浅谈范数正则化
作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
这篇博客介绍不同范数作为正则化项时的作用。首先介绍了常见的向量范数与矩阵范数,然后说明添加正则化项的原因,之后介绍向量的$L_0$,$L_1$,$L_2$范数及其作为正则化项的作用,对三者进行比较分析,并用贝叶斯观点解释传统线性模型与正则化项。随后,介绍矩阵的$L_{2, 1}$范数及其推广形式$L_{p, q}$范数,以及矩阵的核范数及其推广形式Schatten范数。最后,用MATLAB程序编写了Laplace分布与Gauss分布的概率密度函数图。有关矩阵范数优化求解问题可参考:一类涉及矩阵范数的优化问题 - 凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园
1. 向量范数与矩阵范数

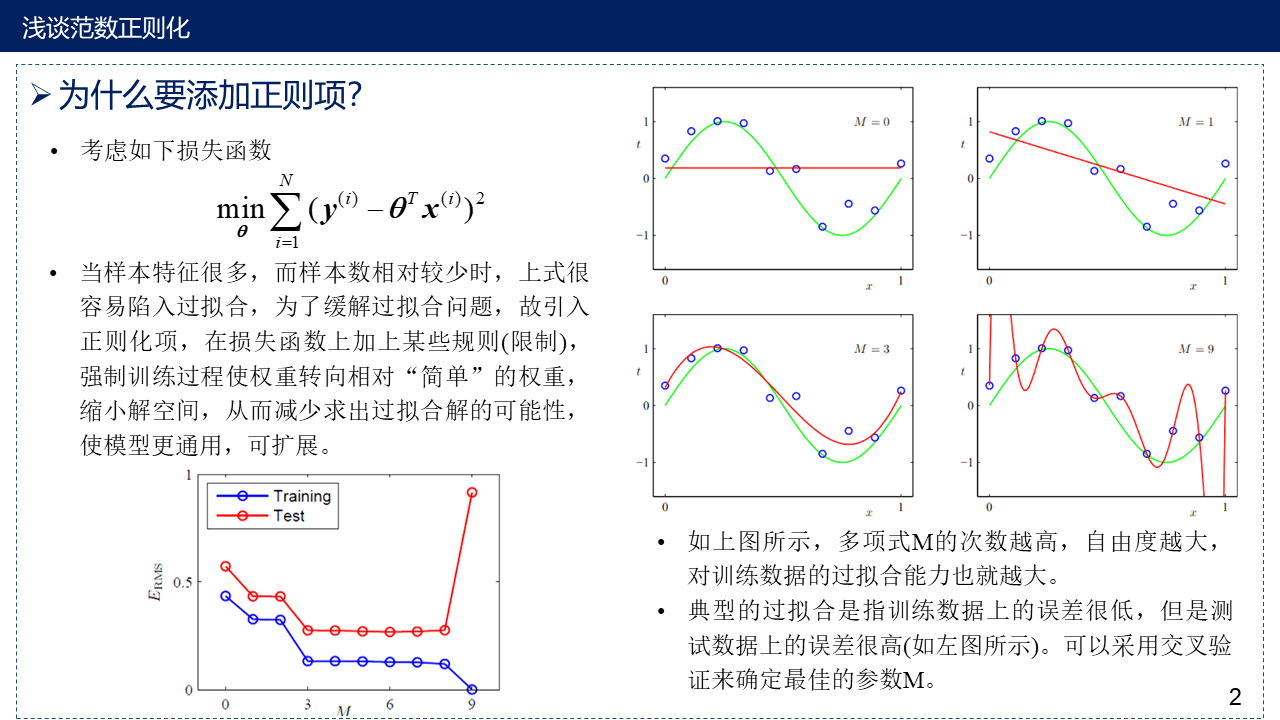
2. 为什么要添加正则项?
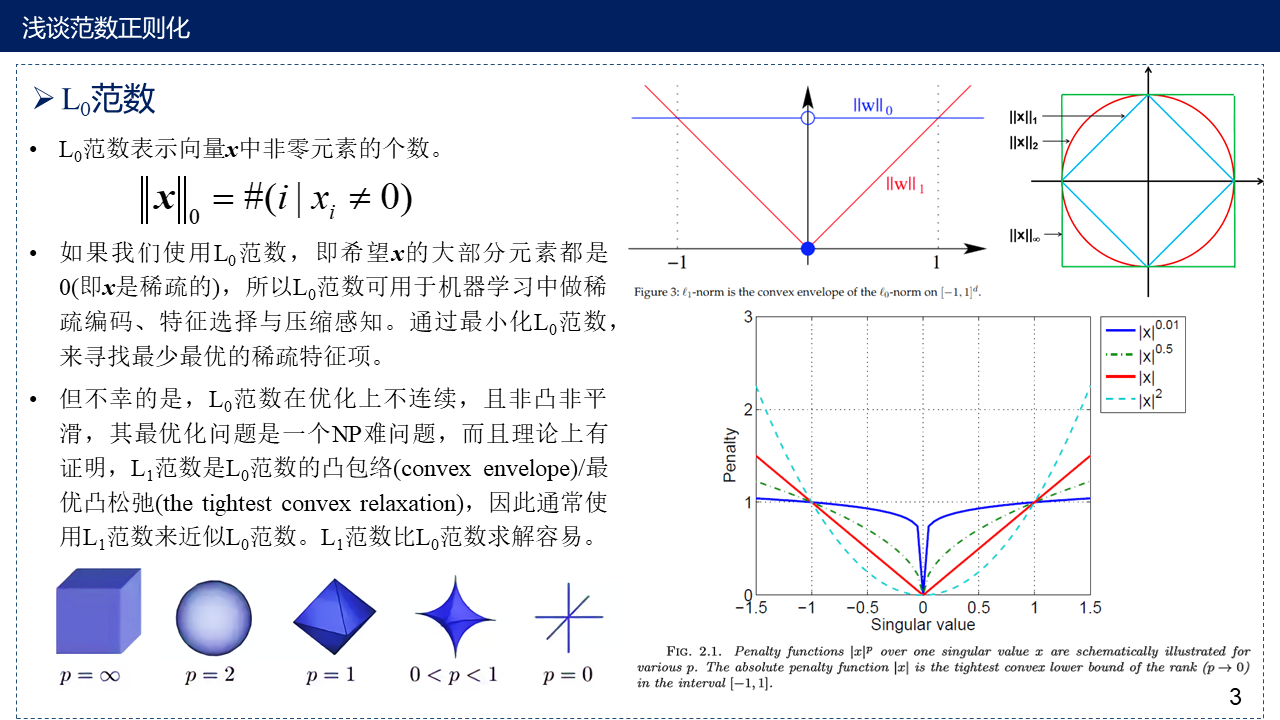
3. $L_0$范数
4. $L_1$范数

5. $L_2$范数

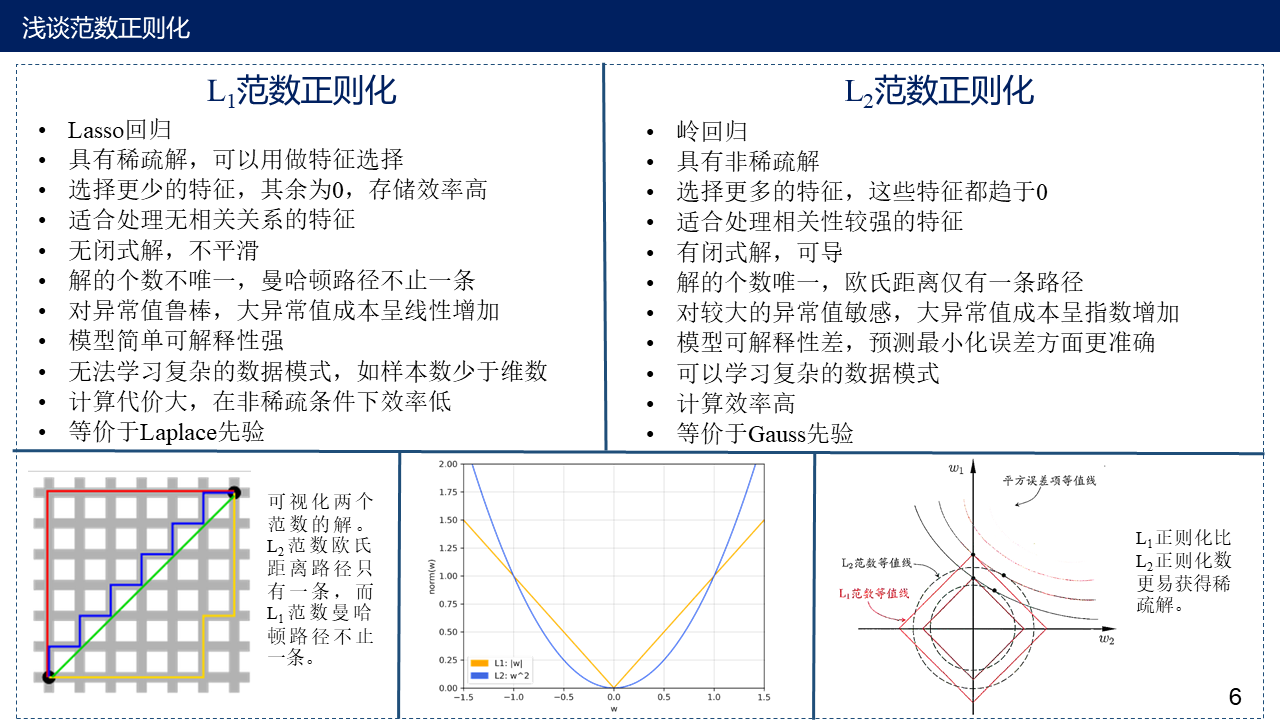
6. $L_1$范数与$L_2$范数作为正则项的区别
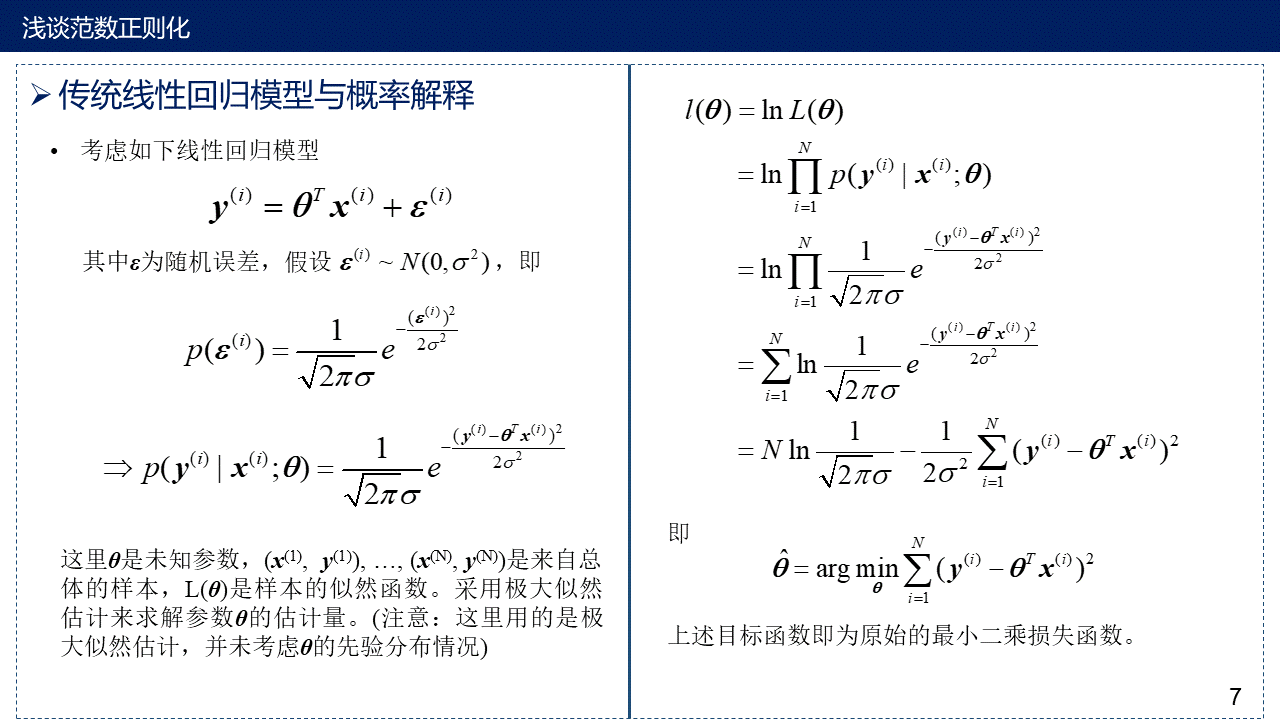
7. 用概率解释传统线性回归模型
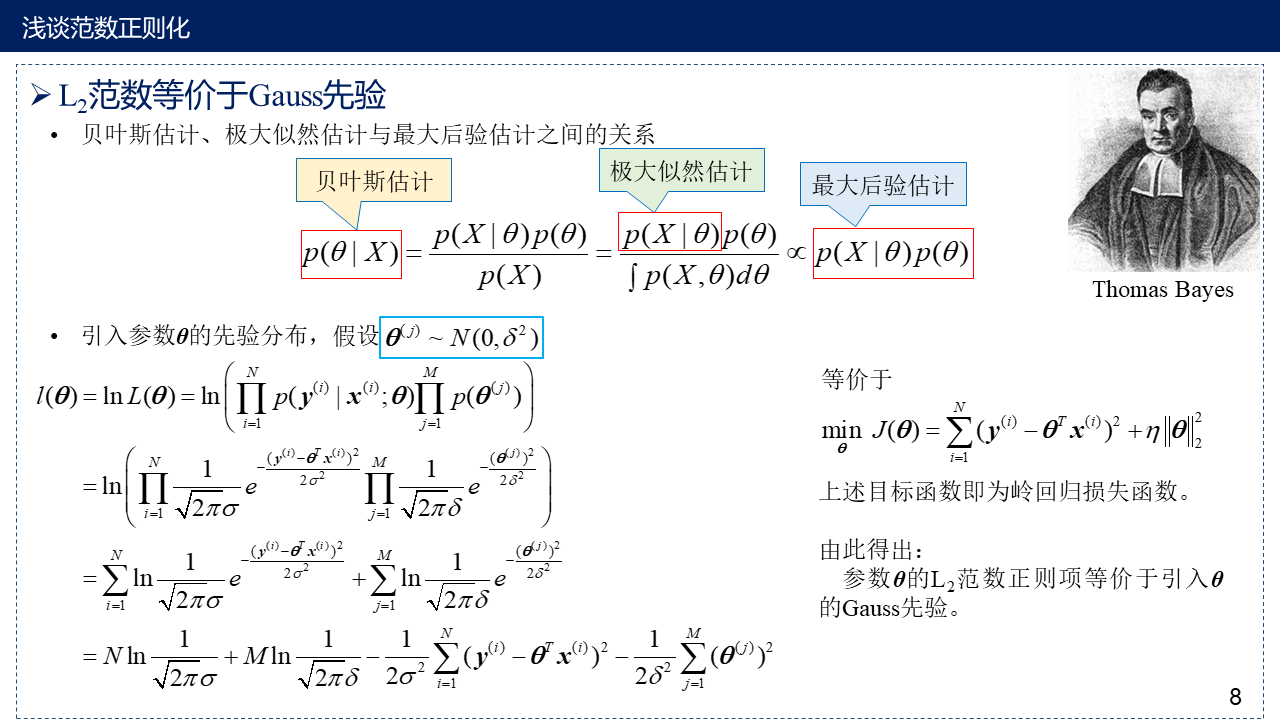
8. $L_2$范等价于Gauss先验
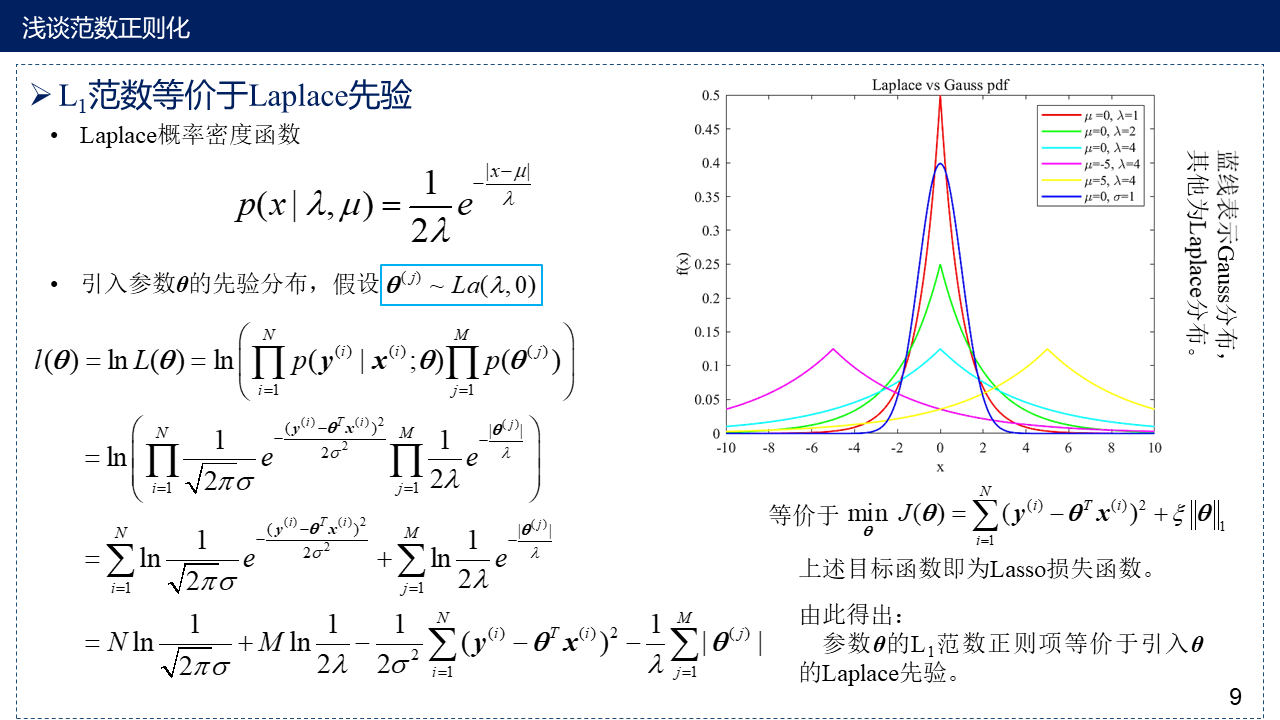
9. $L_1$范数等价于Laplace先验
10. 矩阵的$L_{2, 1}$范数及$L_{p, q}$范数

11. 矩阵的核范数及Schatten范数

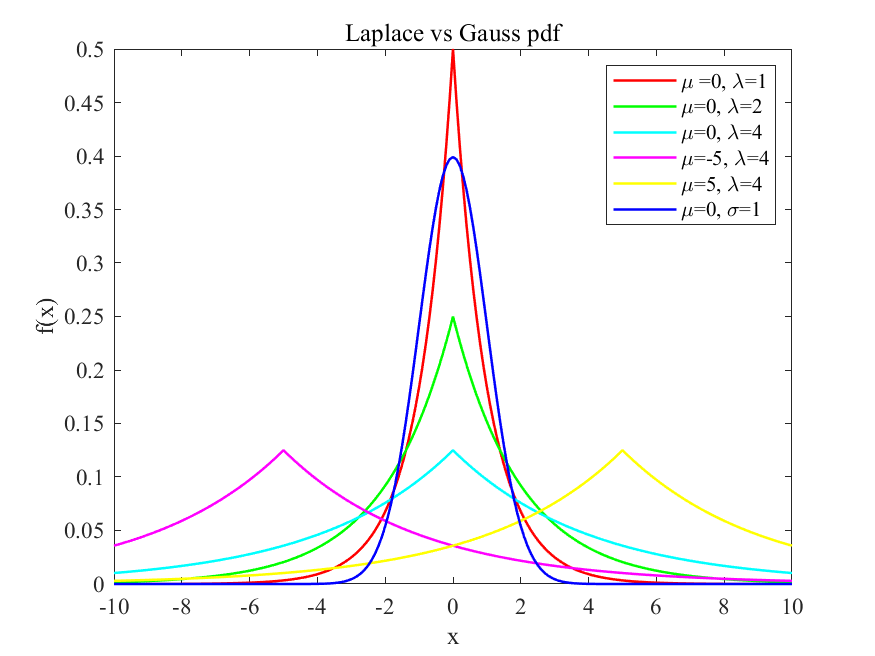
12. MATLAB程序:Laplace分布与Gauss分布的概率密度函数图
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | %% Demo of Laplace Density Function% x : variable% lambda : size para%miu: location paraclearclcx = -10:0.1:10;y_1=Laplace_distribution(x, 0, 1);y_2=Laplace_distribution(x, 0, 2);y_3=Laplace_distribution(x, 0, 4);y_4=Laplace_distribution(x, -5, 4);y_5=Laplace_distribution(x, 5, 4);y_6=normpdf(x,0,1);plot(x, y_1, 'r-', x, y_2, 'g-', x, y_3, 'c-', x, y_4, 'm-', x, y_5, 'y-', x, y_6, 'b-', 'LineWidth',1.2);legend('\mu =0, \lambda=1','\mu=0, \lambda=2','\mu=0, \lambda=4','\mu=-5, \lambda=4','\mu=5, \lambda=4', '\mu=0, \sigma=1'); %图例的设置xlabel('x');ylabel('f(x)');title('Laplace vs Gauss pdf');set(gca, 'FontName', 'Times New Roman', 'FontSize',11);saveas(gcf,sprintf('demo_Laplace_Gauss.jpg'),'bmp'); %保存图片%% Laplace Density Functionfunction y=Laplace_distribution(x, miu, lambda) y = 1 / (2*lambda) * exp( -abs(x-miu)/lambda);end |
13. 参考文献
[1] 证明核范数是矩阵秩的凸包络
EJ Candès, Recht B . Exact Matrix Completion via Convex Optimization[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2009, 9(6):717.
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.312.1183&rep=rep1&type=pdf
[2] 关于说明$L_1$范数是$L_0$范数的凸包络的文献及教案
Donoho D L , Huo X . Uncertainty Principles and Ideal Atomic Decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2001, 47(7):2845-2862.
Learning with Combinatorial Structure Note for Lecture 12
http://people.csail.mit.edu/stefje/fall15/notes_lecture12.pdf
L1-norm Methods for Convex-Cardinality Problems
https://web.stanford.edu/class/ee364b/lectures/l1_slides.pdf
[3] 有关过拟合的教案及图片来源
2017 Lecture 2: Overfitting. Regularization
https://www.cs.mcgill.ca/~dprecup/courses/ML/Lectures/ml-lecture02.pdf
[4] 一些可供参考的资料
The difference between L1 and L2 regularization
https://explained.ai/regularization/L1vsL2.html
Why L1 norm for sparse models
https://stats.stackexchange.com/questions/45643/why-l1-norm-for-sparse-models
Why L1 regularization can “zero out the weights” and therefore leads to sparse models? [duplicate]
What are L1, L2 and Elastic Net Regularization in neural networks?
Introduction. Sharpness Enhancement and Denoising of Image Using L1-Norm Minimization Technique in Adaptive Bilateral Filter.



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 一个奇形怪状的面试题:Bean中的CHM要不要加volatile?
· [.NET]调用本地 Deepseek 模型
· 一个费力不讨好的项目,让我损失了近一半的绩效!
· 在鹅厂做java开发是什么体验
· 百万级群聊的设计实践
· WPF到Web的无缝过渡:英雄联盟客户端的OpenSilver迁移实战
· 永远不要相信用户的输入:从 SQL 注入攻防看输入验证的重要性
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析