简介
一直以为是一个高深的算法,好像据说在量子计算机中可以应用。发现原理并不难
参考链接
https://blog.csdn.net/google19890102/article/details/45395257
https://blog.csdn.net/wfrainn/article/details/80303138
算法缺点
这个算法怎么感觉概率的地方基本不受控制,温度降到最后还是大量接受随机解?
模拟退火就是这样的,因为它到了最优解过后还能跳出最优解域,因此能找到别的解域的最优解的值。因此一定要记录下历史最优解。
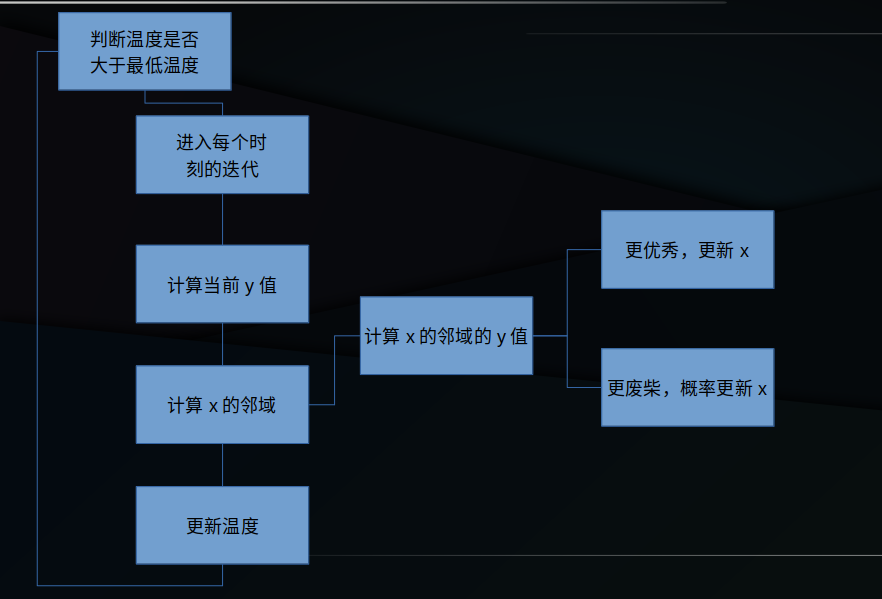
算法流程图
code
对https://blog.csdn.net/wfrainn/article/details/80303138进行的代码更新
result
直接输出 39.72958243492729 -32148.550564632504
记录最小数值 40.033185051881034 -32154.066628802473
发现保留的最小值确实更接近最小值
code
#coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
from monituihuo import aimFunction
import math
T=1000 # initiate temperature
Tmin=10 # minimun value of terperature
x = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=100) # initiate x
k=50 # times of internal circulation
y = 0 # initiate result
t=0 # time
xmin = 100
ymin = 100 # 观察凸显给出的数值
while T>Tmin:
for i in range(k):
y=aimFunction(x)
# generate a new x in the neighboorhood of x by transform function
xNew = x + np.random.uniform(low=-0.055, high=0.055) * T
if(0<=xNew and xNew <=100):
yNew=aimFunction(xNew)
if(yNew - y <= 0):
x = xNew
if(yNew < ymin):
xmin = x
ymin = yNew
else:
#metropolis principle
p = math.exp(-(yNew-y) / T)
r = np.random.uniform(low=0, high=1)
if r < p:
x=xNew
t+=1
# print(t)
T=(1000)/(1+t)
print('直接输出',x, aimFunction(x))
print('记录最小数值',xmin, aimFunction(xmin))
#coding=utf-8
from __future__ import division # 将新版本的特性引入
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
def aimFunction(x):
y=x**3-60*x**2-4*x+6
return y
x = [i/10 for i in range(1000)]
y = [0 for i in range(1000)]
for i in range(1000):
y[i] = aimFunction(x[i])
plt.plot(x,y)
# plt.show()
---------------------------我的天空里没有太阳,总是黑夜,但并不暗,因为有东西代替了太阳。虽然没有太阳那么明亮,但对我来说已经足够。凭借着这份光,我便能把黑夜当成白天。我从来就没有太阳,所以不怕失去。
--------《白夜行》


