cifar10数据集
CIFAR-10 是由 Hinton 的学生 Alex Krizhevsky 和 Ilya Sutskever 整理的一个用于识别普适物体的小型数据集。一共包含 10 个类别的 RGB 彩色图片 :飞机( airplane )、汽车( automobile )、鸟类( bird )、猫( cat )、鹿( deer )、 狗( dog )、蛙类( frog )、马( horse )、船( ship )和卡车( truck )。图片的尺寸为 32 × 32 ,数据集中一共有 50000 张训练图片和 10000 张测试图片。本文训练过程可见官方示例:https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/images/deep_cnn
下载脚本内容如下:
# coding:utf-8 import tensorflow as tf from six.moves import urllib import os import sys import tarfile # tf.app.flags.FLAGS是TensorFlow内部的一个全局变量存储器,同时可以用于命令行参数的处理 FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS # 定义tf.app.flags.FLAGS.data_dir为CIFAR-10的数据路径 tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_data', """Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.""") # 我们把这个路径改为cifar10_data FLAGS.data_dir = 'cifar10_data/' DATA_URL = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz' # 如果不存在数据文件,就会执行下载 def maybe_download_and_extract(): """Download and extract the tarball from Alex's website.""" dest_directory = FLAGS.data_dir if not os.path.exists(dest_directory): os.makedirs(dest_directory) filename = DATA_URL.split('/')[-1] filepath = os.path.join(dest_directory, filename) if not os.path.exists(filepath): def _progress(count, block_size, total_size): sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' % (filename,float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0)) sys.stdout.flush() filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(DATA_URL, filepath, _progress) print() statinfo = os.stat(filepath) print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.') extracted_dir_path = os.path.join(dest_directory, 'cifar-10-batches-bin') if not os.path.exists(extracted_dir_path): tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dest_directory) if __name__=='__main__': maybe_download_and_extract()
 txt文本文件中存储了每个类别的英文名称,每个bin文件有1w张图像
txt文本文件中存储了每个类别的英文名称,每个bin文件有1w张图像
数据读取
TensorFlow程序读取数据方式可查看官方中文文档:http://tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/how_tos/reading_data.html
一般情况是将数据读入内存,再交由GPU或CPU进行运算。假设读入用时0.1s ,计算用时 0.9s ,那么就意昧着每过1s, GPU 都会有0.1s无事可做,这大大降低了运算的效率。
解决方法: 将读入数据和计算分别放在两个线程中,将数据读入内存的一个队列
读取线程源源不断地将文件系统中的图片读入一个内存的队列中,而负责计算的是另一个线程,计算需要数据肘,直接从内存队列中取就可以了 。这样可以解决 GPU 因为 I/O而空闲的问题!
在机器学习中有个概念:epoch。一次epoch相当于将整个训练集中的图片计算一次,考虑到epoch的情况,在内存队列前添加了“文件名队列”
TensorFlow 使用“文件名队列+内存队列”双队列的形式读入文件 ,可以很好地管理 epoch 。
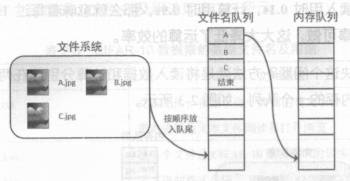 以A,B,C三张图片,epoch=1为例展示,内存队列会从文件名队列中取
以A,B,C三张图片,epoch=1为例展示,内存队列会从文件名队列中取
- 文件名队列:tf.train.string_input_producer 传入文件列表[A.jpg, B.jpg, C.jpg],两个重要参数num_epochs(相当于epoch),shuffle(一个epoch进文件名队列是否打乱,默认为True)
- 内存队列:无须自己建立,使用reader对象从文件名队列中读取即可
- 真正执行:tf.train.start_ queue_runners 只有运行完此步,才会向文件名队列中装东西,启动填充队列的线程
测试代码如下:
# coding:utf-8 import os if not os.path.exists('read'): os.makedirs('read/') # 导入TensorFlow import tensorflow as tf # 新建一个Session with tf.Session() as sess: # 我们要读三幅图片A.jpg, B.jpg, C.jpg filename = ['A.jpg', 'B.jpg', 'C.jpg'] # string_input_producer会产生一个文件名队列 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filename, shuffle=False, num_epochs=5) # reader从文件名队列中读数据。对应的方法是reader.read reader = tf.WholeFileReader() key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) # tf.train.string_input_producer定义了一个epoch变量,要对它进行初始化 tf.local_variables_initializer().run() # 使用start_queue_runners之后,才会开始填充队列 threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) i = 0 while True: i += 1 # 获取图片数据并保存 image_data = sess.run(value) with open('read/test_%d.jpg' % i, 'wb') as f: f.write(image_data) # 程序最后会抛出一个OutOfRangeError,这是epoch跑完,队列关闭的标志
运行结果:

2018-10-30 16:28:09.015742: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:137] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 26, in <module> image_data = sess.run(value) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 889, in run run_metadata_ptr) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1120, in _run feed_dict_tensor, options, run_metadata) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1317, in _do_run [root@node5 chapter_02]# python test.py 2018-10-30 16:28:27.836579: I tensorflow/core/platform/cpu_feature_guard.cc:137] Your CPU supports ins tructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AVX AVX2 FMA Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 26, in <module> image_data = sess.run(value) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 889, in run run_metadata_ptr) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1120, in _run feed_dict_tensor, options, run_metadata) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1317, in _do_run options, run_metadata) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/client/session.py", line 1336, in _do_call raise type(e)(node_def, op, message)tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.OutOfRangeError: FIFOQueue '_0_input_producer' is closed and h as insufficient elements (requested 1, current size 0) [[Node: ReaderReadV2 = ReaderReadV2[_device="/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0"](WholeFileReaderV2, input_producer)]] Caused by op u'ReaderReadV2', defined at: File "test.py", line 17, in <module> key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/io_ops.py", line 195, in read return gen_io_ops._reader_read_v2(self._reader_ref, queue_ref, name=name) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/gen_io_ops.py", line 673, in _reader_read_v2 queue_handle=queue_handle, name=name) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/op_def_library.py", line 787, in _apply_op_helper op_def=op_def) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/ops.py", line 2956, in create_op op_def=op_def) File "/usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/framework/ops.py", line 1470, in __init__ self._traceback = self._graph._extract_stack() # pylint: disable=protected-access OutOfRangeError (see above for traceback): FIFOQueue '_0_input_producer' is closed and has insufficient elements (requested 1, current size 0) [[Node: ReaderReadV2 = ReaderReadV2[_device="/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0"](WholeFileReaderV2, input_producer)]]
保存为图片
一个样本由 3073 个字节组成,第一个字节为标签( label ),剩下 3072 个字节为图像数据。样本和样本之间没有多余的字节分割,因此这几个二进制文件的大小都是 30730000 字节 。
如何用 TensorFlow 读取 CIFAR-10 数据呢?
- 第一步,用 tf.train.string_input_producer 建立队列。
- 第二步,通过 reader.read 读数据。在之前例子中,一个文件就是一张图片,因此用的 reader 是 tf.WholeFileReader()。CIFAR-10 数据是以固定字节存在文件中的,一个文件中含有多个样本。因此不能使用 tf.WholeFileReader(),而是用 tf.FixedLengthRecordReader()。
- 第三步,调用 tf.train.start_queue_runners。
- 最后,通过 sess.run()取出图片结果。
#coding: utf-8 import tensorflow as tf import os import scipy.misc # 从queue中读取文件 def read_cifar10(filename_queue): """Reads and parses examples from CIFAR10 data files. Recommendation: if you want N-way read parallelism, call this function N times. This will give you N independent Readers reading different files & positions within those files, which will give better mixing of examples. Args: filename_queue: A queue of strings with the filenames to read from. Returns: An object representing a single example, with the following fields: height: number of rows in the result (32) width: number of columns in the result (32) depth: number of color channels in the result (3) key: a scalar string Tensor describing the filename & record number for this example. label: an int32 Tensor with the label in the range 0..9. uint8image: a [height, width, depth] uint8 Tensor with the image data """ class CIFAR10Record(object): pass result = CIFAR10Record() label_bytes = 1 # 2 for CIFAR-100 result.height = 32 result.width = 32 result.depth = 3 image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth # Every record consists of a label followed by the image, with a fixed number of bytes for each. record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes # Read a record, getting filenames from the filename_queue.
# No header or footer in the CIFAR-10 format, so we leave header_bytes and footer_bytes at their default of 0. reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes) result.key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) # Convert from a string to a vector of uint8 that is record_bytes long. record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) # The first bytes represent the label, which we convert from uint8->int32. result.label = tf.cast(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32) # The remaining bytes after the label represent the image, which we reshape # from [depth * height * width] to [depth, height, width]. depth_major = tf.reshape(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes],[label_bytes + image_bytes]), [result.depth, result.height, result.width]) # Convert from [depth, height, width] to [height, width, depth]. result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0]) return result def inputs_origin(data_dir): # filenames一共5个,从data_batch_1.bin到data_batch_5.bin # 读入的都是训练图像 filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i) for i in xrange(1, 6)] # 判断文件是否存在 for f in filenames: if not tf.gfile.Exists(f): raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f) # 将文件名的list包装成TensorFlow中queue的形式 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames) # 返回的结果read_input的属性uint8image就是图像的Tensor read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue) # 将图片转换为实数形式 reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32) # 返回的reshaped_image是一张图片的tensor # 我们应当这样理解reshaped_image:每次使用sess.run(reshaped_image),就会取出一张图片 return reshaped_image if __name__ == '__main__': # 创建一个会话sess, # 为什么不能用with tf.Session() as sess, 解答https://blog.csdn.net/chengqiuming/article/details/80293220 sess = tf.Session() # 调用inputs_origin。cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin是我们下载的数据的文件夹位置 reshaped_image = inputs_origin('cifar10_data/cifar-10-batches-bin') # 这一步start_queue_runner很重要。 # 我们之前有filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames) # 这个queue必须通过start_queue_runners才能启动 缺少start_queue_runners程序将不能执行 threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # 变量初始化 sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 创建文件夹cifar10_data/raw/ if not os.path.exists('cifar10_data/raw/'): os.makedirs('cifar10_data/raw/') # 保存30张图片 for i in range(30): # 每次sess.run(reshaped_image),都会取出一张图片 image_array = sess.run(reshaped_image) # 将图片保存 scipy.misc.toimage(image_array).save('cifar10_data/raw/%d.jpg' % i)
数据增强
对于图像类型的训练、数据,所谓的数据增强( Data Augmentation )方法是指利用平移 、 缩放、颜色等变躁,人工增大训练集样本的个数,从而获得更充足的训练数据,使模型训练的效果更好 。
常用的图像数据增强的方法如下。
- 平移 :将图像在一定尺度范围内平移。
- 旋转:将图像在一定角度范围内旋转。
- 翻转 :水平翻转或上下翻转图像。
- 裁剪 :在原有图像上裁剪出一块。
- 缩放 :将图像在一定尺度内放大或缩小。
- 颜色变换:对图像的 RGB 颜色空间进行一些变换。
- 噪声扰动:给图像加入一些人工生成的噪声。
使用数据增强方法的前提是,这些数据增强方法不会改变图像的原有标签。
# 随机剪裁图片,从32*32到24*24 distorted_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [height, width, 3]) # 随机翻转图片,每张图片有50%的概率被水平左右翻转,另有50%的概率保持不变 distorted_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(distorted_image) # 随机改变亮度和对比度 distorted_image = tf.image.random_brightness(distorted_image, max_delta=63) distorted_image = tf.image.random_contrast(distorted_image,lower=0.2, upper=1.8)
原始的训练图片是 reshaped_image。最后会得到一个数据增强后的训练样本 distorted_image 。训练时,直接使用 distorted_image 进行训练即可。
训练
代码逻辑如下:
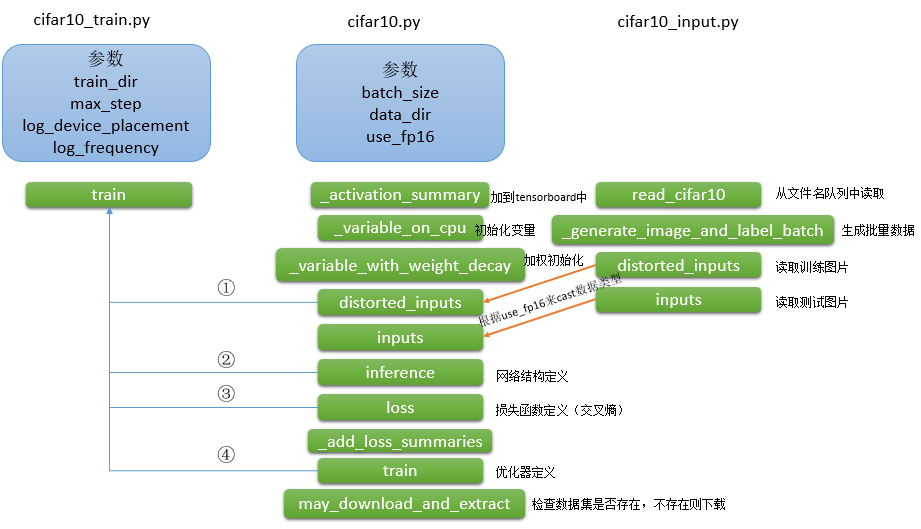
cifar10_input.py
该文件中包含三个和训练过程相关的函数: read_cifar10, _generate_image_and_label_batch, distorted_inputs三个函数,下面依次来看函数的实现
文件头的定义
#encoding=utf-8 from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function import os from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin import tensorflow as tf # 注意此处不是原图的size 32*32,因为后续会做剪裁,如果修改了此值,整个模型架构会被改变需要重新训练整个模型 IMAGE_SIZE = 24 # 全局常量 NUM_CLASSES = 10 NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = 50000 NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = 10000
read_cifar10
从文件名队列中取图片,一次运行取到一张

def read_cifar10(filename_queue): ''' 从文件名队列中按字节读取图像数据 返回值:一个对象 height,width,depth,key(filename),label(an int32 Tensor),uint8image(a [height, width, depth] uint8 Tensor with the image data) 建议:if you want N-way read parallelism, call this function N times. This will give you N independent Readers reading different files & positions within those files, which will give better mixing of examples. ''' class CIFAR10Record(object): pass result = CIFAR10Record() # CIFAR-10数据集中图片的各维. 详情见 http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html label_bytes = 1 # 2 for CIFAR-100 result.height = 32 result.width = 32 result.depth = 3 image_bytes = result.height * result.width * result.depth # 每条记录的构成是<label><image> record_bytes = label_bytes + image_bytes # 读取固定字节的内容,key是文件名,value中包含label和image reader = tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes=record_bytes) result.key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) # 编码转换 Convert from a string to a vector of uint8 that is record_bytes long. record_bytes = tf.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) # 第一个/第二个字节表示label, 并做转换 uint8->int32. result.label = tf.cast(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [0], [label_bytes]), tf.int32) # 标签字节后面是图像相关字节[depth * height * width]重塑成[depth, height, width]. depth_major = tf.reshape(tf.strided_slice(record_bytes, [label_bytes], [label_bytes + image_bytes]), [result.depth, result.height, result.width]) # 转置 Convert from [depth, height, width] to [height, width, depth]. result.uint8image = tf.transpose(depth_major, [1, 2, 0]) return result
涉及不熟悉的tf操作:
- tf.decode_raw:https://blog.csdn.net/u012571510/article/details/82112452
- tf.strided_slice:https://blog.csdn.net/banana1006034246/article/details/75092388
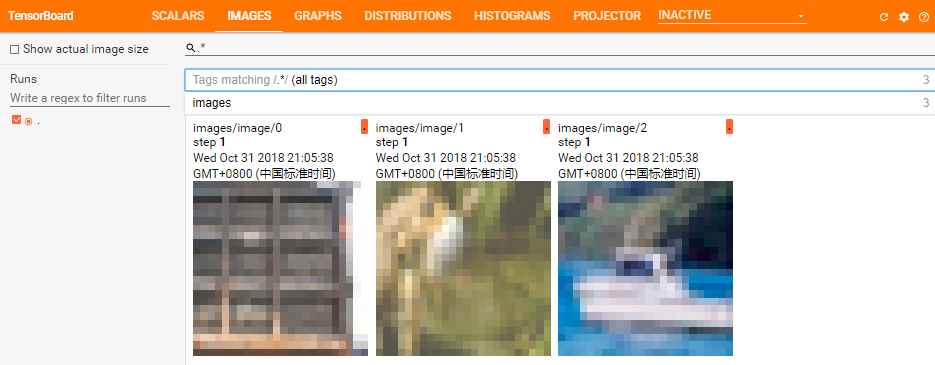
_generate_image_and_label_batch
生成批次的训练数据

def _generate_image_and_label_batch(image, label, min_queue_examples, batch_size, shuffle): """ 生成一个batch的数据 Args: image: 3-D Tensor of [height, width, 3] of type.float32. label: 1-D Tensor of type.int32 min_queue_examples: int32, minimum number of samples to retain in the queue that provides of batches of examples. batch_size: 每批次数据数目 shuffle: 是否打乱 Returns: images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, height, width, 3] size. labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size. """ # Create a queue that shuffles the examples, and then read 'batch_size' images + labels from the example queue. num_preprocess_threads = 16 if shuffle: images, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch( [image, label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=num_preprocess_threads, capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size, min_after_dequeue=min_queue_examples) else: images, label_batch = tf.train.batch( [image, label], batch_size=batch_size, num_threads=num_preprocess_threads, capacity=min_queue_examples + 3 * batch_size) # Display the training images in the visualizer. tf.summary.image('images', images) return images, tf.reshape(label_batch, [batch_size])
涉及不熟悉的tf操作:
- tf.train.batch && tf.train.shuffle_batch:https://blog.csdn.net/ying86615791/article/details/73864381
- tf.summary.image:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/summary/image
效果如下:
distorted_inputs
利用上面两个函数生成要训练的数据

def distorted_inputs(data_dir, batch_size): ''' 调用read_cifar10读取图片并做数据增强,继而调用_generate_image_and_label_batch产生一个batch的数据 返回值: images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size. labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size. ''' filenames = [os.path.join(data_dir, 'data_batch_%d.bin' % i) for i in xrange(1, 6)] for f in filenames: if not tf.gfile.Exists(f): raise ValueError('Failed to find file: ' + f) # 文件名队列 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames) # 从文件名队列中读取图片 read_input = read_cifar10(filename_queue) reshaped_image = tf.cast(read_input.uint8image, tf.float32) height = IMAGE_SIZE width = IMAGE_SIZE # 数据增强 distorted_image = tf.random_crop(reshaped_image, [height, width, 3]) distorted_image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(distorted_image) distorted_image = tf.image.random_brightness(distorted_image, max_delta=63) distorted_image = tf.image.random_contrast(distorted_image, lower=0.2, upper=1.8) # Subtract off the mean and divide by the variance of the pixels. float_image = tf.image.per_image_standardization(distorted_image) # Set the shapes of tensors. float_image.set_shape([height, width, 3]) read_input.label.set_shape([1]) # Ensure that the random shuffling has good mixing properties. min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue = 0.4 min_queue_examples = int(NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN * min_fraction_of_examples_in_queue) print('Filling queue with %d CIFAR images before starting to train. % min_queue_examples) # Generate a batch of images and labels by building up a queue of examples. return _generate_image_and_label_batch(float_image, read_input.label, min_queue_examples, batch_size, shuffle=True)
- tf.gfile:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/gfile https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31536538
- tf.image.per_image_standardization:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/image/per_image_standardization
cifar10_train.py
知道cifar10.py是真正的训练网络实现文件,先来看cifar10_train.py的调用,再进而学习每个步骤是如何实现的。
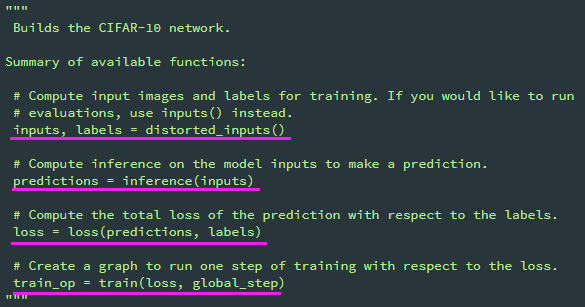
完整代码:

from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function from datetime import datetime import time import tensorflow as tf import cifar10 # tf.app.flags.FLAGS 是 TensorFlow 内部的一个全局变量存储器,同时可以用于命令行参数的处理 FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('train_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_train', "Directory where to write event logs and checkpoint.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('max_steps', 100000, "Number of batches to run.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('log_device_placement', False, "Whether to log device placement.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('log_frequency', 100, "How often to log results to the console.") def train(): """Train CIFAR-10 for a number of steps.""" with tf.Graph().as_default(): global_step = tf.contrib.framework.get_or_create_global_step() # Get images and labels for CIFAR-10. images, labels = cifar10.distorted_inputs() # Build a Graph that computes the logits predictions from the inference model. logits = cifar10.inference(images) # Calculate loss. loss = cifar10.loss(logits, labels) # Build a Graph that trains the model with one batch of examples and updates the model parameters. train_op = cifar10.train(loss, global_step) class _LoggerHook(tf.train.SessionRunHook): """记录损失loss和运行时间""" def begin(self): self._step = -1 self._start_time = time.time() def before_run(self, run_context): self._step += 1 return tf.train.SessionRunArgs(loss) # Asks for loss value. def after_run(self, run_context, run_values): if self._step % FLAGS.log_frequency == 0: current_time = time.time() duration = current_time - self._start_time self._start_time = current_time loss_value = run_values.results examples_per_sec = FLAGS.log_frequency * FLAGS.batch_size / duration sec_per_batch = float(duration / FLAGS.log_frequency) format_str = ('%s: step %d, loss = %.2f (%.1f examples/sec; %.3f sec/batch)') print(format_str % (datetime.now(), self._step, loss_value, examples_per_sec, sec_per_batch)) with tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession( checkpoint_dir=FLAGS.train_dir, hooks=[tf.train.StopAtStepHook(last_step=FLAGS.max_steps), tf.train.NanTensorHook(loss), _LoggerHook()], config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=FLAGS.log_device_placement)) as mon_sess: while not mon_sess.should_stop(): mon_sess.run(train_op) def main(argv=None): # pylint: disable=unused-argument cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract() if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.train_dir): tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.train_dir) tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.train_dir) train() if __name__ == '__main__': tf.app.run()
- tf.train.MonitoredTrainingSession:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/train/MonitoredTrainingSession
- tf.train.SessionRunHook:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/train/SessionRunHook
cifar10.py
该文件是关键,他实现了整个网络架构

#encoding=utf-8 # pylint: disable=missing-docstring from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function import os import re import sys import tarfile from six.moves import urllib import tensorflow as tf import cifar10_input FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS # Basic model parameters. tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 128, "Number of images to process in a batch.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_data', "Path to the CIFAR-10 data directory.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('use_fp16', False, "Train the model using fp16.") # Global constants describing the CIFAR-10 data set. IMAGE_SIZE = cifar10_input.IMAGE_SIZE NUM_CLASSES = cifar10_input.NUM_CLASSES NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL = cifar10_input.NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_EVAL # Constants describing the training process. MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.9999 # The decay to use for the moving average. NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY = 350.0 # Epochs after which learning rate decays. LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR = 0.1 # Learning rate decay factor. INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE = 0.1 # Initial learning rate. # If a model is trained with multiple GPUs, prefix all Op names with tower_name # to differentiate the operations. Note that this prefix is removed from the # names of the summaries when visualizing a model. TOWER_NAME = 'tower' DATA_URL = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-binary.tar.gz'
一些辅助函数:

def _activation_summary(x): """Helper to create summaries for activations. Creates a summary that provides a histogram of activations. Creates a summary that measures the sparsity of activations. Args: x: Tensor """ # Remove 'tower_[0-9]/' from the name in case this is a multi-GPU training session. # This helps the clarity of presentation on tensorboard. tensor_name = re.sub('%s_[0-9]*/' % TOWER_NAME, '', x.op.name) tf.summary.histogram(tensor_name + '/activations', x) tf.summary.scalar(tensor_name + '/sparsity', tf.nn.zero_fraction(x))

def _variable_on_cpu(name, shape, initializer): """Helper to create a Variable stored on CPU memory. Args: name: name of the variable shape: list of ints initializer: initializer for Variable Returns: Variable Tensor """ with tf.device('/cpu:0'): dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32 var = tf.get_variable(name, shape, initializer=initializer, dtype=dtype) return var

def _variable_with_weight_decay(name, shape, stddev, wd): """Helper to create an initialized Variable with weight decay. Note that the Variable is initialized with a truncated normal distribution. A weight decay is added only if one is specified. Args: name: name of the variable shape: list of ints stddev: standard deviation of a truncated Gaussian wd: add L2Loss weight decay multiplied by this float. If None, weight decay is not added for this Variable. Returns: Variable Tensor """ dtype = tf.float16 if FLAGS.use_fp16 else tf.float32 var = _variable_on_cpu(name,shape, tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev, dtype=dtype)) if wd is not None: weight_decay = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_loss(var), wd, name='weight_loss') tf.add_to_collection('losses', weight_decay) return var

def maybe_download_and_extract(): """Download and extract the tarball from Alex's website.""" dest_directory = FLAGS.data_dir if not os.path.exists(dest_directory): os.makedirs(dest_directory) filename = DATA_URL.split('/')[-1] filepath = os.path.join(dest_directory, filename) if not os.path.exists(filepath): def _progress(count, block_size, total_size): sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' % (filename, float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0)) sys.stdout.flush() filepath, _ = urllib.request.urlretrieve(DATA_URL, filepath, _progress) print() statinfo = os.stat(filepath) print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.') extracted_dir_path = os.path.join(dest_directory, 'cifar-10-batches-bin') if not os.path.exists(extracted_dir_path): tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dest_directory)
- tf.get_variable()和tf.Variable()的区别:https://blog.csdn.net/u012223913/article/details/78533910?locationNum=8&fps=1
distorted_inputs
把cifar10_input.py中distorted_inputs函数添加了一层,根据配置参数use_fp16决定是否采用float16的数据类型进行计算

def distorted_inputs(): """Construct distorted input for CIFAR training using the Reader ops. Returns: images: Images. 4D tensor of [batch_size, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, 3] size. labels: Labels. 1D tensor of [batch_size] size. Raises: ValueError: If no data_dir """ if not FLAGS.data_dir: raise ValueError('Please supply a data_dir') data_dir = os.path.join(FLAGS.data_dir, 'cifar-10-batches-bin') images, labels = cifar10_input.distorted_inputs(data_dir=data_dir, batch_size=FLAGS.batch_size) if FLAGS.use_fp16: images = tf.cast(images, tf.float16) labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.float16) return images, labels
inference

def inference(images): """Build the CIFAR-10 model. Args: images: Images returned from distorted_inputs() or inputs(). Returns: Logits. """ # We instantiate all variables using tf.get_variable() instead of tf.Variable() in order to share variables across multiple GPU training runs. # If we only ran this model on a single GPU, we could simplify this function by replacing all instances of tf.get_variable() with tf.Variable(). # 卷积层 with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope: kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[5, 5, 3, 64], stddev=5e-2, wd=0.0) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name) _activation_summary(conv1) pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool1') # 这是局部响应归一化层(LRN),现在的模型大多不采用 norm1 = tf.nn.lrn(pool1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm1') with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope: kernel = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64], stddev=5e-2, wd=0.0) conv = tf.nn.conv2d(norm1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [64], tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases) conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name) _activation_summary(conv2) norm2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9.0, beta=0.75, name='norm2') pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(norm2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME', name='pool2') # 全连接层 with tf.variable_scope('local3') as scope: # 后面不再做卷积了,所以把pool2进行reshape,方便做全连接 reshape = tf.reshape(pool2, [FLAGS.batch_size, -1]) dim = reshape.get_shape()[1].value weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[dim, 384], stddev=0.04, wd=0.004) biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [384], tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) local3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name) _activation_summary(local3) with tf.variable_scope('local4') as scope: weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', shape=[384, 192], stddev=0.04, wd=0.004) biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [192], tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) local4 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(local3, weights) + biases, name=scope.name) _activation_summary(local4) # 这里不显示i进行softmax变换,只输出变换前的Logit(即变量softmax_linear) # tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits accepts the unscaled logits and performs the softmax internally for efficiency. with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope: weights = _variable_with_weight_decay('weights', [192, NUM_CLASSES], stddev=1/192.0, wd=0.0) biases = _variable_on_cpu('biases', [NUM_CLASSES], tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) softmax_linear = tf.add(tf.matmul(local4, weights), biases, name=scope.name) _activation_summary(softmax_linear) return softmax_linear
两层卷积,三层全连接
loss

def loss(logits, labels): """Add L2Loss to all the trainable variables. Add summary for "Loss" and "Loss/avg". Args: logits: Logits from inference(). labels: Labels from distorted_inputs or inputs(). 1-D tensor of shape [batch_size] Returns: Loss tensor of type float. """ # Calculate the average cross entropy loss across the batch. labels = tf.cast(labels, tf.int64) cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits( labels=labels, logits=logits, name='cross_entropy_per_example') cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy, name='cross_entropy') tf.add_to_collection('losses', cross_entropy_mean) # The total loss is defined as the cross entropy loss plus all of the weight decay terms (L2 loss). return tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'), name='total_loss')

def _add_loss_summaries(total_loss): """Add summaries for losses in CIFAR-10 model. Generates moving average for all losses and associated summaries for visualizing the performance of the network. Args: total_loss: Total loss from loss(). Returns: loss_averages_op: op for generating moving averages of losses. """ # Compute the moving average of all individual losses and the total loss. loss_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(0.9, name='avg') losses = tf.get_collection('losses') loss_averages_op = loss_averages.apply(losses + [total_loss]) # Attach a scalar summary to all individual losses and the total loss; do the same for the averaged version of the losses. for l in losses + [total_loss]: # Name each loss as '(raw)' and name the moving average version of the loss as the original loss name. tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name + ' (raw)', l) tf.summary.scalar(l.op.name, loss_averages.average(l)) return loss_averages_op
train

def train(total_loss, global_step): """Train CIFAR-10 model. Create an optimizer and apply to all trainable variables. Add moving average for all trainable variables. Args: total_loss: Total loss from loss(). global_step: Integer Variable counting the number of training steps processed. Returns: train_op: op for training. """ # Variables that affect learning rate. num_batches_per_epoch = NUM_EXAMPLES_PER_EPOCH_FOR_TRAIN / FLAGS.batch_size decay_steps = int(num_batches_per_epoch * NUM_EPOCHS_PER_DECAY) # Decay the learning rate exponentially based on the number of steps. lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(INITIAL_LEARNING_RATE, global_step, decay_steps, LEARNING_RATE_DECAY_FACTOR, staircase=True) tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', lr) # Generate moving averages of all losses and associated summaries. loss_averages_op = _add_loss_summaries(total_loss) # Compute gradients. with tf.control_dependencies([loss_averages_op]): opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(lr) grads = opt.compute_gradients(total_loss) # Apply gradients. apply_gradient_op = opt.apply_gradients(grads, global_step=global_step) # Add histograms for trainable variables. for var in tf.trainable_variables(): tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name, var) # Add histograms for gradients. for grad, var in grads: if grad is not None: tf.summary.histogram(var.op.name + '/gradients', grad) # Track the moving averages of all trainable variables. variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step) variables_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables()) with tf.control_dependencies([apply_gradient_op, variables_averages_op]): train_op = tf.no_op(name='train') return train_op
- tf.train.exponential_decay:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f9f66a89f6ba
- tf.control_dependencies:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/control_dependencies
- tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage:https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/train/ExponentialMovingAverage
以上是训练过程代码的学习,执行python cifar10_train.py --train_dir cifar10_train/ --data_dir cifar10_data/即可运行,运行tensorboard --logdir cifar10_train/即可在tensorboard中查看训练进度
我是100K steps (256 epochs of data) 训练的,差不多花了3.5h
测试

from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function from datetime import datetime import math import time import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import cifar10 FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('eval_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_eval', "Directory where to write event logs.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('eval_data', 'test', "Either 'test' or 'train_eval'.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('checkpoint_dir', '/tmp/cifar10_train', "Directory where to read model checkpoints.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('eval_interval_secs', 60 * 5, "How often to run the eval.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('num_examples', 10000, "Number of examples to run.") tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean('run_once', False, "Whether to run eval only once.") def eval_once(saver, summary_writer, top_k_op, summary_op): """Run Eval once. Args: saver: Saver. summary_writer: Summary writer. top_k_op: Top K op. summary_op: Summary op. """ with tf.Session() as sess: ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(FLAGS.checkpoint_dir) if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path: # Restores from checkpoint saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path) # Assuming model_checkpoint_path looks something like: /my-favorite-path/cifar10_train/model.ckpt-0 #extract global_step from it. global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1] else: print('No checkpoint file found') return # Start the queue runners. coord = tf.train.Coordinator() try: threads = [] for qr in tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS): threads.extend(qr.create_threads(sess, coord=coord, daemon=True, start=True)) num_iter = int(math.ceil(FLAGS.num_examples / FLAGS.batch_size)) true_count = 0 # Counts the number of correct predictions. total_sample_count = num_iter * FLAGS.batch_size step = 0 while step < num_iter and not coord.should_stop(): predictions = sess.run([top_k_op]) true_count += np.sum(predictions) step += 1 # Compute precision @ 1. precision = true_count / total_sample_count print('%s: precision @ 1 = %.3f' % (datetime.now(), precision)) summary = tf.Summary() summary.ParseFromString(sess.run(summary_op)) summary.value.add(tag='Precision @ 1', simple_value=precision) summary_writer.add_summary(summary, global_step) except Exception as e: # pylint: disable=broad-except coord.request_stop(e) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads, stop_grace_period_secs=10) def evaluate(): """Eval CIFAR-10 for a number of steps.""" with tf.Graph().as_default() as g: # Get images and labels for CIFAR-10. eval_data = FLAGS.eval_data == 'test' images, labels = cifar10.inputs(eval_data=eval_data) # Build a Graph that computes the logits predictions from the # inference model. logits = cifar10.inference(images) # Calculate predictions. top_k_op = tf.nn.in_top_k(logits, labels, 1) # Restore the moving average version of the learned variables for eval. variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(cifar10.MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY) variables_to_restore = variable_averages.variables_to_restore() saver = tf.train.Saver(variables_to_restore) # Build the summary operation based on the TF collection of Summaries. summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all() summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(FLAGS.eval_dir, g) while True: eval_once(saver, summary_writer, top_k_op, summary_op) if FLAGS.run_once: break time.sleep(FLAGS.eval_interval_secs) def main(argv=None): # pylint: disable=unused-argument cifar10.maybe_download_and_extract() if tf.gfile.Exists(FLAGS.eval_dir): tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(FLAGS.eval_dir) tf.gfile.MakeDirs(FLAGS.eval_dir) evaluate() if __name__ == '__main__': tf.app.run()
运行命令:python cifar10_eval.py --data_dir cifar10_data/ --eval_dir cifar10_eval/ --checkpoint_dir cifar10_train/
可以通过tensorboard看:tensorboard --logdir cifar10_eval/ --port 6007
为什么测试的时候要再开一个tensorboard,可以根据步数观察测试效果。训练和测试同时进行,测试会去读取模型文件中最新的模型,实际上到 6 万步左右时,模型就有了 86%的准确率,到10万步时的准确率为 86.3%,到15万步后的准确率基本稳定在 86.6%左右。
多GPU训练
暂缓。。。。。。先把第三章的训练先学了,工作需要!!!再学习下tf操作的summary,衰减梯度下降部分函数。。。。。sad



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号