Spring boot starter主要作用是简化依赖管理、自动配置,让开发者能够快速启动和运行特定功能应用程序。
Springboot主要功能:
依赖管理和功能模块化:将一组相关依赖打包在一起,按需方便引用,保证程序轻量级
自动配置:根据spring.factory中配置,自动配置spring应用程序
1. Starter加载原理
Spring boot Starter是开发者开发完功能进行打包后,在其他项目中可以通过maven或者gradle进行引用,用于在其他项目中快速集成starter功能。
Springboot通过SpringBootApplication注解启动项目,springboot启动的时候,会将项目中所有声明为bean对象的实例加载到IOC容器。除此之外也会将starter里的bean信息加载到ioc容器,从而做到0配置,开箱即用。
1.1加载starter:
Springboot项目启动时,Springboot通过@SpringBootApplicaiton——>EnableAutoConfiguration注解进行加载starter.具体加载是有@EnableAutoConfiguration竹节虾import一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector加载器实现的
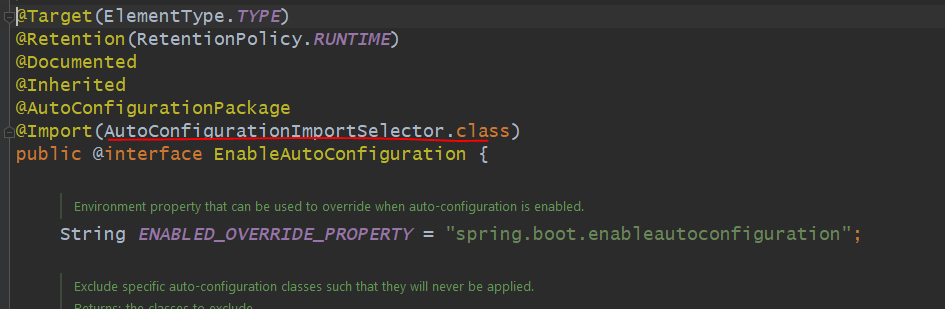
这个AutoConfigurationImportSelector会去所引用的依赖jar包下,找到一个spring.factories文件,一般spring.factories文件里会声明该依赖所提供的核心功能bean配置信息。spring.factories一般在META-INF文件夹下

1.2自定义starter
某个springboot项目加载配置文件中starter原理其实就是加载依赖jar包下spring.factories文件。所以我们自定义starter就需要在项目中建立一个META-INFde文件,然后在文件夹下建一个spring.factories文件,文件里将需要提供的bean实例信息配置好就行。
1.2.1 META-INF文件夹下新建spring.factories文件

1.2.2 新建统一配置类--配置类作用是统一封装1.2.3节后中多个提供服务的service,如果仅有一个service被调用可以不用统一配置类,只需要在需要被调用service上添加@Service注解即可
package com.yxj.demostarter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationDemo {
@Autowired
private DemoService demoService;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Bean
public DemoService demoService(){
return demoService;
}
@Bean
public UserService userService(){
return userService;
}
}
1.2.3 服务提供类
package com.yxj.demostarter;
@Service
public class DemoService {
public String testDemo(String demo){
return demo;
}
}
package com.yxj.demostarter;
@Service public class UserService { public String testUser(String user){ return user; } }
1.2.4 统一配置类DemoConfig配置到spring.factories中
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.yxj.demostarter.DemoConfig
1.2.5 将该项目打包上传到maven仓库
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
1.2.6 依赖测试
在另一个项目中引入刚刚打包的pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.yxj</groupId>
<artifactId>demoStarter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
1.2.7 调用测试
@RestController public class DemoController { @Autowired private DemoService demoService; @Autowired private UserService userService; @GetMapping("demo") public ResponseEntity demo(){ String service = demoService.getService("demotest"); return new ResponseEntity(service, HttpStatus.OK); } @GetMapping("user") public ResponseEntity user(){ String service = userService.getService("testuser"); return new ResponseEntity(service, HttpStatus.OK); } }
参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42394044/article/details/123906401



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号