Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On——Tabular Learning and the Bellman Equation
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
更多请看:Reinforcement Learning - 随笔分类 - 凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 https://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/category/2038931.html
这一篇博文参考了书目《Deep Reinforcement Learning Hands-On Second Edition》第5章与第6章内容,主要学习两个贝尔曼最优方程:最优状态值函数方程:${{V}^{*}}(s)={{\max }_{a}}{{\mathbb{E}}_{s'\tilde{\ }p(s'|s,a)}}[r(s,a,s')+\gamma {{V}^{*}}(s')]$与最优状态动作值函数:${{Q}^{*}}(s,a)={{\mathbb{E}}_{s'\tilde{\ }p(s'|s,a)}}[r(s,a,s')+\gamma {{\max }_{a'}}{{Q}^{*}}(s',a')]$,并用Python实现对应的值迭代(Value Iteration)算法、Q迭代(Q Iteration)算法与Q学习(Q Learning)算法。值迭代建立的值表仅有状态,而Q迭代建立的值表有动作与状态。所用的游戏环境为FrozenLake-v1,其中S: initial stat 起点,F: frozen lake 冰湖,H: hole 窟窿,G: the goal 目的地,agent要学会从起点走到目的地,并且不要掉进窟窿。
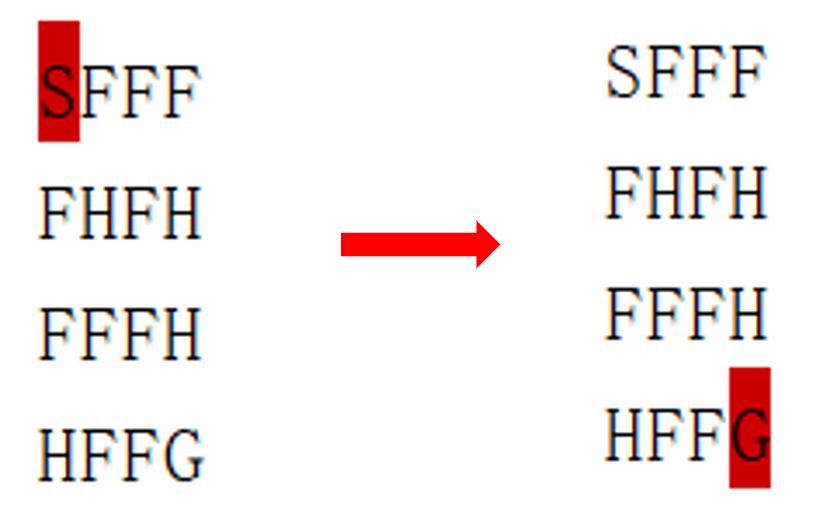
由于事先随机选择动作建立值表,因此每次得到的结果并非一致。所用的模块的版本为:
# packages in environment at D:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\envs\RL: # _pytorch_select 1.2.0 gpu http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main absl-py 1.0.0 <pip> ale-py 0.7.3 <pip> astunparse 1.6.3 <pip> atari-py 1.2.2 <pip> backcall 0.2.0 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main blas 1.0 mkl http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main Box2D 2.3.10 <pip> box2d-py 2.3.8 <pip> ca-certificates 2021.10.26 haa95532_2 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main cached-property 1.5.2 <pip> cachetools 5.0.0 <pip> certifi 2020.6.20 py37_0 anaconda cffi 1.15.0 py37h2bbff1b_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main charset-normalizer 2.0.11 <pip> cloudpickle 2.0.0 <pip> colorama 0.4.4 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main cudatoolkit 10.1.243 h74a9793_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main cycler 0.11.0 <pip> Cython 0.29.26 <pip> decorator 5.1.0 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main fasteners 0.16.3 <pip> ffmpeg 1.4 <pip> flatbuffers 2.0 <pip> fonttools 4.28.5 <pip> freetype 2.10.4 hd328e21_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main gast 0.5.3 <pip> ghostscript 0.7 <pip> glfw 2.5.0 <pip> google-auth 2.6.0 <pip> google-auth-oauthlib 0.4.6 <pip> google-pasta 0.2.0 <pip> grpcio 1.43.0 <pip> gym 0.21.0 <pip> h5py 3.6.0 <pip> idna 3.3 <pip> imageio 2.13.5 <pip> importlib-metadata 2.0.0 py_1 anaconda importlib-metadata 4.10.0 <pip> importlib-resources 5.4.0 <pip> intel-openmp 2019.4 245 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main ipython 7.29.0 py37hd4e2768_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main jedi 0.18.0 py37haa95532_1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main jpeg 9b hb83a4c4_2 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main keras 2.8.0 <pip> Keras-Preprocessing 1.1.2 <pip> kiwisolver 1.3.2 <pip> libclang 13.0.0 <pip> libmklml 2019.0.5 haa95532_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main libpng 1.6.37 h2a8f88b_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main libtiff 4.2.0 hd0e1b90_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main libuv 1.40.0 he774522_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main libwebp 1.2.0 h2bbff1b_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main lockfile 0.12.2 <pip> lz4-c 1.9.3 h2bbff1b_1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main Markdown 3.3.6 <pip> matplotlib 3.5.1 <pip> matplotlib-inline 0.1.2 pyhd3eb1b0_2 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main mkl 2019.4 245 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main mkl-service 2.3.0 py37h196d8e1_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main mkl_fft 1.3.0 py37h46781fe_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main mkl_random 1.1.0 py37h675688f_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main mujoco-py 1.50.1.68 <pip> ninja 1.10.2 py37h559b2a2_3 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main numpy 1.19.2 py37hadc3359_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main numpy 1.21.5 <pip> numpy-base 1.19.2 py37ha3acd2a_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main oauthlib 3.2.0 <pip> olefile 0.46 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main opencv-python 4.5.5.62 <pip> openssl 1.0.2t vc14h62dcd97_0 [vc14] anaconda opt-einsum 3.3.0 <pip> packaging 21.3 <pip> parso 0.8.3 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main pickleshare 0.7.5 pyhd3eb1b0_1003 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main Pillow 9.0.0 <pip> pillow 8.4.0 py37hd45dc43_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main pip 20.2.4 py37_0 anaconda prompt-toolkit 3.0.20 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main protobuf 3.19.4 <pip> pyasn1 0.4.8 <pip> pyasn1-modules 0.2.8 <pip> pycparser 2.21 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main pyglet 1.5.21 <pip> pygments 2.10.0 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main pyparsing 3.0.6 <pip> python 3.7.1 h33f27b4_4 anaconda python-dateutil 2.8.2 <pip> pytorch 1.7.1 py3.7_cuda101_cudnn7_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch requests 2.27.1 <pip> requests-oauthlib 1.3.1 <pip> rsa 4.8 <pip> setuptools 50.3.0 py37h9490d1a_1 anaconda six 1.16.0 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main sqlite 3.20.1 vc14h7ce8c62_1 [vc14] anaconda swig 3.0.12 h047fa9f_3 anaconda tensorboard 2.8.0 <pip> tensorboard-data-server 0.6.1 <pip> tensorboard-plugin-wit 1.8.1 <pip> tensorboardX 2.4.1 <pip> tensorflow 2.8.0 <pip> tensorflow-io-gcs-filesystem 0.24.0 <pip> termcolor 1.1.0 <pip> tf-estimator-nightly 2.8.0.dev2021122109 <pip> tk 8.6.11 h2bbff1b_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main torchaudio 0.7.2 py37 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch torchvision 0.8.2 py37_cu101 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/cloud/pytorch traitlets 5.1.1 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main typing_extensions 4.0.1 <pip> typing_extensions 3.10.0.2 pyh06a4308_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main urllib3 1.26.8 <pip> vc 14.2 h21ff451_1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main vs2015_runtime 14.27.29016 h5e58377_2 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main wcwidth 0.2.5 pyhd3eb1b0_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main Werkzeug 2.0.2 <pip> wheel 0.37.0 pyhd3eb1b0_1 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main wincertstore 0.2 py37_0 anaconda wrappers 0.1.9 <pip> wrapt 1.13.3 <pip> xz 5.2.5 h62dcd97_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main zipp 3.7.0 <pip> zipp 3.3.1 py_0 anaconda zlib 1.2.11 h8cc25b3_4 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main zstd 1.4.9 h19a0ad4_0 http://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/main
1. 值迭代(Value Iteration)
1.1 算法流程

1.2 Python程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
# Value iteration for FrozenLake
# https://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
import gym
import collections
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
import time
ENV_NAME = "FrozenLake-v1" #游戏环境
'''
S: initial stat 起点
F: frozen lake 冰湖
H: hole 窟窿
G: the goal 目的地
agent要学会从起点走到目的地,并且不要掉进窟窿
'''
GAMMA = 0.9 # 折扣率
TEST_EPISODES = 20 # 玩几局游戏
class Agent: #保存表格,并包含将在训练循环中使用的函数
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make(ENV_NAME) #创建游戏环境
self.state = self.env.reset() # 用于重置环境
self.rewards = collections.defaultdict(float)
self.transits = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
self.values = collections.defaultdict(float)
'''
此功能用于从环境中收集随机经验,并更新奖励和过渡表。
注意,我们不需要等到一局游戏(回合)结束才开始学习;
我们只需执行N个步骤,并记住它们的结果。
这是值迭代和交叉熵方法的区别之一,交叉熵方法只能在完整的回合中学习。
'''
def play_n_random_steps(self, count): # 玩100步,得到回报表与转换表
for _ in range(count):
action = self.env.action_space.sample() # 随机采样选择动作
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = self.env.step(action) # 根据动作,与环境互动得到的新的状态与奖励
self.rewards[(self.state, action, new_state)] = reward # 回报表:源状态,动作,目标状态
self.transits[(self.state, action)][new_state] += 1 # 转换表:状态,动作,新状态的概率
self.state = self.env.reset() if is_done else new_state
def calc_action_value(self, state, action): # 步骤5:给定s, a, 计算Q(s, a)
target_counts = self.transits[(state, action)] # 转换表:状态,动作
total = sum(target_counts.values())
action_value = 0.0
for tgt_state, count in target_counts.items():
reward = self.rewards[(state, action, tgt_state)] # 回报表:源状态,动作,目标状态
val = reward + GAMMA * self.values[tgt_state] # 值表只有一个:目标状态
action_value += (count / total) * val # 期望值——状态动作值函数(Q值)
return action_value # Q值
def select_action(self, state): # 步骤6:给定状态,找最优动作
best_action, best_value = None, None
for action in range(self.env.action_space.n): # 遍历所有动作
action_value = self.calc_action_value(state, action) # 步骤5:Q值
if best_value is None or best_value < action_value:
best_value = action_value
best_action = action
return best_action # 找使Q值最大的那个动作——最优动作 a = argmax Q(s, a)
def play_episode(self, env): # 玩一局游戏
total_reward = 0.0
state = env.reset() # 用于重置环境
while True:
action = self.select_action(state) # 步骤6:最优动作
# 不同于"Windows下OpenAI gym环境的使用"中的随机采样动作
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = env.step(action) # 根据动作,与环境交互得到的新的状态与奖励
self.rewards[(state, action, new_state)] = reward # 更新表
self.transits[(state, action)][new_state] += 1 # 转换表
total_reward += reward
if is_done:
break
state = new_state
return total_reward # 得到一局游戏过后的总体奖励
def value_iteration(self): # 值迭代循环
# 用s状态下可用的动作的最大值来更新当前状态的值
# 任意s,π(s) = arg max Q(s, a)
for state in range(self.env.observation_space.n): # 步骤2-4:遍历状态空间,找使Q值最大的最优策略
state_values = [
self.calc_action_value(state, action) # 计算Q(s, a)
for action in range(self.env.action_space.n) # 遍历动作空间
]
self.values[state] = max(state_values) # 步骤3:对于每个状态,V(s) = max Q(s, a)
# 更新V值表,最优状态值函数,贝尔曼最优方程
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_env = gym.make(ENV_NAME)
agent = Agent()
writer = SummaryWriter(comment="-v-iteration")
iter_no = 0
best_reward = 0.0
while True: # 重复试验,直到20局游戏的平均奖励大于0.8,迭代终止
iter_no += 1 # iter_no:重复试验的迭代次数
agent.play_n_random_steps(100) # 步骤1:每一局游戏执行100个随机步骤,填充回报和转换表
agent.value_iteration() # 步骤2-4:100步之后,对所有的状态进行一次值迭代循环,更新V值表,作为策略
# time.sleep(0.1) #为了让显示变慢,否则画面会非常快
# test_env.render() # 用于渲染出当前的智能体以及环境的状态
reward = 0.0
for _ in range(TEST_EPISODES): # 玩20局游戏
reward += agent.play_episode(test_env) # 用到步骤5-6, 20局游戏奖励之和
reward /= TEST_EPISODES # 20局的平均奖励
writer.add_scalar("reward", reward, iter_no)
if reward > best_reward:
print("Best reward updated %.3f -> %.3f" % (
best_reward, reward))
best_reward = reward # 找到最优的奖励
if reward > 0.80: # 重复试验次数,直到奖励>0.8,停止迭代
print("Solved in %d iterations!" % iter_no)
break
writer.close()
1.3 结果
Best reward updated 0.000 -> 0.100 Best reward updated 0.100 -> 0.350 Best reward updated 0.350 -> 0.500 Best reward updated 0.500 -> 0.600 Best reward updated 0.600 -> 0.750 Best reward updated 0.750 -> 0.850 Solved in 14 iterations!
2. Q迭代(Q Iteration)
2.1 算法流程

2.2 Python程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
# Q-learning for FrozenLake
# 1. 值表变了。上例保留了状态的值,因此字典中的键只是一个状态。
# 现在需要存储Q函数的值,它有两个参数:状态和动作,因此值表中的键现在是复合键。
# 2. 不需要calc_action_value()函数。因为我们的动作值存储在值表中。
# 3. value_iteration()变了。
# https://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
import gym
import collections
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
ENV_NAME = "FrozenLake-v1" #游戏环境
'''
S: initial stat 起点
F: frozen lake 冰湖
H: hole 窟窿
G: the goal 目的地
agent要学会从起点走到目的地,并且不要掉进窟窿
'''
GAMMA = 0.9 # 折扣率
TEST_EPISODES = 20 # 玩几局游戏
class Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make(ENV_NAME) #创建游戏环境
self.state = self.env.reset() # 用于重置环境
self.rewards = collections.defaultdict(float)
self.transits = collections.defaultdict(collections.Counter)
self.values = collections.defaultdict(float)
def play_n_random_steps(self, count): # 玩100步,得到回报表与转换表
for _ in range(count):
action = self.env.action_space.sample() # 随机采样选择动作
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = self.env.step(action) # 根据动作,与环境互动得到的新的状态与奖励
self.rewards[(self.state, action, new_state)] = reward # 回报表:源状态,动作,目标状态
self.transits[(self.state, action)][new_state] += 1 # 转换表:状态,动作
self.state = self.env.reset() if is_done else new_state
def select_action(self, state): # 给定状态s, a = argmax Q(s, a)
best_action, best_value = None, None
for action in range(self.env.action_space.n): # 遍历所有动作
action_value = self.values[(state, action)] # Q值表里有两个:状态与动作
if best_value is None or best_value < action_value:
best_value = action_value
best_action = action
return best_action # 直接建立Q表,从Q值表里找最优动作
def play_episode(self, env): # 玩一局游戏
total_reward = 0.0
state = env.reset() # 用于重置环境
while True:
action = self.select_action(state) # 给定状态s, 最优动作a = argmax Q(s, a)
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = env.step(action) # 根据动作,与环境交互得到的新的状态与奖励
self.rewards[(state, action, new_state)] = reward # 更新表
self.transits[(state, action)][new_state] += 1
total_reward += reward
if is_done:
break
state = new_state # 步骤8
return total_reward # 得到一局游戏过后的总体奖励
def value_iteration(self): # 变了
# 选择具有最大Q值的动作,然后把这个Q值作为目标状态的值
for state in range(self.env.observation_space.n): # 步骤2-10:其中3:遍历状态空间
for action in range(self.env.action_space.n): # 步骤4-9:遍历动作空间
action_value = 0.0
target_counts = self.transits[(state, action)] # 转换表:状态,动作
total = sum(target_counts.values())
for tgt_state, count in target_counts.items():
reward = self.rewards[(state, action, tgt_state)] # 回报表:源状态,动作,目标状态
best_action = self.select_action(tgt_state) # 给定状态s, 最优动作a = argmax Q(s, a)
val = reward + GAMMA * self.values[(tgt_state, best_action)] # 值表:目标状态,最优动作
action_value += (count / total) * val # 期望值——最优状态动作值函数(Q值)(其中动作为最优动作)
# 贝尔曼最优方程
self.values[(state, action)] = action_value # 更新Q值表:状态,动作
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_env = gym.make(ENV_NAME)
agent = Agent()
writer = SummaryWriter(comment="-q-iteration")
iter_no = 0
best_reward = 0.0
while True: # 重复试验,直到20局游戏的平均奖励大于0.8,迭代终止
iter_no += 1 # iter_no:重复试验的迭代次数
agent.play_n_random_steps(100) # 步骤1:每一局游戏执行100个随机步骤,填充回报和转换表
agent.value_iteration() # 步骤2-10:100步之后,对所有的状态进行一次值迭代循环,更新Q值表,作为策略
# time.sleep(0.1) #为了让显示变慢,否则画面会非常快
# test_env.render() # 用于渲染出当前的智能体以及环境的状态
reward = 0.0
for _ in range(TEST_EPISODES): # 玩20局游戏
reward += agent.play_episode(test_env) # 20局游戏奖励之和
reward /= TEST_EPISODES # 20局的平均奖励
writer.add_scalar("reward", reward, iter_no)
if reward > best_reward:
print("Best reward updated %.3f -> %.3f" % (best_reward, reward))
best_reward = reward # 找到最优的奖励
if reward > 0.80: # 重复试验次数,直到奖励>0.8,停止迭代
print("Solved in %d iterations!" % iter_no)
break
writer.close()
2.3 结果
Best reward updated 0.000 -> 0.250 Best reward updated 0.250 -> 0.300 Best reward updated 0.300 -> 0.500 Best reward updated 0.500 -> 0.600 Best reward updated 0.600 -> 0.850 Solved in 33 iterations!
3. Q学习(Tabular Q-Learning)
3.1 算法流程
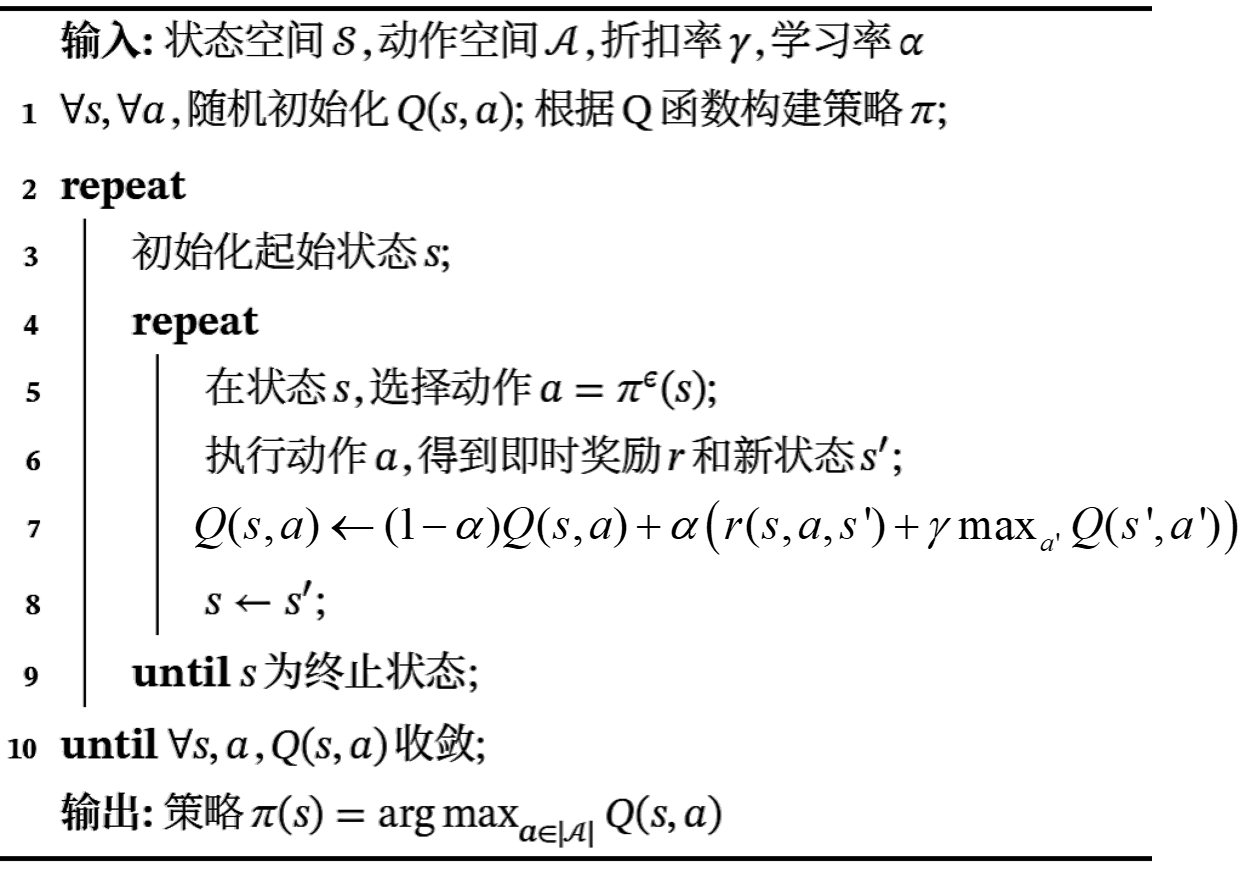
3.2 Python程序
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding=utf-8 -*-
# Q-learning for FrozenLake
# https://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
# 与上一个值迭代法相比,这个版本使用了更多的迭代来解决问题。
# 其原因是不再使用测试过程中获得的经验。
# 在上一个Q迭代例子中,周期性的测试会引起Q表统计的更新。
# 本算法在测试过程中不接触Q值,这在环境得到解决之前会造成更多的迭代。
# 总的来说,环境所需的样本总数几乎是一样的。
import gym
import collections
from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter
ENV_NAME = "FrozenLake-v1"
GAMMA = 0.9 # 折扣率
ALPHA = 0.2 # 平滑指数
TEST_EPISODES = 20 # 玩几局游戏
class Agent:
def __init__(self):
self.env = gym.make(ENV_NAME)
self.state = self.env.reset()
self.values = collections.defaultdict(float)
def sample_env(self): # 随机采样动作
action = self.env.action_space.sample()
old_state = self.state
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = self.env.step(action)
self.state = self.env.reset() if is_done else new_state
return old_state, action, reward, new_state
def best_value_and_action(self, state): # 从Q表中选择最优值与动作
best_value, best_action = None, None
for action in range(self.env.action_space.n):
action_value = self.values[(state, action)]
if best_value is None or best_value < action_value:
best_value = action_value
best_action = action
return best_value, best_action
def value_update(self, s, a, r, next_s): # 平滑
best_v, _ = self.best_value_and_action(next_s)
new_v = r + GAMMA * best_v # r(s, a, s') + γ * max Q(s, a)
old_v = self.values[(s, a)]
self.values[(s, a)] = old_v * (1-ALPHA) + new_v * ALPHA # 这变了,Q值平滑收敛
# Q(s, a) <- (1-α) * Q(s, a) + α * (r(s, a, s') + γ * max Q(s, a))
def play_episode(self, env): # 玩一局游戏
total_reward = 0.0
state = env.reset()
while True:
_, action = self.best_value_and_action(state) # 给定状态,从Q表中选择最优动作
new_state, reward, is_done, _ = env.step(action)
total_reward += reward
if is_done:
break
state = new_state
return total_reward
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_env = gym.make(ENV_NAME)
agent = Agent()
writer = SummaryWriter(comment="-q-learning")
iter_no = 0
best_reward = 0.0
while True:
iter_no += 1
s, a, r, next_s = agent.sample_env() # 执行一个随机步骤
agent.value_update(s, a, r, next_s)
reward = 0.0
for _ in range(TEST_EPISODES):
reward += agent.play_episode(test_env)
reward /= TEST_EPISODES
writer.add_scalar("reward", reward, iter_no)
if reward > best_reward:
print("Best reward updated %.3f -> %.3f" % (
best_reward, reward))
best_reward = reward
if reward > 0.80:
print("Solved in %d iterations!" % iter_no)
break
writer.close()
3.3 结果
Best reward updated 0.000 -> 0.200 Best reward updated 0.200 -> 0.250 Best reward updated 0.250 -> 0.350 Best reward updated 0.350 -> 0.500 Best reward updated 0.500 -> 0.550 Best reward updated 0.550 -> 0.600 Best reward updated 0.600 -> 0.650 Best reward updated 0.650 -> 0.700 Best reward updated 0.700 -> 0.800 Best reward updated 0.800 -> 0.850 Solved in 16682 iterations!
4. 参考文献
[1] https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Deep-Reinforcement-Learning-Hands-On-Second-Edition
[2] 邱锡鹏,神经网络与深度学习,机械工业出版社,https://nndl.github.io/, 2020.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号