Hadoop基础-07-MapReduce概述
源码见:https://github.com/hiszm/hadoop-train
MapReduce概述
是一个分布式计算框架 ,用于编写批处理应用程序。编写好的程序可以提交到 Hadoop 集群上用于并行处理大规模的数据集。MapReduce 作业通过将输入的数据集拆分为独立的块,这些块由
map以 并行 的方式处理,框架对map的输出进行排序,然后输入到reduce中
- 源自于Google的MapReduce论文 ,论文发表于2004年12月
- Hadoop MapReduce是Google MapReduce的克隆版
- MapReduce优点:海量数据离线处理&易开发&易运行
- MapReduce缺点:实时流式计算
MapReduce编程模型
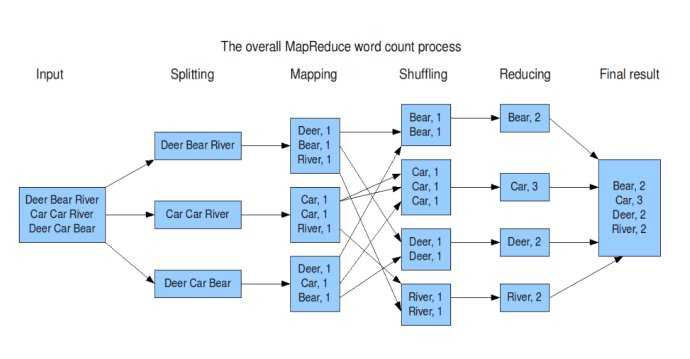
我们编程主要关注的是如何Splitting和如何Reduce
MapReduce 框架专门用于 <key,value> 键值对处理,它将作业的输入视为一组 <key,value> 对,并生成一组 <key,value> 对作为输出。
MapReduce将作业拆分成Map阶段和Reduce阶段
-
input : 读取文本文件;
-
splitting : 将文件按照行进行拆分,此时得到的
K1行数,V1表示对应行的文本内容; -
mapping : 并行将每一行按照空格进行拆分,拆分得到的
List(K2,V2),其中K2代表每一个单词,由于是做词频统计,所以V2的值为 1,代表出现 1 次; -
shuffling:由于
Mapping操作可能是在不同的机器上并行处理的,所以需要通过shuffling将相同key值的数据分发到同一个节点上去合并,这样才能统计出最终的结果,此时得到K2为每一个单词,List(V2)为可迭代集合,V2就是 Mapping 中的 V2; -
Reducing : 这里的案例是统计单词出现的总次数,所以
Reducing对List(V2)进行归约求和操作,最终输出。
(input) <k1, v1> -> map -> <k2, v2> -> combine -> <k2, v2> -> reduce -> <k3, v3> (output)
Mapper
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience.Public;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability.Stable;
@Public
@Stable
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
public Mapper() {
}
protected void setup(Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value, Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, value);
}
protected void cleanup(Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
public void run(Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
this.setup(context);
try {
while(context.nextKeyValue()) {
this.map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
this.cleanup(context);
}
}
public abstract class Context implements MapContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
public Context() {
}
}
}
Reducer
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Iterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience.Public;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability.Stable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.ReduceContext.ValueIterator;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.annotation.Checkpointable;
@Checkpointable
@Public
@Stable
public class Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
public Reducer() {
}
protected void setup(Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
protected void reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Iterator i$ = values.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
VALUEIN value = i$.next();
context.write(key, value);
}
}
protected void cleanup(Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
public void run(Reducer<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
this.setup(context);
try {
while(context.nextKey()) {
this.reduce(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getValues(), context);
Iterator<VALUEIN> iter = context.getValues().iterator();
if (iter instanceof ValueIterator) {
((ValueIterator)iter).resetBackupStore();
}
}
} finally {
this.cleanup(context);
}
}
public abstract class Context implements ReduceContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
public Context() {
}
}
}
MapReduce编程模型之执行步骤
- 准备map处理的输入数据
- Mapper处理
- Shuffle
- Reduce
- 输出结果
MapReduce编程模型之核心概念
- Split
- InputFormat
- OutputFormat
- Combiner
- Partitioner

|
🐳 作者:hiszm 📢 版权:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,万分感谢。 💬 留言:同时 , 如果文中有什么错误,欢迎指出。以免更多的人被误导。 |
 |


