Python小练习:Sinkhorn-Knopp算法
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
本文介绍Sinkhorn-Knopp算法的Python实现,通过参考并修改两种不同的实现方法,来真正弄懂算法原理。详细的原理部分可参考文末给出的参考文献。
公式为:$P = diag(u)\exp \left( {\frac{{ - S}}{\varepsilon }} \right)diag(v)$。输入S,输出P,其中u与v是renormalization向量,eps用来控制P的平滑性。通常情况下,S与P对应的值成反比,S某一元素越大,相应的P值越小。
1. sinkhorn_test.py
1 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 2 # Author:凯鲁嘎吉 Coral Gajic 3 # https://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/ 4 # Sinkhorn-Knopp算法(以方阵为例) 5 # 对于一个n*n方阵 6 # 1) 先逐行做归一化:将第一行的每个元素除以第一行所有元素之和,得到新的"第一行",每行都做相同的操作 7 # 2) 再逐列做归一化,操作同上 8 # 重复以上的两步1)与2),最终可以收敛到一个行和为1,列和也为1的双随机矩阵。 9 import torch 10 import numpy as np 11 import time 12 import seaborn as sns 13 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 14 # 方法1: 15 ''' 16 https://github.com/miralab-ustc/rl-cbm 17 ''' 18 # numpy转换成tensor 19 def sinkhorn(scores, eps = 5, n_iter = 3): 20 def remove_infs(x): # 替换掉数据里面的INF与0 21 mm = x[torch.isfinite(x)].max().item() # m是x的最大值 22 x[torch.isinf(x)] = mm # 用最大值替换掉数据里面的INF 23 x[x==0] = 1e-38 # 将数据里面的0元素替换为1e-38 24 return x 25 # 若以(2, 8)为例 26 scores = torch.tensor(scores) 27 t0 = time.time() 28 n, m = scores.shape # torch.Size([2, 8]) 29 scores1 = scores.view(n*m) # torch.Size([16]) 30 Q = torch.softmax(-scores1/eps, dim=0) # softmax 31 Q = remove_infs(Q).view(n,m).T # torch.Size([8, 2]) 32 r, c = torch.ones(n), torch.ones(m) * (n / m) 33 # 确保sum(r)=sum(c) 34 # 对应地P的行和为r,列和为c 35 for _ in range(n_iter): 36 u = (c/torch.sum(Q, dim=1)) # torch.sum(Q, dim=1)按列求和,得到1行8列的数torch.Size([8]) 37 Q *= remove_infs(u).unsqueeze(1) # torch.Size([8, 2]) 38 v = (r/torch.sum(Q,dim=0)) # torch.sum(Q,dim=0)按行求和,得到torch.Size([2]) 39 Q *= remove_infs(v).unsqueeze(0) # torch.Size([8, 2]) 40 bsum = torch.sum(Q, dim=0, keepdim=True) # 按行求和,torch.Size([1, 2]) 41 Q = Q / remove_infs(bsum) 42 # bsum = torch.sum(Q, dim=1, keepdim=True) 43 # Q = Q / remove_infs(bsum) 44 P = Q.T # 转置,torch.Size([2, 8]) 45 t1 = time.time() 46 compute_time = t1 - t0 47 assert torch.isnan(P.sum())==False 48 P = np.array(P) 49 scores = np.array(scores) 50 dist = np.sum(P * scores) 51 return P, dist, compute_time 52 53 # 方法2: 54 # Sinkhorn-Knopp算法 55 ''' 56 https://michielstock.github.io/posts/2017/2017-11-5-OptimalTransport/ 57 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/542379144 58 ''' 59 # numpy 60 def compute_optimal_transport(scores, eps = 5, n_iter = 3): 61 """ 62 Computes the optimal transport matrix and Sinkhorn distance using the 63 Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm 64 Inputs: 65 - scores : cost matrix (n * m) 66 - r : vector of marginals (n, ) 67 - c : vector of marginals (m, ) 68 - eps : strength of the entropic regularization 69 - epsilon : convergence parameter 70 Outputs: 71 - P : optimal transport matrix (n x m) 72 - dist : Sinkhorn distance 73 """ 74 t0 = time.time() 75 n, m = scores.shape 76 r = np.ones(n) # P矩阵列和为r 77 c = np.ones(m)*(n/m) # P矩阵行和为c 78 # 确保:np.sum(r)==np.sum(c) 79 P = np.exp(- scores / eps) 80 P /= P.sum() 81 u = np.zeros(n) 82 # normalize this matrix 83 # while np.max(np.abs(u - P.sum(1))) > epsilon: 84 for _ in range(n_iter): 85 u = P.sum(1) 86 P *= (r / u).reshape((-1, 1)) # 行归r化 87 P *= (c / P.sum(0)).reshape((1, -1)) # 列归c化 88 t1 = time.time() 89 compute_time = t1 - t0 90 dist = np.sum(P * scores) 91 return P, dist, compute_time 92 93 np.random.seed(1) 94 n = 5 # 行数 95 m = 5 # 列数 96 num = 3 # 保留小数位数 97 n_iter = 100 # 迭代次数 98 eps = 0.5 99 scores = np.random.rand(n ,m) # cost matrix 100 print('原始数据:\n', np.around(scores, num)) 101 print('------------------------------------------------') 102 # 方法1: 103 P, dist, compute_time_1 = sinkhorn(scores, eps = eps, n_iter = n_iter) 104 print('1. 处理后的结果:\n', np.around(P, num)) 105 print('1. 行和:\n', np.sum(P, axis = 0)) 106 print('1. 列和:\n', np.sum(P, axis = 1)) 107 print('1. Sinkhorn距离:', np.around(dist, num)) 108 print('1. 计算时间:', np.around(compute_time_1, 8), '秒') 109 print('------------------------------------------------') 110 # 方法2: 111 P, dist, compute_time_2 = compute_optimal_transport(scores, eps = eps, n_iter = n_iter) 112 print('2. 处理后的结果:\n', np.around(P, num)) 113 print('2. 行和:\n', np.sum(P, axis = 0)) 114 print('2. 列和:\n', np.sum(P, axis = 1)) 115 print('2. Sinkhorn距离:', np.around(dist, num)) 116 print('2. 计算时间:', np.around(compute_time_2, 8), '秒') 117 if True: 118 # 绘制热力图 119 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 7)) 120 for axs in ax: 121 axs.tick_params(labelsize=15) 122 sns.set(font_scale=1.5, font='Times New Roman') 123 sns.heatmap(scores, ax=ax[0], cmap = 'Blues') 124 sns.heatmap(P, ax=ax[1], cmap = 'Blues') 125 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['KaiTI'] 126 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False 127 ax[0].set_title("原始数据", fontsize=20) 128 ax[1].set_title("处理后的数据", fontsize=20) 129 plt.tight_layout() 130 plt.savefig("confusion_matrix.png", dpi = 500) 131 plt.show()
2. 结果
D:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\python.exe "D:/Python code/2023.3 exercise/Sinkhorn-Knopp算法/sinkhorn_test.py" 原始数据: [[0.417 0.72 0. 0.302 0.147] [0.092 0.186 0.346 0.397 0.539] [0.419 0.685 0.204 0.878 0.027] [0.67 0.417 0.559 0.14 0.198] [0.801 0.968 0.313 0.692 0.876]] ------------------------------------------------ 1. 处理后的结果: [[0.178 0.121 0.263 0.214 0.225] [0.308 0.318 0.119 0.161 0.093] [0.212 0.155 0.209 0.081 0.342] [0.117 0.242 0.094 0.324 0.222] [0.185 0.164 0.314 0.22 0.117]] 1. 行和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 1. 列和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 1. Sinkhorn距离: 1.802 1. 计算时间: 0.01741338 秒 ------------------------------------------------ 2. 处理后的结果: [[0.178 0.121 0.263 0.214 0.225] [0.308 0.318 0.119 0.161 0.093] [0.212 0.155 0.209 0.081 0.342] [0.117 0.242 0.094 0.324 0.222] [0.185 0.164 0.314 0.22 0.117]] 2. 行和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 2. 列和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 2. Sinkhorn距离: 1.802 2. 计算时间: 0.00100136 秒 Process finished with exit code 0
热力图:
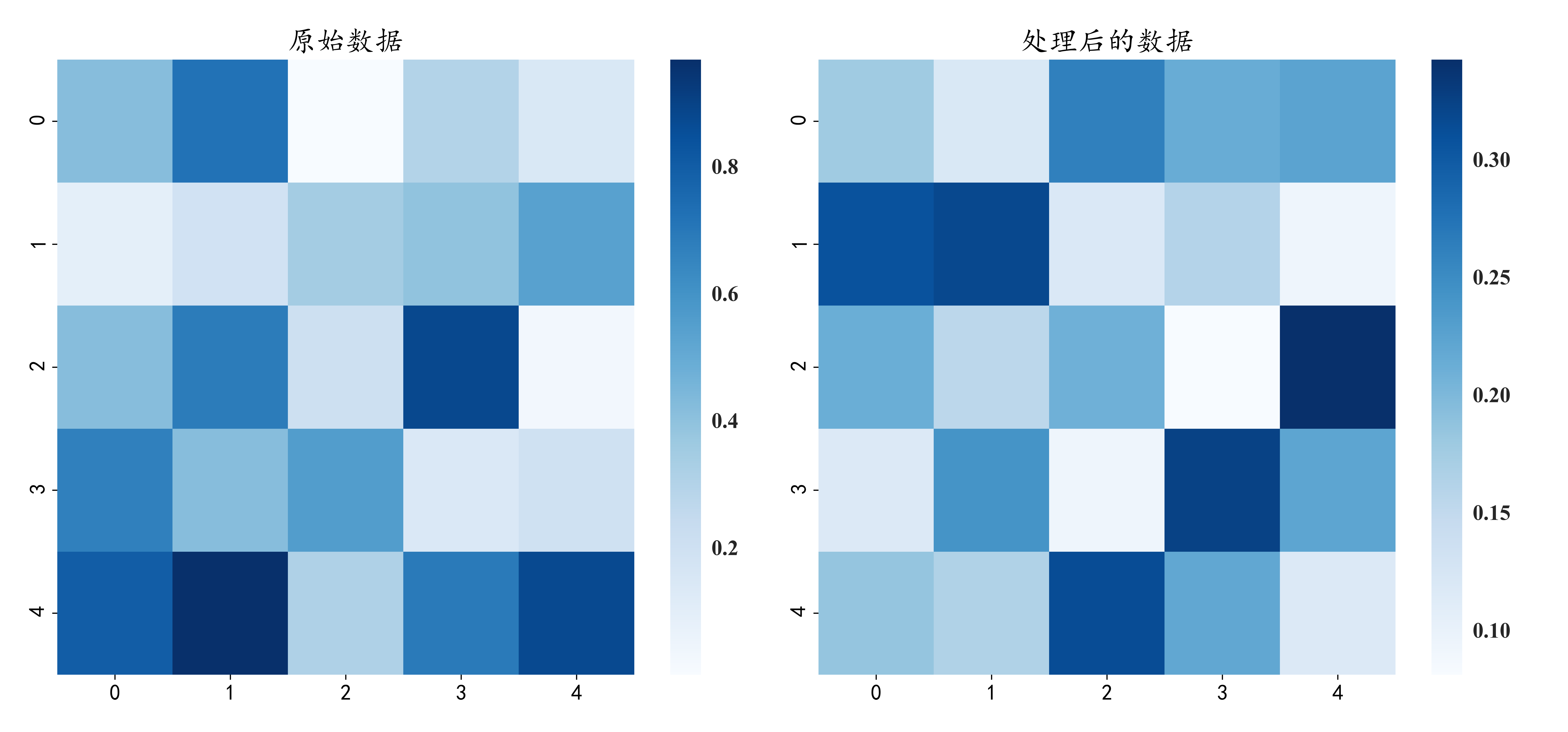
当 n=10, m=5 时,结果为
D:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\python.exe "D:/Python code/2023.3 exercise/sinkhorn_test.py" 原始数据: [[0.417 0.72 0. 0.302 0.147] [0.092 0.186 0.346 0.397 0.539] [0.419 0.685 0.204 0.878 0.027] [0.67 0.417 0.559 0.14 0.198] [0.801 0.968 0.313 0.692 0.876] [0.895 0.085 0.039 0.17 0.878] [0.098 0.421 0.958 0.533 0.692] [0.316 0.687 0.835 0.018 0.75 ] [0.989 0.748 0.28 0.789 0.103] [0.448 0.909 0.294 0.288 0.13 ]] ------------------------------------------------ 1. 处理后的结果: [[0.17 0.111 0.299 0.183 0.237] [0.308 0.306 0.141 0.143 0.102] [0.2 0.141 0.234 0.068 0.356] [0.118 0.234 0.112 0.29 0.246] [0.177 0.152 0.358 0.188 0.124] [0.063 0.385 0.268 0.231 0.053] [0.422 0.265 0.058 0.151 0.104] [0.268 0.153 0.072 0.415 0.091] [0.082 0.16 0.259 0.105 0.393] [0.191 0.091 0.199 0.225 0.293]] 1. 行和: [2. 2. 2. 2. 2.] 1. 列和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 1. Sinkhorn距离: 3.356 1. 计算时间: 0.02233005 秒 ------------------------------------------------ 2. 处理后的结果: [[0.17 0.111 0.299 0.183 0.237] [0.308 0.306 0.141 0.143 0.102] [0.2 0.141 0.234 0.068 0.356] [0.118 0.234 0.112 0.29 0.246] [0.177 0.152 0.358 0.188 0.124] [0.063 0.385 0.268 0.231 0.053] [0.422 0.265 0.058 0.151 0.104] [0.268 0.153 0.072 0.415 0.091] [0.082 0.16 0.259 0.105 0.393] [0.191 0.091 0.199 0.225 0.293]] 2. 行和: [2. 2. 2. 2. 2.] 2. 列和: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] 2. Sinkhorn距离: 3.356 2. 计算时间: 0.00100446 秒 Process finished with exit code 0
热力图:
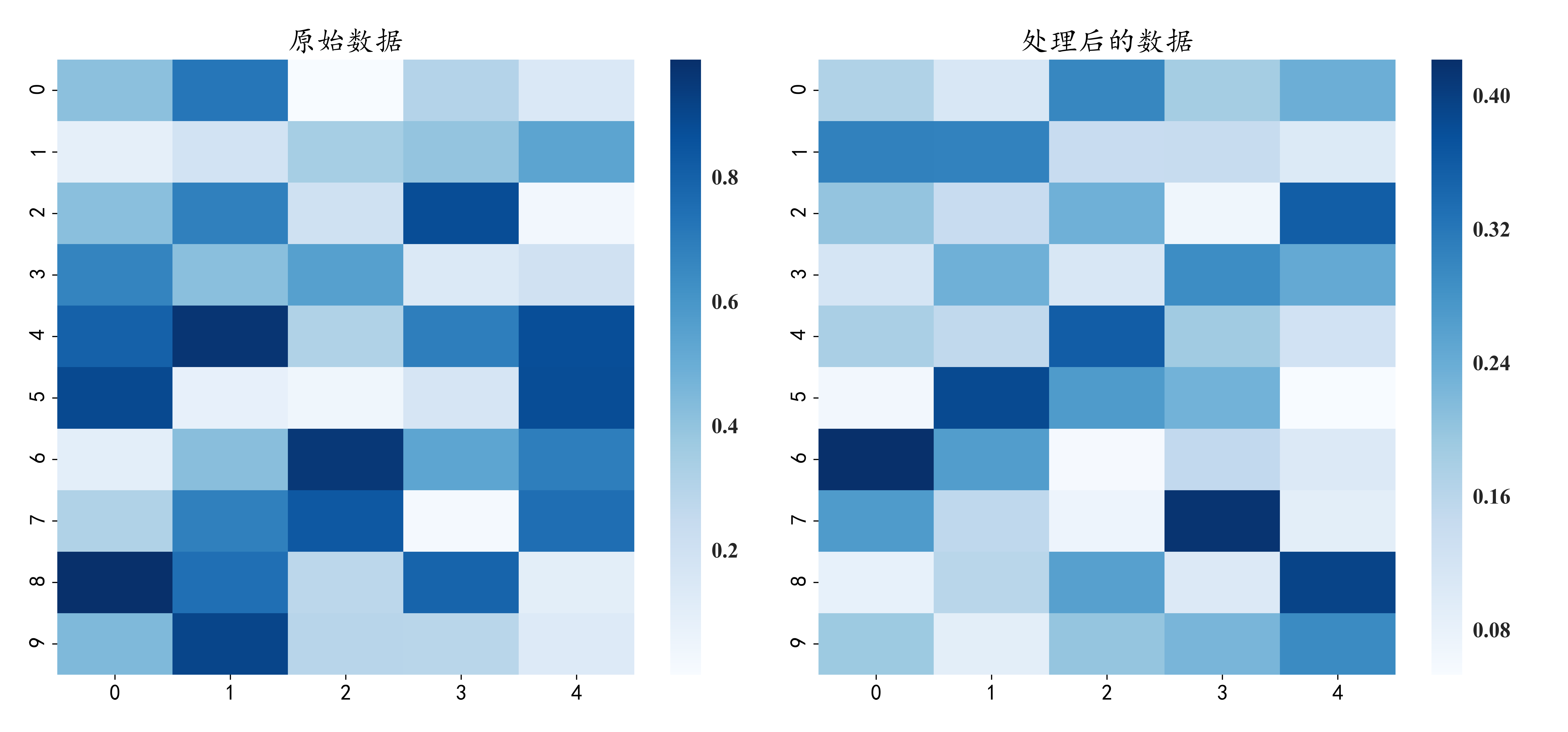
从热力图中也可以看出左边颜色深的块到了右边对应位置,颜色就成了浅色,说明S与P成反比。
3. 参考文献
[1] Cuturi M. Sinkhorn distances: Lightspeed computation of optimal transport[C]. NIPS, 2013.
[2] Liu Q, Zhou Q, Yang R, et al. Robust Representation Learning by Clustering with Bisimulation Metrics for Visual Reinforcement Learning with Distractions[C]. AAAI, 2023.
[3] Michiel Stock, Notes on Optimal Transport, https://michielstock.github.io/posts/2017/2017-11-5-OptimalTransport/
[4] 最优传输问题(Optimal Transport Problem) - 套娃的套娃 - 知乎



