHUANG@IEEE.ORG 36 %%%% WEBSITE: http://www.ntu.edu.sg/eee/icis/cv/egbhuang.htm 37 %%%% DATE: APRIL 2004 38 39 %%%%%%%%%%% Macro definition 40 REGRESSION=0; 41 CLASSIFIER=1; 42 43 %%%%%%%%%%% Load training dataset 44 train_data=load(TrainingData_File); 45 T=train_data(:,1)'; 46 P=train_data(:,2:size(train_data,2))'; 47 clear train_data; % Release raw training data array 48 49 %%%%%%%%%%% Load testing dataset 50 test_data=load(TestingData_File); 51 TV.T=test_data(:,1)'; 52 TV.P=test_data(:,2:size(test_data,2))'; 53 clear test_data; % Release raw testing data array 54 55 NumberofTrainingData=size(P,2); 56 NumberofTestingData=size(TV.P,2); 57 NumberofInputNeurons=size(P,1); 58 59 if Elm_Type~=REGRESSION 60 %%%%%%%%%%%% Preprocessing the data of classification 61 sorted_target=sort(cat(2,T,TV.T),2); 62 label=zeros(1,1); % Find and save in 'label' class label from training and testing data sets 63 label(1,1)=sorted_target(1,1); 64 j=1; 65 for i = 2:(NumberofTrainingData+NumberofTestingData) 66 if sorted_target(1,i) ~= label(1,j) 67 j=j+1; 68 label(1,j) = sorted_target(1,i); 69 end 70 end 71 number_class=j; 72 NumberofOutputNeurons=number_class; 73 74 %%%%%%%%%% Processing the targets of training 75 temp_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTrainingData); 76 for i = 1:NumberofTrainingData 77 for j = 1:number_class 78 if label(1,j) == T(1,i) 79 break; 80 end 81 end 82 temp_T(j,i)=1; 83 end 84 T=temp_T*2-1; 85 86 %%%%%%%%%% Processing the targets of testing 87 temp_TV_T=zeros(NumberofOutputNeurons, NumberofTestingData); 88 for i = 1:NumberofTestingData 89 for j = 1:number_class 90 if label(1,j) == TV.T(1,i) 91 break; 92 end 93 end 94 temp_TV_T(j,i)=1; 95 end 96 TV.T=temp_TV_T*2-1; 97 98 end % end if of Elm_Type 99 100 %%%%%%%%%%% Calculate weights & biases 101 start_time_train=cputime; 102 103 %%%%%%%%%%% Random generate input weights InputWeight (w_i) and biases BiasofHiddenNeurons (b_i) of hidden neurons 104 InputWeight=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,NumberofInputNeurons)*2-1; 105 BiasofHiddenNeurons=rand(NumberofHiddenNeurons,1); 106 tempH=InputWeight*P; 107 clear P; % Release input of training data 108 ind=ones(1,NumberofTrainingData); 109 BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H 110 tempH=tempH+BiasMatrix; 111 112 %%%%%%%%%%% Calculate hidden neuron output matrix H 113 switch lower(ActivationFunction) 114 case {'sig','sigmoid'} 115 %%%%%%%% Sigmoid 116 H = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH)); 117 case {'sin','sine'} 118 %%%%%%%% Sine 119 H = sin(tempH); 120 case {'hardlim'} 121 %%%%%%%% Hard Limit 122 H = double(hardlim(tempH)); 123 case {'tribas'} 124 %%%%%%%% Triangular basis function 125 H = tribas(tempH); 126 case {'radbas'} 127 %%%%%%%% Radial basis function 128 H = radbas(tempH); 129 %%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here 130 end 131 clear tempH; % Release the temparary array for calculation of hidden neuron output matrix H 132 133 %%%%%%%%%%% Calculate output weights OutputWeight (beta_i) 134 OutputWeight=pinv(H') * T'; % implementation without regularization factor //refer to 2006 Neurocomputing paper 135 %OutputWeight=inv(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') * H * T'; % faster method 1 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper 136 %implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications 137 %OutputWeight=(eye(size(H,1))/C+H * H') \ H * T'; % faster method 2 //refer to 2012 IEEE TSMC-B paper 138 %implementation; one can set regularizaiton factor C properly in classification applications 139 140 %If you use faster methods or kernel method, PLEASE CITE in your paper properly: 141 142 %Guang-Bin Huang, Hongming Zhou, Xiaojian Ding, and Rui Zhang, "Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multi-Class Classification," submitted to IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, October 2010. 143 144 end_time_train=cputime; 145 TrainingTime=end_time_train-start_time_train % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent for training ELM 146 147 %%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the training accuracy 148 Y=(H' * OutputWeight)'; % Y: the actual output of the training data 149 if Elm_Type == REGRESSION 150 TrainingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(T - Y)) % Calculate training accuracy (RMSE) for regression case 151 end 152 clear H; 153 154 %%%%%%%%%%% Calculate the output of testing input 155 start_time_test=cputime; 156 tempH_test=InputWeight*TV.P; 157 clear TV.P; % Release input of testing data 158 ind=ones(1,NumberofTestingData); 159 BiasMatrix=BiasofHiddenNeurons(:,ind); % Extend the bias matrix BiasofHiddenNeurons to match the demention of H 160 tempH_test=tempH_test + BiasMatrix; 161 switch lower(ActivationFunction) 162 case {'sig','sigmoid'} 163 %%%%%%%% Sigmoid 164 H_test = 1 ./ (1 + exp(-tempH_test)); 165 case {'sin','sine'} 166 %%%%%%%% Sine 167 H_test = sin(tempH_test); 168 case {'hardlim'} 169 %%%%%%%% Hard Limit 170 H_test = hardlim(tempH_test); 171 case {'tribas'} 172 %%%%%%%% Triangular basis function 173 H_test = tribas(tempH_test); 174 case {'radbas'} 175 %%%%%%%% Radial basis function 176 H_test = radbas(tempH_test); 177 %%%%%%%% More activation functions can be added here 178 end 179 TY=(H_test' * OutputWeight)'; % TY: the actual output of the testing data 180 end_time_test=cputime; 181 TestingTime=end_time_test-start_time_test % Calculate CPU time (seconds) spent by ELM predicting the whole testing data 182 183 if Elm_Type == REGRESSION 184 TestingAccuracy=sqrt(mse(TV.T - TY)) % Calculate testing accuracy (RMSE) for regression case 185 end 186 187 if Elm_Type == CLASSIFIER 188 %%%%%%%%%% Calculate training & testing classification accuracy 189 MissClassificationRate_Training=0; 190 MissClassificationRate_Testing=0; 191 192 for i = 1 : size(T, 2) 193 [x, label_index_expected]=max(T(:,i)); 194 [x, label_index_actual]=max(Y(:,i)); 195 if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected 196 MissClassificationRate_Training=MissClassificationRate_Training+1; 197 end 198 end 199 TrainingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Training/size(T,2) 200 for i = 1 : size(TV.T, 2) 201 [x, label_index_expected]=max(TV.T(:,i)); 202 [x, label_index_actual]=max(TY(:,i)); 203 if label_index_actual~=label_index_expected 204 MissClassificationRate_Testing=MissClassificationRate_Testing+1; 205 end 206 end 207 TestingAccuracy=1-MissClassificationRate_Testing/size(TV.T,2) 208 end
我对ELM算法的解读




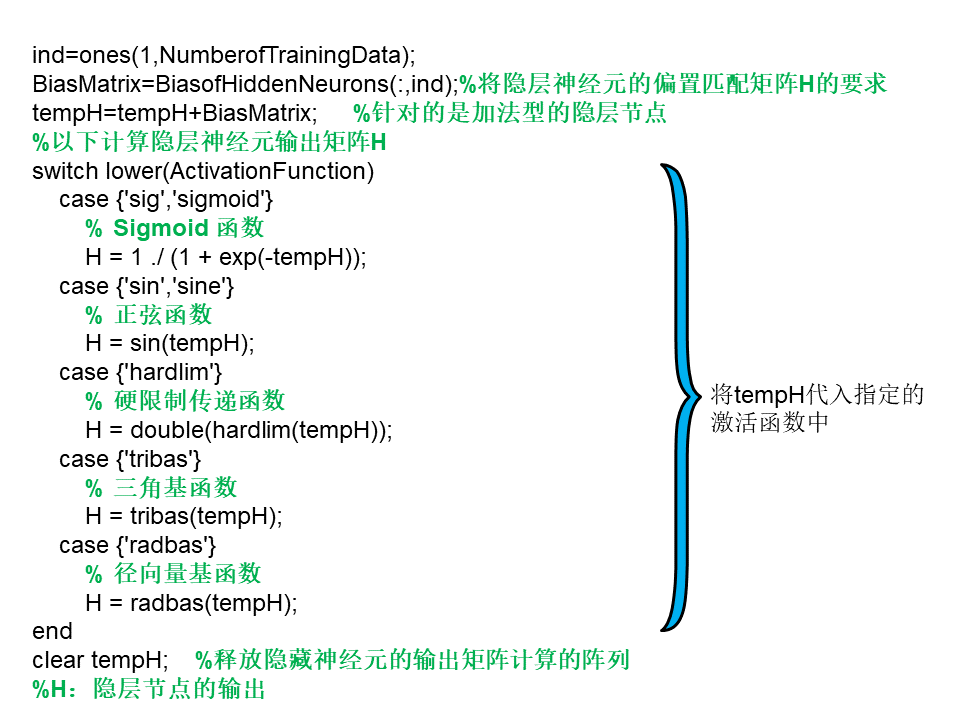



这是我很久之前写的神经网络ELM代码及解读,只有知道ELM的数学原理,再看程序,才会有所理解。如有不足之处,望指点。


