写在前面:
IIS是Windows平台非常关键的组件,它是微软自带的Web服务器,可以很方便的帮助我们运行起一个网站,WebApi等服务,提供给外部来访问。即使它被很多java或者ruby的同学各种鄙视,被.Net平台的同学们吐槽性能不好,不够灵活,部署受限等等,它依然在默默的帮助我们非常轻松的构建起一个Web应用。在.Net Core中微软提供了更为强大的Web服务器 Kestrel ,它 是一个跨平台ASP.NET Core 的 web 服务器基于libuv,跨平台的异步 I/O 库。它可以单独使用来host一个web服务,也可以与反向代理服务器(如 IIS、Nginx 或 Apache)结合使用。 反向代理服务器接收到来自 Internet 的 HTTP 请求,并在进行一些初步处理后将这些请求转发到 Kestrel。
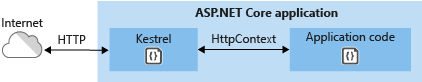
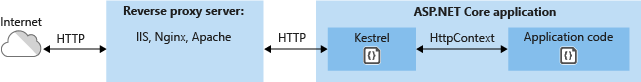
那么今天我们来聊一聊另外的两种可以self host的解决方案:
第一种方式:Owin
Owin 是 Open Web Interface for .NET 的简称,从字面意思解释可以看出OWIN是针对.NET平台的开放Web接口。那Web接口是谁和谁之间的接口呢?是Web应用程序与Web服务器之间的 接口,OWIN就是.NET Web应用程序与Web服务器之间的接口。为什么需要这样一个接口呢?因为.NET Web应用程序是运行于Web服务器之中的,.NET Web应用程序需要通过Web服务器接收用户的请求,并且通过Web服务器将响应内容发送用户。如果没有这样一个接口,.NET Web应用程序就要依赖于所运行的具体Web服务器,比如ASP.NET应用程序要依赖于IIS。有了这个接口,ASP.NET应用程序只需依赖这个抽象接口,不用关心所运行的Web服务器。所以我们可以得出下面的结论:
OWIN的作用就是通过引入一组抽象接口,解耦了.NET Web应用程序与Web服务器,再次体现了接口的重要性。
而我们知道在软件开发中,每次解耦都是一次很大的进步。
更近一层我们可以理解为:OWIN是对ASP.NET Runtime的抽象。它将应用与服务器解耦, 使得便携式 .NET Web 应用以及跨平台的愿望成为现实, 标准的 OWIN 应用可以在任何OWIN 兼容的服务器上运行,不再依赖与 Windows 和 IIS,我们更可以不用装一大堆笨重的IDE(如 visual studio)来开发web应用程序,也不再那么的依赖于IIS去Host我们的程序。 我们可以用下面的一张图来表示它究竟可以做什么:

具体使用如下:
新建EventsController 继承自:System.Web.Http.ApiController
public class EventsController : ApiController
{
[Authorize]
[Route("events")]
public IEnumerable<Event> Get()
{
return GetAllEventsFromRepo();
}
[Route("events/{id}")]
public Event GetById(Guid id)
{
return GetAllEventsFromRepo().First(x => x.EventId == id);
}
[Route("events")]
public IEnumerable<Event> GetByType(string type)
{
return GetAllEventsFromRepo().Where(x => x.EventType.Equals(type, StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase));
}
[Route("events")]
public HttpResponseMessage Post(Event @event)
{
if (@event == null)
{
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
return new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Created);
}
private IEnumerable<Event> GetAllEventsFromRepo()
{
return new List<Event>
{
new Event
{
EventId = Guid.Parse("45D80D13-D5A2-48D7-8353-CBB4C0EAABF5"),
Timestamp = DateTime.Parse("2014-06-30T01:37:41.0660548"),
EventType = "SearchView"
},
new Event
{
EventId = Guid.Parse("83F9262F-28F1-4703-AB1A-8CFD9E8249C9"),
Timestamp = DateTime.Parse("2014-06-30T01:37:52.2618864"),
EventType = "DetailsView"
},
new Event
{
EventId = Guid.Parse("3E83A96B-2A0C-49B1-9959-26DF23F83AEB"),
Timestamp = DateTime.Parse("2014-06-30T01:38:00.8518952"),
EventType = "SearchView"
}
};
}
}
然后新建一个Startup.cs的class,我们可以看到这里体现了Middleware(中间件)的思想,即插即用,熟悉.Net Core的同学的对它并不陌生。
public class Startup
{
public void Configuration(IAppBuilder app)
{
var config = new HttpConfiguration();
config.MapHttpAttributeRoutes();
app.UseWebApi(config);
var builder = new ContainerBuilder();
builder.RegisterApiControllers(typeof(EventsController).Assembly);
var container = builder.Build();
app.UseAutofacMiddleware(container);
app.UseAutofacWebApi(config);
}
}
上面代码中的ContainerBuilder 是Autofac提供的功能,它可以让我们动态的注册Controller到容器中,还有一个非常重要的东西就是 HttpConfiguration,它用来表示 HttpServer 实例的配置。
然后我们只需要下面一句代码就可以让我们API 工作起来了:
WebApp.Start<TestStartup>("http://localhost:51502")
这样通过 http://localhost:51502 地址就可以访问我们的服务了,非常的简单。
第二种方式:通过进程直接调用iisexpress.exe
iisexpress.exe我们很熟悉,它是windows平台自带的IIS 的运行文件,默认路径在: C:\Program Files\IIS Express 目录下,我们可以在代码中创建进程运行起这个exe就可以了。具体代码如下:
public class IISExpress : IDisposable
{
/// <summary>
/// Stores whether this instance has been disposed.
/// </summary>
private bool _isDisposed;
/// <summary>
/// Stores the IIS Express process.
/// </summary>
private Process _process;
/// <summary>
/// Performs application-defined tasks associated with freeing, releasing, or resetting unmanaged resources.
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts IIS Express using the specified directory path and port.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="directoryPath">
/// The directory path.
/// </param>
/// <param name="port">
/// The port.
/// </param>
/// <param name="address">
/// The address.
/// </param>
public void Start(string directoryPath, int port, Uri address)
{
if (_process != null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("The IISExpress process is already running.");
}
if (address != null)
{
try
{
var request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(address);
var webResponse = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
if (webResponse.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.OK)
{
return;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Trace.WriteLine(ex);
}
}
var iisExpressPath = DetermineIisExpressPath();
var arguments = string.Format(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture, "/path:\"{0}\" /port:{1}", directoryPath, port);
var info = new ProcessStartInfo(iisExpressPath)
{
WindowStyle = ProcessWindowStyle.Hidden,
ErrorDialog = true,
LoadUserProfile = true,
CreateNoWindow = false,
UseShellExecute = false,
Arguments = arguments
};
var startThread = new Thread(() => StartIisExpress(info))
{
IsBackground = true
};
startThread.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// Releases unmanaged and - optionally - managed resources.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing">
/// <c>true</c> to release both managed and unmanaged resources; <c>false</c> to release only unmanaged resources.
/// </param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (_isDisposed)
{
return;
}
if (disposing)
{
if (_process != null)
{
// Free managed resources
if (_process.HasExited == false)
{
SendStopMessageToProcess(_process.Id);
_process.Close();
}
_process.Dispose();
}
}
// Free native resources if there are any
_isDisposed = true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines the IIS express path.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>
/// A <see cref="String" /> instance.
/// </returns>
private static string DetermineIisExpressPath()
{
string iisExpressPath;
if (Environment.Is64BitOperatingSystem)
{
iisExpressPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.ProgramFilesX86);
}
else
{
iisExpressPath = Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.ProgramFiles);
}
iisExpressPath = Path.Combine(iisExpressPath, @"C:\Program Files\IIS Express\iisexpress.exe");
return iisExpressPath;
}
/// <summary>
/// The send stop message to process.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="processId">
/// The process id.
/// </param>
private static void SendStopMessageToProcess(int processId)
{
try
{
for (var ptr = NativeMethods.GetTopWindow(IntPtr.Zero);
ptr != IntPtr.Zero;
ptr = NativeMethods.GetWindow(ptr, 2))
{
uint num;
NativeMethods.GetWindowThreadProcessId(ptr, out num);
if (processId == num)
{
var handle = new HandleRef(null, ptr);
NativeMethods.PostMessage(handle, 0x12, IntPtr.Zero, IntPtr.Zero);
return;
}
}
}
catch (ArgumentException)
{
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts the IIS express.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">
/// The info.
/// </param>
[SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Design", "CA1031:DoNotCatchGeneralExceptionTypes",
Justification = "



