1 什么是Feign
Feign是一种声明式、模板化的HTTP客户端(仅在Application Client中使用)。声明式调用是指,就像调用本地方法一样调用远程方法,无需感知操作远程http请求。
Spring Cloud的声明式调用, 可以做到使用 HTTP请求远程服务时能就像调用本地方法一样的体验,开发者完全感知不到这是远程方法,更感知不到这是个HTTP请求。Feign的应用,让Spring Cloud微服务调用像Dubbo一样,Application Client直接通过接口方法调用Application Service,而不需要通过常规的RestTemplate构造请求再解析返回数据。它解决了让开发者调用远程接口就跟调用本地方法一样,无需关注与远程的交互细节,更无需关注分布式环境开发。
2 使用Feign技术开发时的应用部署结构
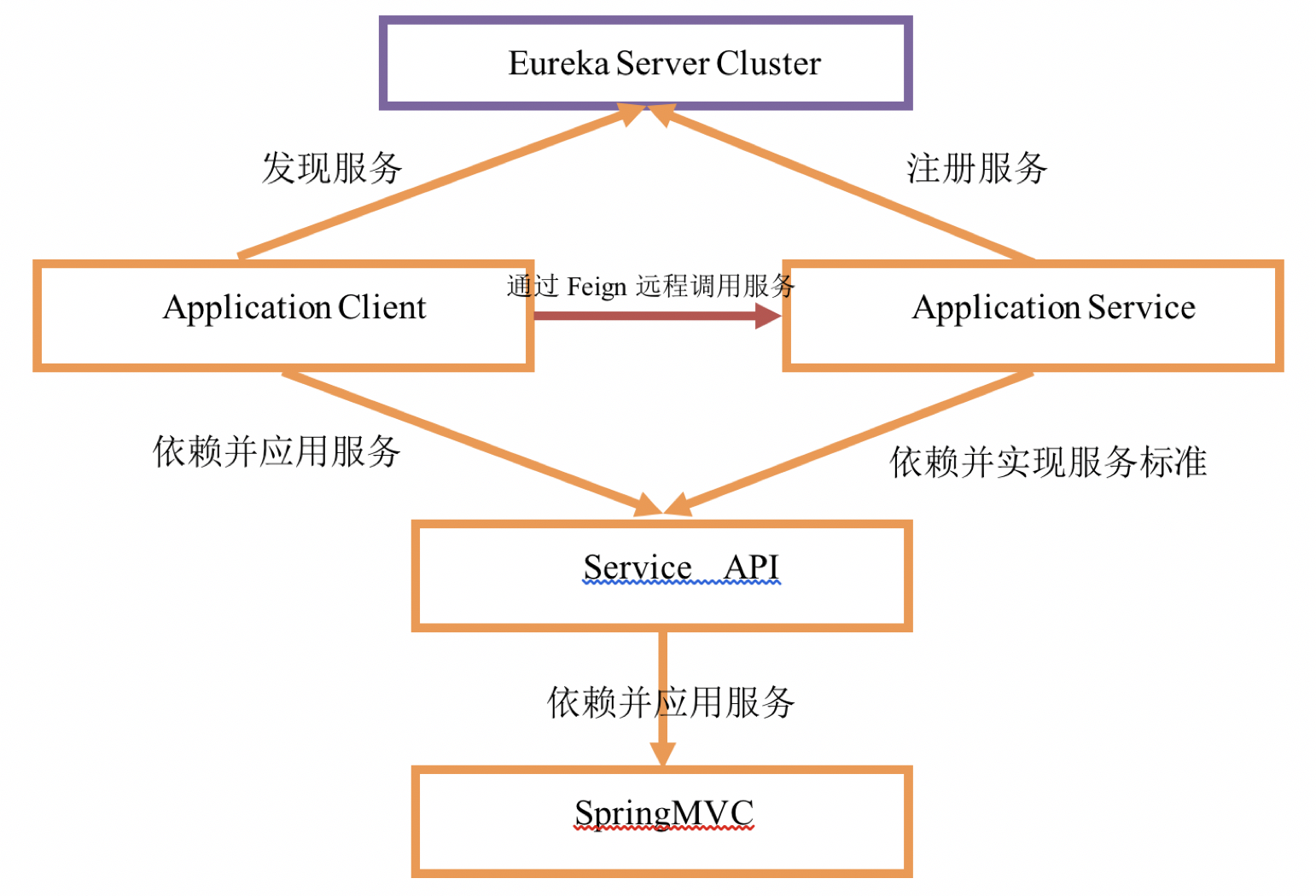
- 在使用Feign技术开发Spring Cloud微服务时,需要先抽取要注册发布的服务标准,将这套标准通过接口的形式定义出来。
- 在Application Service端开发中,依赖抽取的服务标准接口工程,并对接口给予实现。
- 在Application Client端开发中,依赖抽取的服务标准接口工程,并应用接口信息和Feign技术,实现远程服务的调用。
在整体微服务开发中,Eureka Server作为注册中心必不可少,注册中心的作用不变,仍旧是注册和发现服务。
3 Feign入门案例
3.1 创建服务标准工程
服务标准工程,是用于定义Application Service需要对外发布的服务标准接口的工程。这个工程中定义的接口需要使用SpringMVC中的注解来描述,所以工程依赖的资源必须有SpringMVC。在案例中,为了简化依赖复杂度,使用spring-boot中的spring-boot-starter-web资源依赖实现SpringMVC技术的导入。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.16.RELEASE</version> </parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-feign-serviceapi</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- 主要使用其中的SpringMVC相关技术。将请求的URL和服务的方法耦合到一起。 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
定义的服务接口和普通的服务接口没有太大的区别,但是为了让Feign技术可以识别到服务的访问URL,需要使用SpringMVC注解@RequestMapping来描述接口中定义的方法,代表方法对外提供服务时监听的URL路径是什么。
/** * 微服务标准。 * 是Application Service要提供的服务的标准。 * 也是Application Client要调用远程服务的标准。 * 就是一个普通的接口。 */ public interface FirstFeignService { /** * 测试GET请求的方法。 * 请求不传递任何的参数。 * 请求地址是 - /testFeign -> http://ip:port/testFeign * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/testFeign", method=RequestMethod.GET) public List<String> testFeign(); /** * 测试GET请求传递一个普通的参数。 /get?id=xxx * 在为Feign定义服务标准接口的时候,处理请求参数的方法参数,必须使用@RequestParam注解描述。 * 并且,无论方法参数名和请求参数名是否一致,都需要定义@RequestParam注解的value/name属性。 * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/get", method=RequestMethod.GET) public FeignTestPOJO getById(@RequestParam(value="id") Long id); /** * 测试使用POST请求传递一个普通参数 * 在Feign技术中,默认的发起POST请求的时候,请求的参数,都是在请求体中使用JSON数据传递的。 * 不是name=value对传递的。 * 必须使用@RequestBody注解来解析请求体中的数据。 * * 如果使用POST方式发起请求,传递多个普通参数,是使用请求头传递的参数。可以使用@RequestParam注解来处理请求参数。 * POST请求的请求体类型还是application/json。feign会通过请求头传递多个请求参数: /xxx?a=xxx&b=xxx&c=xxx * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/get", method=RequestMethod.POST) public FeignTestPOJO getByIdWithPOST(@RequestBody Long id); /** * 使用GET请求传递多个普通参数。 /add?id=xxx&name=xxx * 必须使用@RequestParam注解处理请求参数。 * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/add", method=RequestMethod.GET) public FeignTestPOJO add(@RequestParam("id") Long id, @RequestParam("name") String name); /** * 错误案例 * 使用GET请求传递特殊参数。自定义类型的参数。 * 在Feign发起的默认的请求中,GET请求方式不能传递自定义类型数据。只能通过POST请求传递。 * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/addWithGET", method=RequestMethod.GET) public FeignTestPOJO add(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo); /** * 使用POST请求传递特殊参数。自定义类型的参数。 * 默认环境中,只要是Feign发起的POST请求,请求参数都是JSON数据。 * 必须使用@RequestBody处理。 * @return */ @RequestMapping(value="/addWithPOST", method=RequestMethod.POST) public FeignTestPOJO addWithPOST(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo); }
3.2 创建Application Service工程
服务提供者在开发的时候,需要实现服务标准工程中定义的服务接口,并注册服务到Eureka Server注册中心上,所以需要依赖的资源必须有eureka和服务标准接口。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.16.RELEASE</version> </parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-feign-appservice</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Edgware.SR4</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <!-- web启动器。 springmvc相关内容 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud 默认配置启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud Eureka Client 启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 自定义的服务标准工程。 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-feign-serviceapi</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
在Spring Cloud微服务架构中,服务是由Controller对外提供的,是基于HTTP协议发布的REST服务。所以实现服务接口的是控制器。注意,服务不代表服务层代码。
/** * 自定义的服务控制器 * 对外提供服务的Application Service。 * 不能随便的定义服务了。如果想让Application Client可以通过Feign技术访问当前类型提供的服务, * 则必须遵循服务标准。 */ @RestController public class TestFeignAppServiceController implements FirstFeignService { /** * 因为当前的方法都是实现接口FirstFeignService中的方法。 * 而在接口中,已经将请求URL和方法耦合到一起了。 * 所以在当前的控制器中,不能重复定义@RequestMapping来约束请求URL。 */ @Override public List<String> testFeign() { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); result.add("test feign"); result.add("this is first spring cloud with feign"); return result; } @Override public FeignTestPOJO getById(Long id) { return new FeignTestPOJO(id, "getById"); } /** * 如果方法参数是处理POST请求的JSON数据的。 * 那么还是需要定义@RequestBody注解来描述方法参数的。 */ @Override public FeignTestPOJO getByIdWithPOST(@RequestBody Long id) { return new FeignTestPOJO(id, "getByIdWithPOST"); } @Override public FeignTestPOJO add(Long id, String name) { System.out.println( "add(Long id, String name)" ); return new FeignTestPOJO(id, name); } /** * 在默认的情况下,Feign不能通过GET请求传递自定义类型的请求参数。 */ @Override public FeignTestPOJO add(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo) { System.out.println( "add(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo)" ); return pojo; } @Override public FeignTestPOJO addWithPOST(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo) { System.out.println( "addWithPOST(@RequestBody FeignTestPOJO pojo)" ); return pojo; } }
3.3 创建Application Client工程
服务消费者在开发的时候,需要在Eureka Server中发现可用服务,并通过Feign来实现远程服务调用。在这个过程中,需要依赖于服务标准工程中定义的服务接口。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.16.RELEASE</version> </parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-feign-appclient</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>Edgware.SR4</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud 默认配置启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- spring cloud Eureka Client 启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- feign启动器。封装了所有的feign相关资源的jar包。提供的是默认环境。 feign技术在请求远程服务的时候,依托于http协议。 默认底层使用JDK提供的HttpUrlConnection来实现http远程访问的。 httpurlconnection技术不支持http连接池。所以效率上较低。 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 服务标准工程。 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-feign-serviceapi</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
启动器:
/** * @EnableFeignClients - 启动FeignClient技术。 * 开启Feign的应用。 * * @EnableDiscoveryClient - 启动发现机制。 * 就是辅助Feign技术,发现服务,定义服务动态代理的辅助技术。 * * @EnableEurekaClient 注解删除。是使用Discovery来发现服务的。discovery是辅助feign技术的一个发现客户端。 */ @EnableFeignClients @EnableDiscoveryClient @SpringBootApplication public class FeignApplicationClientApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(FeignApplicationClientApplication.class, args); } }
在通过Feign来实现远程服务调用时,需要提供一个本地接口来继承服务标准工程提供的服务接口。这个本地接口不需要给予任何实现,在底层Spring容器会为这个接口提供一个基于JDK实现的代理对象,这个代理对象由Feign技术提供具体的HandlerInterceptor逻辑,实现远程的调用。实现过程类似通过代码调用LoadBalancerClient实现的Rest远程访问。
而本地接口继承服务标准接口后,需要提供注解@FeignClient,注解的属性name代表当前接口要调用的远程服务的应用命名。
/** * 本地接口,继承服务标准接口。 * 在接口上增加注解@FeignClient,代表当前接口是一个Feign技术中的客户端。 * 需要发起远程的http请求。 * 注解有属性name - 代表当前的FeignClient在请求application service的时候,是调用哪一个服务? * 所谓的哪一个服务,就是application service全局配置文件中的spring.application.name属性值。 */ @FeignClient(name="test-feign-application-service") public interface FirstClientFeignService extends FirstFeignService { }
控制器中可以像调用本地定义服务对象那样来调用远程服务。
/** * Application Client中的控制器。是和用户直接交互的控制器。 * 像平时开发代码一样。调用本地的一个service接口。通过service接口远程访问Application Service。 */ @RestController public class TestFeignAppClientController { /** * 本地定义的服务接口。用于实现远程调用application service的接口。 */ @Autowired private FirstClientFeignService service; /** * 无参 * @return */ @GetMapping("/testFeign") public List<String> testFeign(){ System.out.println(this.service.getClass().getName()); return this.service.testFeign(); } }
4 参数处理
在Feign处理远程服务调用时,传递参数是通过HTTP协议传递的,参数存在的位置是请求头或请求体中。请求头传递的参数必须依赖@RequestParam注解来处理请求参数,请求体传递的参数必须依赖@RequestBody注解来处理请求参数。
上述的要求是指Feign技术传递参数,也就是Application Client远程调用Application Service过程。
4.1 处理请求头传参
使用请求头传递参数时,定义的服务标准接口中,必须使用@RequestParam注解来描述方法参数,且注解属性value/name必须指定,代表从请求头中获取的请求参数命名是什么。
在默认环境中,使用请求头传递参数时,Application Service中的控制器无法使用SpringMVC中的自动对象封装能力。只能处理简单数据类型。如:数学类型,字符串类型,数组类型等。无法处理自定义对象类型。
4.2 处理请求体传参
使用请求体传递参数时,定义的服务标准接口中,必须使用@RequestBody注解来描述方法参数,因为Feign技术发起的POST请求,请求参数是使用JSON字符串来传递的,且form表单类型为RAW。
使用请求体传递参数时,Application Service中的控制器必须使用@RequestBody注解来描述方法参数,且RAW类型的form表单上传的是一个文本内容,只能转换为唯一的一个参数。
如果使用POST方式提交请求,并传递多个普通类型的参数时,Feign不会通过请求体传递参数,是通过请求头传递的参数。也就是请求路径为 : http://applicationserver:port/url?paramName=paramValue。
5 Feign通讯优化:GZIP压缩
5.1 GZIP简介
gzip介绍:gzip是一种数据格式,采用deflate算法压缩数据;gzip是一种流行的数据压缩算法,应用十分广泛,尤其是在Linux平台。
gzip能力:当Gzip压缩到一个纯文本数据时,效果是非常明显的,大约可以减少70%以上的数据大小。
gzip作用:网络数据经过压缩后实际上降低了网络传输的字节数,最明显的好处就是可以加快网页加载的速度。网页加载速度加快的好处不言而喻,除了节省流量,改善用户的浏览体验外,另一个潜在的好处是Gzip与搜索引擎的抓取工具有着更好的关系。例如 Google就可以通过直接读取gzip文件来比普通手工抓取更快地检索网页。
5.2 HTTP协议中关于压缩传输的规定

如图所示:
第一:客户端向服务器请求头中带有:Accept-Encoding:gzip, deflate 字段,向服务器表示,客户端支持的压缩格式(gzip或者deflate),如果不发送该消息头,服务器是不会压缩的。
第二:服务端在收到请求之后,如果发现请求头中含有Accept-Encoding字段,并且支持该类型的压缩,就对响应报文压缩之后返回给客户端,并且携带Content-Encoding:gzip消息头,表示响应报文是根据该格式压缩过的。
第三:客户端接收到响应之后,先判断是否有Content-Encoding消息头,如果有,按该格式解压报文。否则按正常报文处理。
5.3 在Feign技术中应用GZIP压缩
在Spring Cloud微服务体系中,一次请求的完整流程如下:
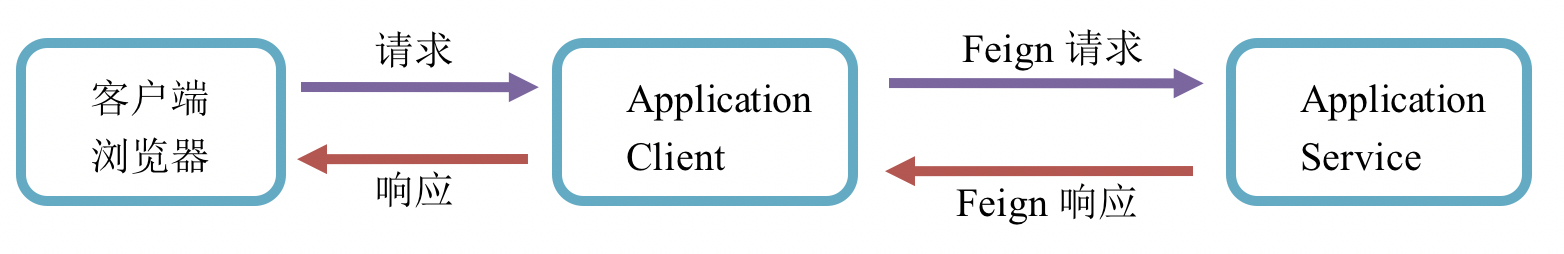
在整体流程中,如果使用GZIP压缩来传输数据,涉及到两次请求-应答。而这两次请求-应答的连接点是Application Client,那么我们需要在Application Client中配置开启GZIP压缩,来实现压缩数据传输。
5.3.1 只配置Feign请求-应答的GZIP压缩
这里只开启Feign请求-应答过程中的GZIP,也就是浏览器-Application Client之间的请求应答不开启GZIP压缩。在全局配置文件中,使用下述配置来实现Feign请求-应答的GZIP压缩:
# feign gzip
# 局部配置。只配置feign技术相关的http请求-应答中的gzip压缩。
# 配置的是application client和application service之间通讯是否使用gzip做数据压缩。
# 和浏览器到application client之间的通讯无关。
# 开启feign请求时的压缩, application client -> application service
feign.compression.request.enabled=true
# 开启feign技术响应时的压缩, application service -> application client
feign.compression.response.enabled=true
# 设置可以压缩的请求/响应的类型。
feign.compression.request.mime-types=text/xml,application/xml,application/json
# 当请求的数据容量达到多少的时候,使用压缩。默认是2048字节。
feign.compression.request.min-request-size=512
5.3.2 配置全局的GZIP压缩
在全局配置文件中配置下述内容,来开启所有请求-应答中的GZIP压缩,这里使用的是Spring Boot中的GZIP技术。在Spring Boot中已经集成了GZIP压缩技术,并对所有的请求-应答实现GZIP数据压缩。Spring Cloud中已经集成了Spring Boot技术,所以在配置文件中可以开启Spring Boot中的GZIP压缩技术,对完整流程中与当前节点(Application Client)所有相关的请求-应答开启GZIP压缩。
# spring boot gzip
# 开启spring boot中的gzip压缩。就是针对和当前应用所有相关的http请求-应答的gzip压缩。
server.compression.enabled=true
# 哪些客户端发出的请求不压缩,默认是不限制
server.compression.excluded-user-agents=gozilla,traviata
# 配置想压缩的请求/应答数据类型,默认是 text/html,text/xml,text/plain
server.compression.mime-types=application/json,application/xml,text/html,text/xml,text/plain
# 执行压缩的阈值,默认为2048
server.compression.min-response-size=512
6 Feign的通讯优化:HttpClient客户端替换及HTTP连接池
两台服务器建立HTTP连接的过程是很复杂的一个过程,涉及到多个数据包的交换,并且也很耗时间。HTTP连接需要的3次握手4次挥手开销很大,这一开销对于大量的比较小的HTTP消息来说更大。
那么如何来优化HTTP连接性能?我们可以采用HTTP连接池来提升性能,连接池可以节约大量的3次握手4次挥手的时间,这样能大大提升吞吐率。
6.1 Feign技术的底层实现
Feign的HTTP客户端支持3种框架,分别是;HttpURLConnection、HttpClient、OKHttp。Feign中默认使用HttpURLConnection。
HttpURLConnection是JDK自带的HTTP客户端技术,并不支持连接池,如果要实现连接池的机制,还需要自己来管理连接对象。对于网络请求这种底层相对复杂的操作,如果有可用的其他方案,也没有必要自己去管理连接对象。
Apache提供的HttpClient框架相比传统JDK自带的HttpURLConnection,它封装了访问http的请求头,参数,内容体,响应等等;它不仅使客户端发送HTTP请求变得容易,而且也方便了开发人员测试接口(基于Http协议的),即提高了开发的效率,也方便提高代码的健壮性;另外高并发大量的请求网络的时候,还是用“HTTP连接池”提升吞吐量。
OKHttp是一个处理网络请求的开源项目,是安卓端最火热的轻量级框架,由移动支付Square公司贡献用于替代HttpUrlConnection和Apache HttpClient。OKHttp拥有共享Socket,减少对服务器的请求次数,通过连接池,减少了请求延迟等技术特点。
本案例中,通过替换Feign底层的HTTP客户端实现为HttpClient,来提升Feign的通讯性能。
6.2 Feign中应用HttpClient
资源依赖:Feign技术发起请求的位置是Application Client端,下述依赖只需要在Application Client所在工程中添加即可。
<!-- httpclient相关依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.github.openfeign</groupId> <artifactId>feign-httpclient</artifactId> </dependency>
修改全局配置文件:
# 开启feign技术对底层httpclient的依赖。 切换底层实现技术。
feign.httpclient.enabled=true
提供连接池配置类:
/** * 配置类型 * 用于提供一个HTTP连接池,并实现连接池管理。 * 主要目的是,提供一个合理的资源回收方式。 */ @Configuration public class HttpClientConfiguration { @Bean public HttpClient httpClient(){ System.out.println("init feign httpclient configuration " ); // 生成默认请求配置 RequestConfig.Builder requestConfigBuilder = RequestConfig.custom(); // 超时时间 requestConfigBuilder.setSocketTimeout(5 * 1000); // 连接时间 requestConfigBuilder.setConnectTimeout(5 * 1000); RequestConfig defaultRequestConfig = requestConfigBuilder.build(); // 连接池配置 // 长连接保持30秒 final PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager pollingConnectionManager = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager(30, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 总连接数 pollingConnectionManager.setMaxTotal(5000); // 同路由的并发数 pollingConnectionManager.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(100); // httpclient 配置 HttpClientBuilder httpClientBuilder = HttpClientBuilder.create(); // 保持长连接配置,需要在头添加Keep-Alive httpClientBuilder.setKeepAliveStrategy(new DefaultConnectionKeepAliveStrategy()); httpClientBuilder.setConnectionManager(pollingConnectionManager); httpClientBuilder.setDefaultRequestConfig(defaultRequestConfig); HttpClient client = httpClientBuilder.build(); // 启动定时器,定时回收过期的连接, 最重要。 如果没有定义回收策略。连接池会在运行一段时间后失效。 Timer timer = new Timer(); timer.schedule(new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { pollingConnectionManager.closeExpiredConnections(); pollingConnectionManager.closeIdleConnections(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } }, 10 * 1000, 5 * 1000); System.out.println("===== Apache httpclient 初始化连接池==="); return client; } }
使用HttpClient客户端替换HttpURLConnection,仅需修改Application Client,其余无需修改。当使用HttpClient技术作为Feign的底层HTTP技术应用时,使用GET请求方式请求头传递自定义类型对象是可行的,只要在服务标准对象中定义的方法参数上增加注解@RequestBody即可处理。
7 配置Feign中的请求超时
请求超时/请求时间: 客户端发起请求,服务端响应并成功建立双向链接的时间。
链接超时/链接时间: 双向链接建立成功后,需要多久必须得到服务端的响应结果。
在Feign声明式远程调用中,负载均衡还是使用的Ribbon技术。而Ribbon技术默认的链接超时是1秒,也就是1秒内Application Service没有处理Application Client的请求,且链接请求处理后,1秒之内没有返回响应,Application Client都会抛出超时异常。在商业项目中,部分服务是很难在1秒之内处理链接,并在处理链接后1秒之内返回响应的,所以配置超时信息就很有必要了。
定义超时配置的时候,建议为每个服务定义超时策略。如果有部分服务可以使用同样的超时策略,可以使用全局配置。指定服务配置超时策略,会覆盖全局配置。
超时策略的使用优先级: 指定服务的超时策略 -> 全局配置的超时策略 -> 默认的超时策略。
对Ribbon链接超时的配置都在全局配置文件中定义。具体如下。
7.1 全局服务配置
全局服务配置粒度粗糙。商业项目中不同的服务对响应时长的限制也不同,全局服务配置不推荐应用。
# 全局服务配置
# 请求连接的超时时间 默认的时间为1秒
ribbon.ConnectTimeout=1000
# 请求处理的超时时间
ribbon.ReadTimeout=5000
7.2 部分服务配置
部分服务配置粒度细致,可以为每个具体服务配置不同的超时信息,推荐使用。
# 部分服务配置 服务名.ribbon.属性=属性值
# 对所有操作请求都进行重试
spring-cloud-feign-appservice.ribbon.OkToRetryOnAllOperations=true
# 对当前实例的重试次数
spring-cloud-feign-appservice.ribbon.MaxAutoRetries=2
# 请求连接的超时时间
spring-cloud-feign-appservice.ribbon.ConnectTimeout=3000
# 请求处理的超时时间
spring-cloud-feign-appservice.ribbon.ReadTimeout=3000



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号