引言
我一直在探寻一个高性能的Socket客户端代码。以前,我使用Socket类写了一些基于传统异步编程模型的代码(BeginSend、BeginReceive,等等)
也看过很多博客的知识,在linux中有poll和epoll来实现,在windows下面
微软MSDN中也提供了SocketAsyncEventArgs这个类来实现IOCP
地址:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.net.sockets.socketasynceventargs.aspx
NET Framework中的APM也称为Begin/End模式。这是因为会调用Begin方法来启动异步操作,然后返回一个IAsyncResult 对象。可以选择将一个代理作为参数提供给Begin方法,异步操作完成时会调用该方法。或者,一个线程可以等待 IAsyncResult.AsyncWaitHandle。当回调被调用或发出等待信号时,就会调用End方法来获取异步操作的结果。这种模式很灵活,使用相对简单,在 .NET Framework 中非常常见。
但是,您必须注意,如果进行大量异步套接字操作,是要付出代价的。针对每次操作,都必须创建一个IAsyncResult对象,而且该对象不能被重复使用。由于大量使用对象分配和垃圾收集,这会影响性能。为了解决这个问题,新版本提供了另一个使用套接字上执行异步I/O的方法模式。这种新模式并不要求为每个套接字操作分配操作上下文对象。
代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/zhujunxxxxx/8431289 这里的代码优化了的
目标
在上面微软提供的例子我觉得不是很完整,没有具体一个流程,只是受到客户端消息后发送相同内容给客户端,初学者不容易看懂流程,因为我花了一天的时间来实现一个功能齐全的IOCP服务器,
效果如下
代码
首先是ICOPServer.cs 这个类是IOCP服务器的核心类,目前这个类是网络上比较全的代码,MSDN上面的例子都没有我的全

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Net.Sockets; using System.Net; using System.Threading; namespace ServerTest { /// <summary> /// IOCP SOCKET服务器 /// </summary> public class IOCPServer : IDisposable { const int opsToPreAlloc = 2; #region Fields /// <summary> /// 服务器程序允许的最大客户端连接数 /// </summary> private int _maxClient; /// <summary> /// 监听Socket,用于接受客户端的连接请求 /// </summary> private Socket _serverSock; /// <summary> /// 当前的连接的客户端数 /// </summary> private int _clientCount; /// <summary> /// 用于每个I/O Socket操作的缓冲区大小 /// </summary> private int _bufferSize = 1024; /// <summary> /// 信号量 /// </summary> Semaphore _maxAcceptedClients; /// <summary> /// 缓冲区管理 /// </summary> BufferManager _bufferManager; /// <summary> /// 对象池 /// </summary> SocketAsyncEventArgsPool _objectPool; private bool disposed = false; #endregion #region Properties /// <summary> /// 服务器是否正在运行 /// </summary> public bool IsRunning { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// 监听的IP地址 /// </summary> public IPAddress Address { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// 监听的端口 /// </summary> public int Port { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// 通信使用的编码 /// </summary> public Encoding Encoding { get; set; } #endregion #region Ctors /// <summary> /// 异步IOCP SOCKET服务器 /// </summary> /// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param> /// <param name="maxClient">最大的客户端数量</param> public IOCPServer(int listenPort, int maxClient) : this(IPAddress.Any, listenPort, maxClient) { } /// <summary> /// 异步Socket TCP服务器 /// </summary> /// <param name="localEP">监听的终结点</param> /// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param> public IOCPServer(IPEndPoint localEP, int maxClient) : this(localEP.Address, localEP.Port, maxClient) { } /// <summary> /// 异步Socket TCP服务器 /// </summary> /// <param name="localIPAddress">监听的IP地址</param> /// <param name="listenPort">监听的端口</param> /// <param name="maxClient">最大客户端数量</param> public IOCPServer(IPAddress localIPAddress, int listenPort, int maxClient) { this.Address = localIPAddress; this.Port = listenPort; this.Encoding = Encoding.Default; _maxClient = maxClient; _serverSock = new Socket(localIPAddress.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); _bufferManager = new BufferManager(_bufferSize * _maxClient * opsToPreAlloc, _bufferSize); _objectPool = new SocketAsyncEventArgsPool(_maxClient); _maxAcceptedClients = new Semaphore(_maxClient, _maxClient); } #endregion #region 初始化 /// <summary> /// 初始化函数 /// </summary> public void Init() { // Allocates one large byte buffer which all I/O operations use a piece of. This gaurds // against memory fragmentation _bufferManager.InitBuffer(); // preallocate pool of SocketAsyncEventArgs objects SocketAsyncEventArgs readWriteEventArg; for (int i = 0; i < _maxClient; i++) { //Pre-allocate a set of reusable SocketAsyncEventArgs readWriteEventArg = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); readWriteEventArg.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnIOCompleted); readWriteEventArg.UserToken = null; // assign a byte buffer from the buffer pool to the SocketAsyncEventArg object _bufferManager.SetBuffer(readWriteEventArg); // add SocketAsyncEventArg to the pool _objectPool.Push(readWriteEventArg); } } #endregion #region Start /// <summary> /// 启动 /// </summary> public void Start() { if (!IsRunning) { Init(); IsRunning = true; IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(Address, Port); // 创建监听socket _serverSock = new Socket(localEndPoint.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); //_serverSock.ReceiveBufferSize = _bufferSize; //_serverSock.SendBufferSize = _bufferSize; if (localEndPoint.AddressFamily == AddressFamily.InterNetworkV6) { // 配置监听socket为 dual-mode (IPv4 & IPv6) // 27 is equivalent to IPV6_V6ONLY socket option in the winsock snippet below, _serverSock.SetSocketOption(SocketOptionLevel.IPv6, (SocketOptionName)27, false); _serverSock.Bind(new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.IPv6Any, localEndPoint.Port)); } else { _serverSock.Bind(localEndPoint); } // 开始监听 _serverSock.Listen(this._maxClient); // 在监听Socket上投递一个接受请求。 StartAccept(null); } } #endregion #region Stop /// <summary> /// 停止服务 /// </summary> public void Stop() { if (IsRunning) { IsRunning = false; _serverSock.Close(); //TODO 关闭对所有客户端的连接 } } #endregion #region Accept /// <summary> /// 从客户端开始接受一个连接操作 /// </summary> private void StartAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar) { if (asyniar == null) { asyniar = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); asyniar.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnAcceptCompleted); } else { //socket must be cleared since the context object is being reused asyniar.AcceptSocket = null; } _maxAcceptedClients.WaitOne(); if (!_serverSock.AcceptAsync(asyniar)) { ProcessAccept(asyniar); //如果I/O挂起等待异步则触发AcceptAsyn_Asyn_Completed事件 //此时I/O操作同步完成,不会触发Asyn_Completed事件,所以指定BeginAccept()方法 } } /// <summary> /// accept 操作完成时回调函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">Object who raised the event.</param> /// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param> private void OnAcceptCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { ProcessAccept(e); } /// <summary> /// 监听Socket接受处理 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed accept operation.</param> private void ProcessAccept(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket if (s.Connected) { try { Interlocked.Increment(ref _clientCount);//原子操作加1 SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar = _objectPool.Pop(); asyniar.UserToken = s; Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 连入, 共有 {1} 个连接。", s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), _clientCount)); if (!s.ReceiveAsync(asyniar))//投递接收请求 { ProcessReceive(asyniar); } } catch (SocketException ex) { Log4Debug(String.Format("接收客户 {0} 数据出错, 异常信息: {1} 。", s.RemoteEndPoint, ex.ToString())); //TODO 异常处理 } //投递下一个接受请求 StartAccept(e); } } } #endregion #region 发送数据 /// <summary> /// 异步的发送数据 /// </summary> /// <param name="e"></param> /// <param name="data"></param> public void Send(SocketAsyncEventArgs e, byte[] data) { if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { Socket s = e.AcceptSocket;//和客户端关联的socket if (s.Connected) { Array.Copy(data, 0, e.Buffer, 0, data.Length);//设置发送数据 //e.SetBuffer(data, 0, data.Length); //设置发送数据 if (!s.SendAsync(e))//投递发送请求,这个函数有可能同步发送出去,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件 { // 同步发送时处理发送完成事件 ProcessSend(e); } else { CloseClientSocket(e); } } } } /// <summary> /// 同步的使用socket发送数据 /// </summary> /// <param name="socket"></param> /// <param name="buffer"></param> /// <param name="offset"></param> /// <param name="size"></param> /// <param name="timeout"></param> public void Send(Socket socket, byte[] buffer, int offset, int size, int timeout) { socket.SendTimeout = 0; int startTickCount = Environment.TickCount; int sent = 0; // how many bytes is already sent do { if (Environment.TickCount > startTickCount + timeout) { //throw new Exception("Timeout."); } try { sent += socket.Send(buffer, offset + sent, size - sent, SocketFlags.None); } catch (SocketException ex) { if (ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.WouldBlock || ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.IOPending || ex.SocketErrorCode == SocketError.NoBufferSpaceAvailable) { // socket buffer is probably full, wait and try again Thread.Sleep(30); } else { throw ex; // any serious error occurr } } } while (sent < size); } /// <summary> /// 发送完成时处理函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">与发送完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param> private void ProcessSend(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken; //TODO } else { CloseClientSocket(e); } } #endregion #region 接收数据 /// <summary> ///接收完成时处理函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">与接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param> private void ProcessReceive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success)//if (e.BytesTransferred > 0 && e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { // 检查远程主机是否关闭连接 if (e.BytesTransferred > 0) { Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken; //判断所有需接收的数据是否已经完成 if (s.Available == 0) { //从侦听者获取接收到的消息。 //String received = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(e.Buffer, e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred); //echo the data received back to the client //e.SetBuffer(e.Offset, e.BytesTransferred); byte[] data = new byte[e.BytesTransferred]; Array.Copy(e.Buffer, e.Offset, data, 0, data.Length);//从e.Buffer块中复制数据出来,保证它可重用 string info = Encoding.Default.GetString(data); Log4Debug(String.Format("收到 {0} 数据为 {1}", s.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), info)); //TODO 处理数据 //增加服务器接收的总字节数。 } if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))//为接收下一段数据,投递接收请求,这个函数有可能同步完成,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件 { //同步接收时处理接收完成事件 ProcessReceive(e); } } } else { CloseClientSocket(e); } } #endregion #region 回调函数 /// <summary> /// 当Socket上的发送或接收请求被完成时,调用此函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">激发事件的对象</param> /// <param name="e">与发送或接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param> private void OnIOCompleted(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { // Determine which type of operation just completed and call the associated handler. switch (e.LastOperation) { case SocketAsyncOperation.Accept: ProcessAccept(e); break; case SocketAsyncOperation.Receive: ProcessReceive(e); break; default: throw new ArgumentException("The last operation completed on the socket was not a receive or send"); } } #endregion #region Close /// <summary> /// 关闭socket连接 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">SocketAsyncEventArg associated with the completed send/receive operation.</param> private void CloseClientSocket(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { Log4Debug(String.Format("客户 {0} 断开连接!", ((Socket)e.UserToken).RemoteEndPoint.ToString())); Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket; CloseClientSocket(s, e); } /// <summary> /// 关闭socket连接 /// </summary> /// <param name="s"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void CloseClientSocket(Socket s, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { try { s.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Send); } catch (Exception) { // Throw if client has closed, so it is not necessary to catch. } finally { s.Close(); } Interlocked.Decrement(ref _clientCount); _maxAcceptedClients.Release(); _objectPool.Push(e);//SocketAsyncEventArg 对象被释放,压入可重用队列。 } #endregion #region Dispose /// <summary> /// Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing, /// releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources. /// </summary> public void Dispose() { Dispose(true); GC.SuppressFinalize(this); } /// <summary> /// Releases unmanaged and - optionally - managed resources /// </summary> /// <param name="disposing"><c>true</c> to release /// both managed and unmanaged resources; <c>false</c> /// to release only unmanaged resources.</param> protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing) { if (!this.disposed) { if (disposing) { try { Stop(); if (_serverSock != null) { _serverSock = null; } } catch (SocketException ex) { //TODO 事件 } } disposed = true; } } #endregion public void Log4Debug(string msg) { Console.WriteLine("notice:" + msg); } } }
BufferManager.cs 这个类是缓存管理类,是采用MSDN上面的例子一样的 地址: https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/bb517542.aspx
官网地址:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/api/system.servicemodel.channels.buffermanager?view=netframework-4.5

class BufferManager { int m_numBytes; // the total number of bytes controlled by the buffer pool byte[] m_buffer; // the underlying byte array maintained by the Buffer Manager Stack<int> m_freeIndexPool; // int m_currentIndex; int m_bufferSize; public BufferManager(int totalBytes, int bufferSize) { m_numBytes = totalBytes; m_currentIndex = 0; m_bufferSize = bufferSize; m_freeIndexPool = new Stack<int>(); } // Allocates buffer space used by the buffer pool public void InitBuffer() { // create one big large buffer and divide that // out to each SocketAsyncEventArg object m_buffer = new byte[m_numBytes]; } // Assigns a buffer from the buffer pool to the // specified SocketAsyncEventArgs object // // <returns>true if the buffer was successfully set, else false</returns> public bool SetBuffer(SocketAsyncEventArgs args) { if (m_freeIndexPool.Count > 0) { args.SetBuffer(m_buffer, m_freeIndexPool.Pop(), m_bufferSize); } else { if ((m_numBytes - m_bufferSize) < m_currentIndex) { return false; } args.SetBuffer(m_buffer, m_currentIndex, m_bufferSize); m_currentIndex += m_bufferSize; } return true; } // Removes the buffer from a SocketAsyncEventArg object. // This frees the buffer back to the buffer pool public void FreeBuffer(SocketAsyncEventArgs args) { m_freeIndexPool.Push(args.Offset); args.SetBuffer(null, 0, 0); } }
SocketAsyncEventArgsPool.cs 这个类也是来自MSDN的 地址:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/system.net.sockets.socketasynceventargs.aspx

// Represents a collection of reusable SocketAsyncEventArgs objects. public class SocketAsyncEventArgsPool { Stack<SocketAsyncEventArgs> m_pool; // Initializes the object pool to the specified size // // The "capacity" parameter is the maximum number of // SocketAsyncEventArgs objects the pool can hold public SocketAsyncEventArgsPool(int capacity) { m_pool = new Stack<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(capacity); } // Add a SocketAsyncEventArg instance to the pool // //The "item" parameter is the SocketAsyncEventArgs instance // to add to the pool public void Push(SocketAsyncEventArgs item) { if (item == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("Items added to a SocketAsyncEventArgsPool cannot be null"); } lock (m_pool) { m_pool.Push(item); } } // Removes a SocketAsyncEventArgs instance from the pool // and returns the object removed from the pool public SocketAsyncEventArgs Pop() { lock (m_pool) { return m_pool.Pop(); } } // The number of SocketAsyncEventArgs instances in the pool public int Count { get { return m_pool.Count; } } public void Clear() { m_pool.Clear(); } }
服务器端

static void Main(string[] args) { IOCPServer server = new IOCPServer(8088, 1024); server.Start(); Console.WriteLine("服务器已启动...."); System.Console.ReadLine(); }
客户端
客户端代码也是很简单

static void Main(string[] args) { IPAddress remote = IPAddress.Parse("192.168.3.4"); client c = new client(8088, remote); c.connect(); Console.WriteLine("服务器连接成功!"); while (true) { Console.Write("send>"); string msg = Console.ReadLine(); if (msg == "exit") break; c.send(msg); } c.disconnect(); Console.ReadLine(); }
client.cs

public class client { public TcpClient _client; public int port; public IPAddress remote; public client(int port, IPAddress remote) { this.port = port; this.remote = remote; } public void connect() { this._client = new TcpClient(); _client.Connect(remote, port); } public void disconnect() { _client.Close(); } public void send(string msg) { byte[] data = Encoding.Default.GetBytes(msg); _client.GetStream().Write(data, 0, data.Length); } }
IOCPClient类,使用SocketAsyncEventArgs类建立一个Socket客户端。
虽然MSDN说这个类特别设计给网络服务器应用,但也没有限制在客户端代码中使用APM。
下面给出了IOCPClient类的样例代码:

public class IOCPClient { /// <summary> /// 连接服务器的socket /// </summary> private Socket _clientSock; /// <summary> /// 用于服务器执行的互斥同步对象 /// </summary> private static Mutex mutex = new Mutex(); /// <summary> /// Socket连接标志 /// </summary> private Boolean _connected = false; private const int ReceiveOperation = 1, SendOperation = 0; private static AutoResetEvent[] autoSendReceiveEvents = new AutoResetEvent[] { new AutoResetEvent(false), new AutoResetEvent(false) }; /// <summary> /// 服务器监听端点 /// </summary> private IPEndPoint _remoteEndPoint; public IOCPClient(IPEndPoint local, IPEndPoint remote) { _clientSock = new Socket(local.AddressFamily, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); _remoteEndPoint = remote; } #region 连接服务器 /// <summary> /// 连接远程服务器 /// </summary> public void Connect() { SocketAsyncEventArgs connectArgs = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); connectArgs.UserToken = _clientSock; connectArgs.RemoteEndPoint = _remoteEndPoint; connectArgs.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnConnected); mutex.WaitOne(); if (!_clientSock.ConnectAsync(connectArgs))//异步连接 { ProcessConnected(connectArgs); } } /// <summary> /// 连接上的事件 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> void OnConnected(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { mutex.ReleaseMutex(); //设置Socket已连接标志。 _connected = (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success); } /// <summary> /// 处理连接服务器 /// </summary> /// <param name="e"></param> private void ProcessConnected(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { //TODO } #endregion #region 发送消息 /// <summary> /// 向服务器发送消息 /// </summary> /// <param name="data"></param> public void Send(byte[] data) { SocketAsyncEventArgs asyniar = new SocketAsyncEventArgs(); asyniar.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnSendComplete); asyniar.SetBuffer(data, 0, data.Length); asyniar.UserToken = _clientSock; asyniar.RemoteEndPoint = _remoteEndPoint; autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].WaitOne(); if (!_clientSock.SendAsync(asyniar))//投递发送请求,这个函数有可能同步发送出去,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件 { // 同步发送时处理发送完成事件 ProcessSend(asyniar); } } /// <summary> /// 发送操作的回调方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void OnSendComplete(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { //发出发送完成信号。 autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].Set(); ProcessSend(e); } /// <summary> /// 发送完成时处理函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">与发送完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param> private void ProcessSend(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { //TODO } #endregion #region 接收消息 /// <summary> /// 开始监听服务端数据 /// </summary> /// <param name="e"></param> public void StartRecive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { //准备接收。 Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket; byte[] receiveBuffer = new byte[255]; e.SetBuffer(receiveBuffer, 0, receiveBuffer.Length); e.Completed += new EventHandler<SocketAsyncEventArgs>(OnReceiveComplete); autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].WaitOne(); if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e)) { ProcessReceive(e); } } /// <summary> /// 接收操作的回调方法 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void OnReceiveComplete(object sender, SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { //发出接收完成信号。 autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].Set(); ProcessReceive(e); } /// <summary> ///接收完成时处理函数 /// </summary> /// <param name="e">与接收完成操作相关联的SocketAsyncEventArg对象</param> private void ProcessReceive(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { if (e.SocketError == SocketError.Success) { // 检查远程主机是否关闭连接 if (e.BytesTransferred > 0) { Socket s = (Socket)e.UserToken; //判断所有需接收的数据是否已经完成 if (s.Available == 0) { byte[] data = new byte[e.BytesTransferred]; Array.Copy(e.Buffer, e.Offset, data, 0, data.Length);//从e.Buffer块中复制数据出来,保证它可重用 //TODO 处理数据 } if (!s.ReceiveAsync(e))//为接收下一段数据,投递接收请求,这个函数有可能同步完成,这时返回false,并且不会引发SocketAsyncEventArgs.Completed事件 { //同步接收时处理接收完成事件 ProcessReceive(e); } } } } #endregion public void Close() { _clientSock.Disconnect(false); } /// <summary> /// 失败时关闭Socket,根据SocketError抛出异常。 /// </summary> /// <param name="e"></param> private void ProcessError(SocketAsyncEventArgs e) { Socket s = e.UserToken as Socket; if (s.Connected) { //关闭与客户端关联的Socket try { s.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); } catch (Exception) { //如果客户端处理已经关闭,抛出异常 } finally { if (s.Connected) { s.Close(); } } } //抛出SocketException throw new SocketException((Int32)e.SocketError); } /// <summary> /// 释放SocketClient实例 /// </summary> public void Dispose() { mutex.Close(); autoSendReceiveEvents[SendOperation].Close(); autoSendReceiveEvents[ReceiveOperation].Close(); if (_clientSock.Connected) { _clientSock.Close(); } } }
源码部分截图如下
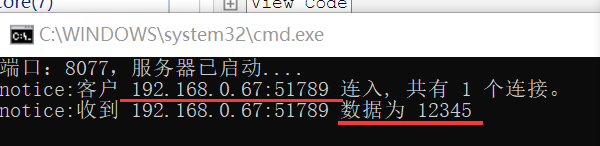
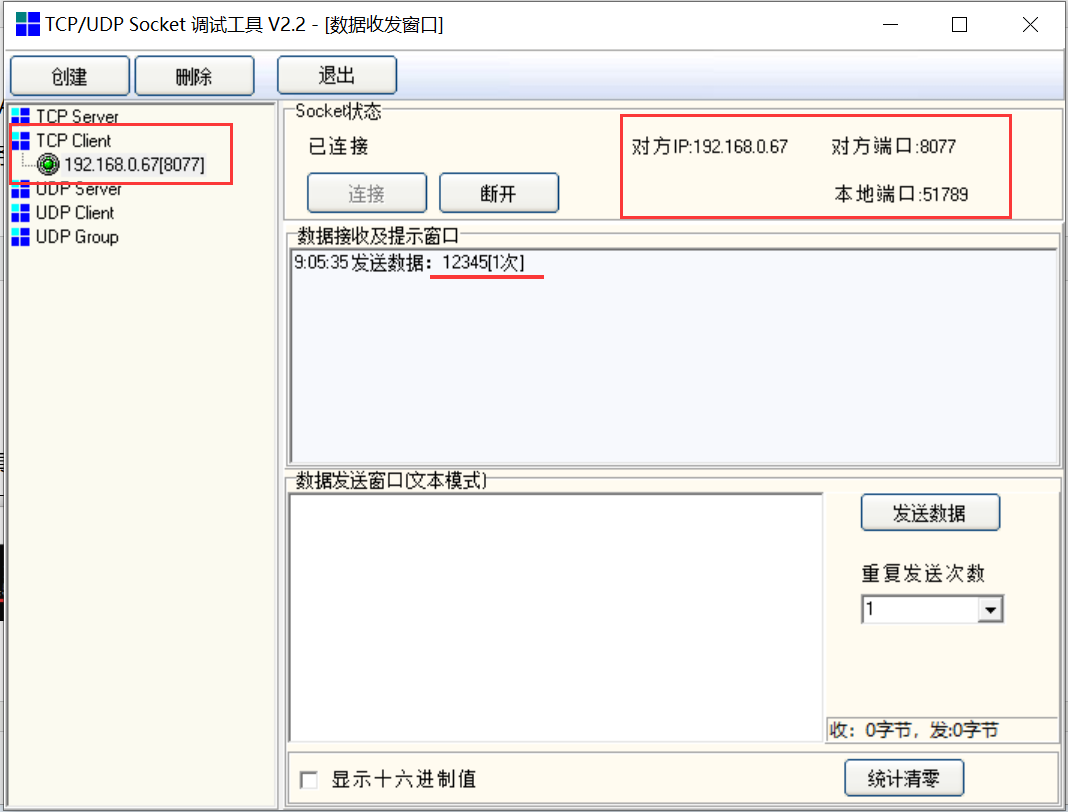
1.服务器使用的程序代码,客户端使用的工具测试
2.服务器和客户端都使用的代码
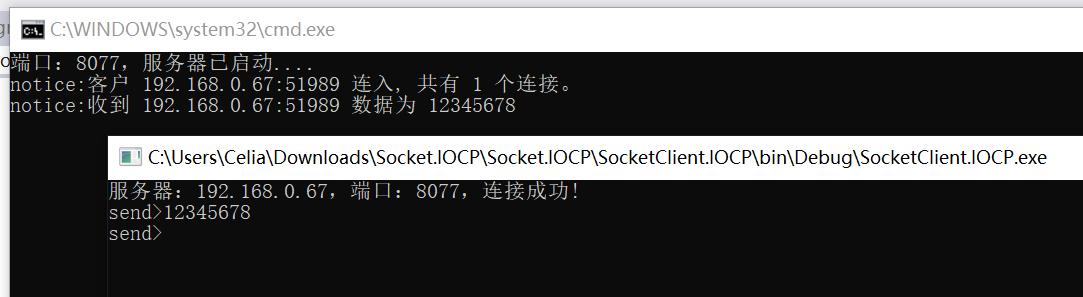
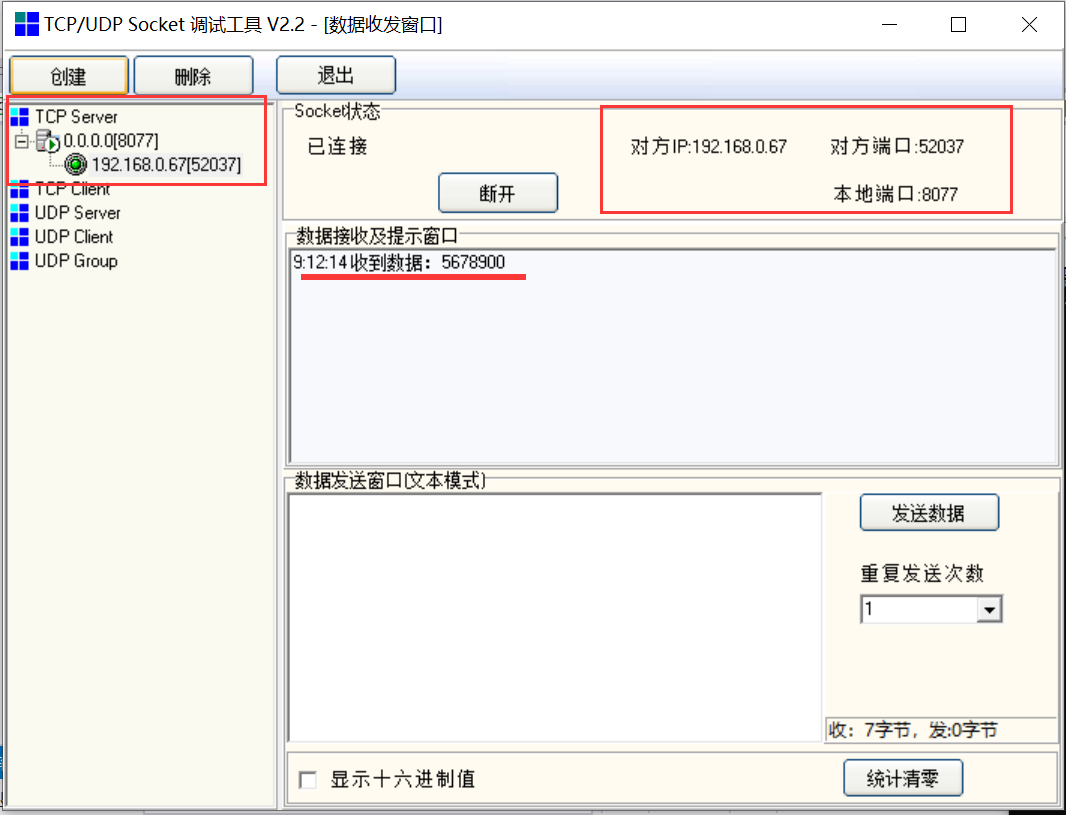
3.客户端使用的程序代码,服务端使用的工具测试
本文引自:https://www.cnblogs.com/tuyile006/p/10980391.html
可供参考:
https://www.iteye.com/blog/freshflower-2285272
https://www.iteye.com/blog/freshflower-2285286







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具