密度峰值聚类算法(DPC)
凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/
具体实例见:密度峰值聚类算法MATLAB程序 - 凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园
1. 简介
基于密度峰值的聚类算法全称为基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法(clustering by fast search and find of density peaks, DPC)。它是2014年在Science上提出的聚类算法,该算法能够自动地发现簇中心,实现任意形状数据的高效聚类。
该算法基于两个基本假设:1)簇中心(密度峰值点)的局部密度大于围绕它的邻居的局部密度;2)不同簇中心之间的距离相对较远。为了找到同时满足这两个条件的簇中心,该算法引入了局部密度的定义。
假设数据点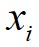 的局部密度为
的局部密度为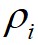 ,数据点
,数据点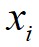 到局部密度比它大且距离最近的数据点
到局部密度比它大且距离最近的数据点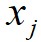 的距离为
的距离为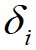 ,则有如下定义:
,则有如下定义:
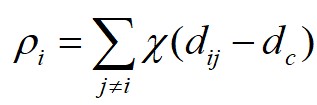
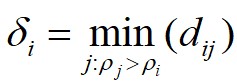
式中,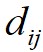 为
为 和
和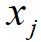 之间的距离;
之间的距离;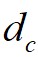 为截断距离;
为截断距离; 为逻辑判断函数,
为逻辑判断函数,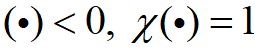 ,否则
,否则 。
。
这里对于局部密度最大的数据点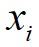 ,它的
,它的 。
。
根据以上定义,通过构造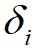 相对于
相对于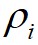 的决策图,进行数据点分配和噪声点剔除,可以快速得到最终的聚类结果。算法1给出了基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法的具体步骤。首先,基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法对任意两个数据点计算它们之间的距离,并依据截断距离计算出任意数据点
的决策图,进行数据点分配和噪声点剔除,可以快速得到最终的聚类结果。算法1给出了基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法的具体步骤。首先,基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法对任意两个数据点计算它们之间的距离,并依据截断距离计算出任意数据点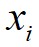 的
的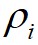 和
和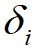 ;然后,算法根据
;然后,算法根据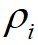 和
和 ,画出对应的聚类决策图;接着,算法利用得到的决策图,将
,画出对应的聚类决策图;接着,算法利用得到的决策图,将 和
和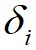 都相对较高的数据点标记为簇的中心,将
都相对较高的数据点标记为簇的中心,将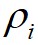 相对较低但是
相对较低但是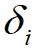 相对较高的点标记为噪声点;最后,算法将剩余的数据点进行分配,分配的规则为将每个剩余的数据点分配到它的最近邻且密度比其大的数据点所在的簇。
相对较高的点标记为噪声点;最后,算法将剩余的数据点进行分配,分配的规则为将每个剩余的数据点分配到它的最近邻且密度比其大的数据点所在的簇。
算法1 基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法

下面举一个简单的例子。在图1中,数据点的分布情况如图1(左)所示,可以看出数据集包含两个簇,分别用蓝色和红色标出,噪声用黑色标出。利用基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值算法,可以得到图1(右)的决策图。在决策过程中可以发现点1和点10的 和
和 都相对较高,因此它们被标记为中心点。点26~点28的
都相对较高,因此它们被标记为中心点。点26~点28的 相对较低但是
相对较低但是 相对较高,因此它们被标记为噪声。其他的点将被分配到它的最近邻且密度比其大的数据点所在的簇中去。
相对较高,因此它们被标记为噪声。其他的点将被分配到它的最近邻且密度比其大的数据点所在的簇中去。
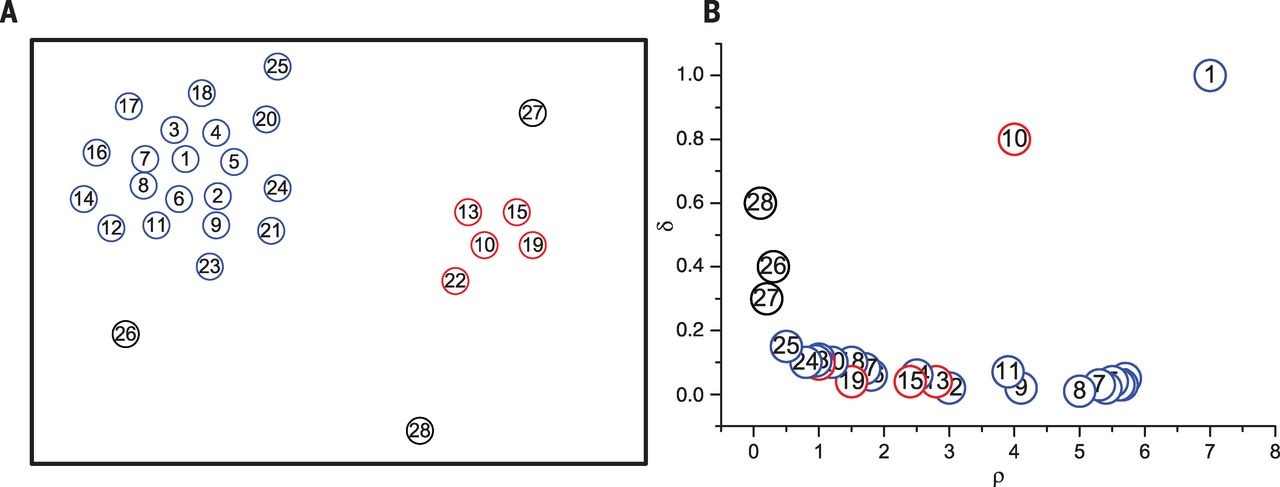
图1 基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法例子
基于快速搜索和发现密度峰值的聚类算法,想法非常直观,能够快速发现密度峰值点,并能够高效进行样本分配和发现噪声点。同时,因为该方法非常适用于大规模数据的聚类分析,因此具有很好的研究价值和应用前景。
2. MATLAB程序
数据请参考文献[3],也可以在这里下载:DPC数据.rar
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 | clear allclose alldisp('The only input needed is a distance matrix file')disp('The format of this file should be: ')disp('Column 1: id of element i')disp('Column 2: id of element j')disp('Column 3: dist(i,j)')%% 从文件中读取数据mdist=input('name of the distance matrix file\n','s');disp('Reading input distance matrix')xx=load(mdist);ND=max(xx(:,2));NL=max(xx(:,1));if (NL>ND) ND=NL; %% 确保 DN 取为第一二列最大值中的较大者,并将其作为数据点总数endN=size(xx,1); %% xx 第一个维度的长度,相当于文件的行数(即距离的总个数)%% 初始化为零for i=1:ND for j=1:ND dist(i,j)=0; endend%% 利用 xx 为 dist 数组赋值,注意输入只存了 0.5*DN(DN-1) 个值,这里将其补成了满矩阵%% 这里不考虑对角线元素for i=1:N ii=xx(i,1); jj=xx(i,2); dist(ii,jj)=xx(i,3); dist(jj,ii)=xx(i,3);end%% 确定 dcpercent=2.0;fprintf('average percentage of neighbours (hard coded): %5.6f\n', percent);position=round(N*percent/100); %% round 是一个四舍五入函数sda=sort(xx(:,3)); %% 对所有距离值作升序排列dc=sda(position);%% 计算局部密度 rho (利用 Gaussian 核)fprintf('Computing Rho with gaussian kernel of radius: %12.6f\n', dc);%% 将每个数据点的 rho 值初始化为零for i=1:ND rho(i)=0.;end% Gaussian kernelfor i=1:ND-1 for j=i+1:ND rho(i)=rho(i)+exp(-(dist(i,j)/dc)*(dist(i,j)/dc)); rho(j)=rho(j)+exp(-(dist(i,j)/dc)*(dist(i,j)/dc)); endend%% "Cut off" kernel%%for i=1:ND-1% for j=i+1:ND% if (dist(i,j)<dc)% rho(i)=rho(i)+1.;% rho(j)=rho(j)+1.;% end% end%end%% 先求矩阵列最大值,再求最大值,最后得到所有距离值中的最大值maxd=max(max(dist));%% 将 rho 按降序排列,ordrho 保持序[rho_sorted,ordrho]=sort(rho,'descend');%% 处理 rho 值最大的数据点delta(ordrho(1))=-1.;nneigh(ordrho(1))=0;%% 生成 delta 和 nneigh 数组for ii=2:ND delta(ordrho(ii))=maxd; for jj=1:ii-1 if(dist(ordrho(ii),ordrho(jj))<delta(ordrho(ii))) delta(ordrho(ii))=dist(ordrho(ii),ordrho(jj)); nneigh(ordrho(ii))=ordrho(jj); % 记录 rho 值更大的数据点中与 ordrho(ii) 距离最近的点的编号 ordrho(jj) end endend%% 生成 rho 值最大数据点的 delta 值delta(ordrho(1))=max(delta(:));%% 决策图disp('Generated file:DECISION GRAPH')disp('column 1:Density')disp('column 2:Delta')fid = fopen('DECISION_GRAPH', 'w');for i=1:ND fprintf(fid, '%6.2f %6.2f\n', rho(i),delta(i));end%% 选择一个围住类中心的矩形disp('Select a rectangle enclosing cluster centers')%% 每台计算机,句柄的根对象只有一个,就是屏幕,它的句柄总是 0%% >> scrsz = get(0,'ScreenSize')%% scrsz =%% 1 1 1280 800%% 1280 和 800 就是你设置的计算机的分辨率,scrsz(4) 就是 800,scrsz(3) 就是 1280scrsz = get(0,'ScreenSize');%% 人为指定一个位置figure('Position',[6 72 scrsz(3)/4. scrsz(4)/1.3]);%% ind 和 gamma 在后面并没有用到for i=1:ND ind(i)=i; gamma(i)=rho(i)*delta(i);end%% 利用 rho 和 delta 画出一个所谓的“决策图”subplot(2,1,1)tt=plot(rho(:),delta(:),'o','MarkerSize',5,'MarkerFaceColor','k','MarkerEdgeColor','k');title ('Decision Graph','FontSize',15.0)xlabel ('\rho')ylabel ('\delta')fig=subplot(2,1,1);rect = getrect(fig);%% getrect 从图中用鼠标截取一个矩形区域, rect 中存放的是%% 矩形左下角的坐标 (x,y) 以及所截矩形的宽度和高度rhomin=rect(1);deltamin=rect(2); %% 作者承认这是个 error,已由 4 改为 2 了!%% 初始化 cluster 个数NCLUST=0;%% cl 为归属标志数组,cl(i)=j 表示第 i 号数据点归属于第 j 个 cluster%% 先统一将 cl 初始化为 -1for i=1:ND cl(i)=-1;end%% 在矩形区域内统计数据点(即聚类中心)的个数for i=1:ND if ( (rho(i)>rhomin) && (delta(i)>deltamin)) NCLUST=NCLUST+1; cl(i)=NCLUST; %% 第 i 号数据点属于第 NCLUST 个 cluster icl(NCLUST)=i; %% 逆映射,第 NCLUST 个 cluster 的中心为第 i 号数据点 endendfprintf('NUMBER OF CLUSTERS: %i \n', NCLUST);disp('Performing assignation')%assignation%% 将其他数据点归类 (assignation)for i=1:ND if (cl(ordrho(i))==-1) cl(ordrho(i))=cl(nneigh(ordrho(i))); endend%halo%% 由于是按照 rho 值从大到小的顺序遍历,循环结束后, cl 应该都变成正的值了. %% 处理光晕点,halo这段代码应该移到 if (NCLUST>1) 内去比较好吧for i=1:ND halo(i)=cl(i);endif (NCLUST>1) % 初始化数组 bord_rho 为 0,每个 cluster 定义一个 bord_rho 值 for i=1:NCLUST bord_rho(i)=0.; end % 获取每一个 cluster 中平均密度的一个界 bord_rho for i=1:ND-1 for j=i+1:ND %% 距离足够小但不属于同一个 cluster 的 i 和 j if ((cl(i)~=cl(j))&& (dist(i,j)<=dc)) rho_aver=(rho(i)+rho(j))/2.; %% 取 i,j 两点的平均局部密度 if (rho_aver>bord_rho(cl(i))) bord_rho(cl(i))=rho_aver; end if (rho_aver>bord_rho(cl(j))) bord_rho(cl(j))=rho_aver; end end end end %% halo 值为 0 表示为 outlier for i=1:ND if (rho(i)<bord_rho(cl(i))) halo(i)=0; end endend%% 逐一处理每个 clusterfor i=1:NCLUST nc=0; %% 用于累计当前 cluster 中数据点的个数 nh=0; %% 用于累计当前 cluster 中核心数据点的个数 for j=1:ND if (cl(j)==i) nc=nc+1; end if (halo(j)==i) nh=nh+1; end end fprintf('CLUSTER: %i CENTER: %i ELEMENTS: %i CORE: %i HALO: %i \n', i,icl(i),nc,nh,nc-nh);endcmap=colormap;for i=1:NCLUST ic=int8((i*64.)/(NCLUST*1.)); subplot(2,1,1) hold on plot(rho(icl(i)),delta(icl(i)),'o','MarkerSize',8,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));endsubplot(2,1,2)disp('Performing 2D nonclassical multidimensional scaling')Y1 = mdscale(dist, 2, 'criterion','metricstress');plot(Y1(:,1),Y1(:,2),'o','MarkerSize',2,'MarkerFaceColor','k','MarkerEdgeColor','k');title ('2D Nonclassical multidimensional scaling','FontSize',15.0)xlabel ('X')ylabel ('Y')for i=1:ND A(i,1)=0.; A(i,2)=0.;endfor i=1:NCLUST nn=0; ic=int8((i*64.)/(NCLUST*1.)); for j=1:ND if (halo(j)==i) nn=nn+1; A(nn,1)=Y1(j,1); A(nn,2)=Y1(j,2); end end hold on plot(A(1:nn,1),A(1:nn,2),'o','MarkerSize',2,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));end%for i=1:ND% if (halo(i)>0)% ic=int8((halo(i)*64.)/(NCLUST*1.));% hold on% plot(Y1(i,1),Y1(i,2),'o','MarkerSize',2,'MarkerFaceColor',cmap(ic,:),'MarkerEdgeColor',cmap(ic,:));% end%endfaa = fopen('CLUSTER_ASSIGNATION', 'w');disp('Generated file:CLUSTER_ASSIGNATION')disp('column 1:element id')disp('column 2:cluster assignation without halo control')disp('column 3:cluster assignation with halo control')for i=1:ND fprintf(faa, '%i %i %i\n',i,cl(i),halo(i));end |
3. 结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | >> cluster_dpThe only input needed is a distance matrix fileThe format of this file should be: Column 1: id of element iColumn 2: id of element jColumn 3: dist(i,j)name of the distance matrix fileexample_distances.datReading input distance matrixaverage percentage of neighbours (hard coded): 2.000000Computing Rho with gaussian kernel of radius: 0.033000Generated file:DECISION GRAPHcolumn 1:Densitycolumn 2:DeltaSelect a rectangle enclosing cluster centersNUMBER OF CLUSTERS: 5 Performing assignationCLUSTER: 1 CENTER: 149 ELEMENTS: 378 CORE: 260 HALO: 118 CLUSTER: 2 CENTER: 451 ELEMENTS: 326 CORE: 250 HALO: 76 CLUSTER: 3 CENTER: 1310 ELEMENTS: 884 CORE: 785 HALO: 99 CLUSTER: 4 CENTER: 1349 ELEMENTS: 297 CORE: 208 HALO: 89 CLUSTER: 5 CENTER: 1579 ELEMENTS: 115 CORE: 115 HALO: 0 Performing 2D nonclassical multidimensional scalingGenerated file:CLUSTER_ASSIGNATIONcolumn 1:element idcolumn 2:cluster assignation without halo controlcolumn 3:cluster assignation with halo control |
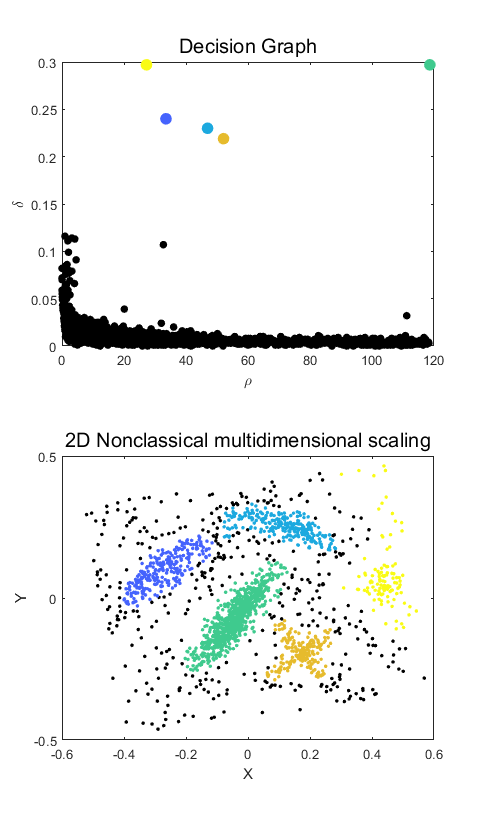
注:出错的话,将Y1 = mdscale(dist, 2, 'criterion','metricstress');换一个准则函数,比如改为Y1 = mdscale(dist, 2, 'criterion','sstress');
4. 参考文献
[1] Rodriguez A, Laio A. Clustering by fast search and find of density peaks [J]. Science, 2014, 344(6191): 1492-1496.
[2] 张宪超. 数据聚类. 北京:科学出版社, 2017.06.
[3] MATLAB程序:Clustering by fast search-and-find of density peaks
[4] 密度峰值聚类算法MATLAB程序



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决