1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 import java.util.Set; 3 import java.util.regex.Matcher; 4 import java.util.regex.Pattern; 5 import java.util.Arrays; 6 import java.util.HashMap; 7 import java.util.Map; 8 9 public class Main { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 12 Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 13 StringBuilder a = new StringBuilder(); 14 String[] key = {"abstract", "assert", "boolean", "break", "byte", "case", "catch", "char", "class", "const", "continue", "default", "do", "double", "else", "enum", "extends", "false", "final", "finally", "float", "for", "goto", "if", "implements", "import", "instanceof", "int", "interface", "long", "native", "new", "null", "package", "private", "protected", "public", "return", "short", "static", "strictfp", "super", "switch", "synchronized", "this", "throw", "throws", "transient", "true", "try", "void", "volatile", "while"}; 15 int n; 16 int flag = 0; 17 String inputLine = input.nextLine(); 18 while (!inputLine.equals("exit")) { 19 a.append(inputLine.replaceAll("//.*", " ").replaceAll("\".*\"", " ")); 20 inputLine = input.nextLine(); 21 flag = 1; 22 } 23 if( flag == 0 ){ 24 System.out.println("wrong format"); 25 return; 26 } 27 String s = a.toString(); 28 Pattern p = Pattern.compile("/\\**(.*?)/"); 29 Matcher m = p.matcher(s); 30 while (m.find()) { 31 s = s.replace(m.group(), " "); 32 m = p.matcher(s); 33 } 34 p = Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); 35 m = p.matcher(s); 36 while (m.find()) { 37 s = s.replace(m.group(), " "); 38 p = Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\""); 39 m = p.matcher(s); 40 } 41 s = s.replace("\\[|\\]\\-\\*\\/\\+\\>\\=\\!\\:\\[^a-zA-Z]\\\\", " "); 42 for (String strr : key) { 43 Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\b" + strr + "\\b"); 44 Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(s); 45 n = 0; 46 while (matcher.find()) { 47 n++; 48 } 49 if (n != 0) { 50 map.put(strr, n); 51 } 52 } 53 Object[] arr = map.keySet().toArray(); 54 Arrays.sort(arr); 55 for (Object k : arr) { 56 System.out.println(map.get(k) + "\t" + k); 57 } 58 } 59 }
源码分析:先将所有关键词存入一份字符串数组,再输入这段源码,去除其中的标点符号,以及//后的内容,再将查找到的关键词存入一个Map,再通过关键词出现次数进行排序,最后再输出结果,还使用了Matcher和Pattern进行对源码有效部分进行比较。
题目集(10) 容器-HashMap-排序:
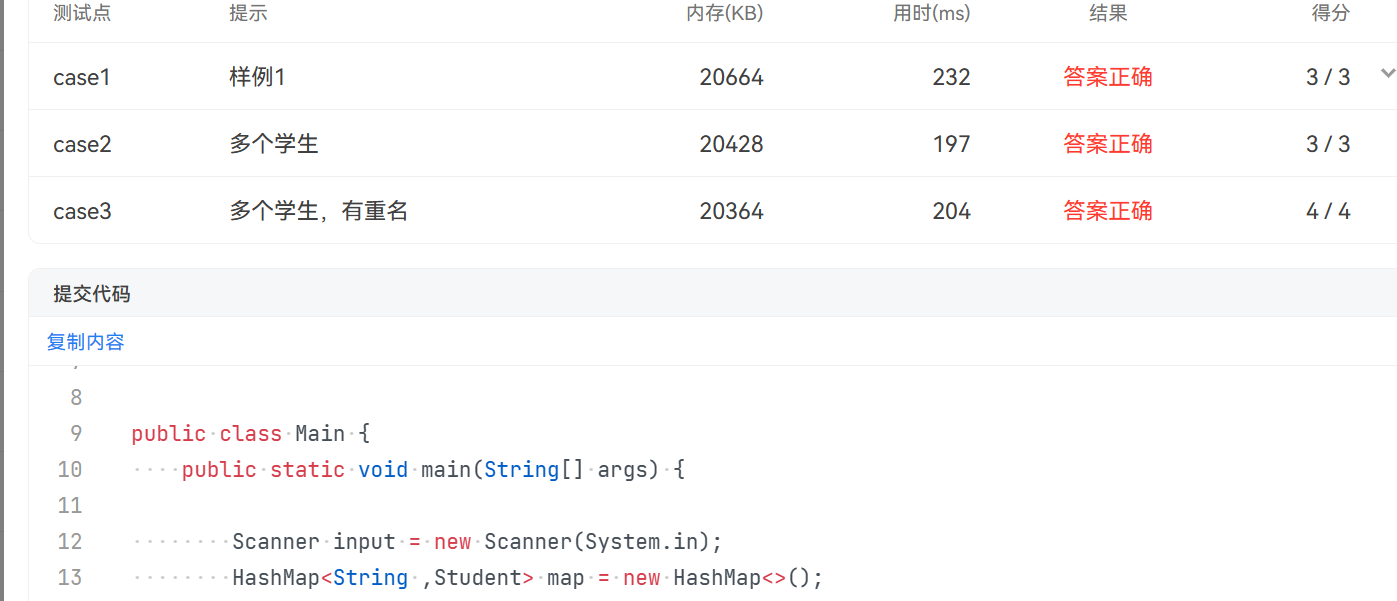
需求分析:输入多个学生的成绩信息,按照学号排序,并同时输出名字和总成绩。
源码:
1 import java.util.HashMap; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 import java.util.Arrays; 4 import java.util.List; 5 import java.util.ArrayList; 6 import java.util.Collections; 7 8 9 public class Main { 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 13 HashMap<String ,Student> map = new HashMap<>(); 14 15 while (true){ 16 String str = input.nextLine(); 17 if(str.equals("end")) break; 18 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 19 Student student = new Student(str1[1],str1[2]); 20 map.put(str1[0], student); 21 } 22 23 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(map.keySet()); 24 Collections.sort(list,Collections.reverseOrder()); 25 26 for (String key : list) { 27 for (HashMap.Entry<String, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) { 28 if (entry.getKey().equals(key)) { 29 System.out.println(entry.getKey()+" "+ entry.getValue().getStudent()+" "+entry.getValue().getGrades()); 30 break; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 public static String getKey(HashMap<String,String> map,String value){ 36 String key = null; 37 38 for(String getKey: map.keySet()){ 39 if(map.get(getKey).equals(value)){ 40 key = getKey; 41 } 42 } 43 return key; 44 } 45 46 } 47 class Student{ 48 private String student; 49 private String grades; 50 public Student(String student,String grades){ 51 this.student = student; 52 this.grades = grades; 53 54 } 55 56 public String getStudent() { 57 return student; 58 } 59 60 public void setStudent(String student) { 61 this.student = student; 62 } 63 64 public String getGrades() { 65 return grades; 66 } 67 68 public void setGrades(String grades) { 69 this.grades = grades; 70 } 71 }
源码分析:创建一个Student类,使Hashmap中的value值为Student型,这样储存信息的时候可以同时储存多项信息,接着就是按行输入学生的信息直到输入end为止,本题还自行定义了一个静态方法,通过value值找到对应的key值。
题目集(11) jmu-Java-04面向对象进阶-03-接口-自定义接口ArrayIntegerStack:
定义IntegerStack接口,用于声明一个存放Integer元素的栈的常见方法:
public Integer push(Integer item);
//如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。如果栈满,也返回null。如果插入成功,返回item。
public Integer pop(); //出栈,如果为空,则返回null。出栈时只移动栈顶指针,相应位置不置为null
public Integer peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如果为空,则返回null.
public boolean empty(); //如果为空返回true
public int size(); //返回栈中元素个数
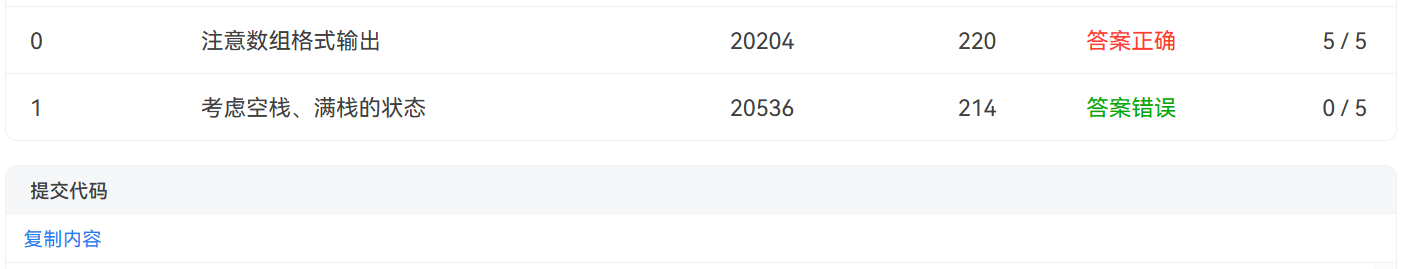
定义IntegerStack的实现类ArrayIntegerStack,内部使用数组实现。创建时,可指定内部数组大小。
源码:
1 import java.io.PrintStream; 2 import java.util.Arrays; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 import java.util.Stack; 5 6 7 8 public class Main { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 11 int n = input.nextInt(); 12 int m = input.nextInt(); 13 ArrayIntegerStack stack = new ArrayIntegerStack(n); 14 15 for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++) { 16 int c = input.nextInt(); 17 System.out.println(stack.push(c)); 18 } 19 System.out.println(stack.peek()+","+stack.empty()+","+stack.size()); 20 System.out.println(stack); 21 22 int x = input.nextInt(); 23 for (int i = 0 ; i < x ; i++){ 24 System.out.println(stack.pop()); 25 } 26 27 System.out.println(stack.peek()+","+stack.empty()+","+stack.size()); 28 System.out.println(stack); 29 30 31 32 } 33 } 34 interface IntegerStack { 35 public Integer push(Integer item); //如果item为null,则不入栈直接返回null。如果栈满,也返回null。如果插入成功,返回item 36 public Integer pop(); //出栈,如果为空,则返回null。出栈时只移动栈顶指针,相应位置不置为null 37 public Integer peek(); //获得栈顶元素,如果为空,则返回null 38 public boolean empty(); //如果为空返回true 39 public int size(); //返回栈中元素个数 40 } 41 42 class ArrayIntegerStack implements IntegerStack{ 43 private Integer[] arr; 44 private int top = 0; 45 46 public ArrayIntegerStack(int n){ 47 arr = new Integer[n]; 48 Arrays.fill(arr, null); 49 } 50 51 public ArrayIntegerStack(){ 52 53 } 54 55 @Override 56 public String toString() { 57 return Arrays.toString(arr); 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public Integer push(Integer item) { 62 if (item == null || arr.length == top){ 63 return null; 64 } 65 arr[top++] = item; 66 return item; 67 } 68 69 @Override 70 public Integer pop() { 71 if (top == 0){ 72 return null; 73 } 74 return arr[--top]; 75 } 76 77 @Override 78 public Integer peek() { 79 if (top == 0){ 80 return null; 81 } 82 return arr[top - 1]; 83 } 84 85 @Override 86 public boolean empty() { 87 return top == 0; 88 } 89 90 @Override 91 public int size() { 92 return top; 93 } 94 }
源码分析:ArrayIntegerStack类跟栈类有点类似。只不过在ArrayIntegerStack中数据是以数组的形式储存的,所以push,pop,peek方法类型都改变了
课程成绩统计系统:
需求分析:需求较多,见原PTA

源码:
1 import java.util.*; 2 import java.util.HashMap; 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Iterator; 5 public class Main { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 8 9 ArrayList<String> allstr = new ArrayList<>(); 10 ArrayList<Course> course = new ArrayList<>(); 11 ArrayList<ChooseCourse> chooseCourses = new ArrayList<>(); 12 ArrayList<String> classes = new ArrayList<>(); 13 HashMap<Integer, String> student = new HashMap<>(); 14 15 for (int i = 0; ; i++) { 16 String str = input.nextLine(); 17 if (str.equals("end")) break; 18 allstr.add(str); 19 } 20 21 for (String str : allstr) { 22 if (str.matches("[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{2}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{2}")) { 23 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 24 if (!str1[1].matches("必修") && !str1[1].matches("选修") || !str1[2].matches("考试") && !str1[2].matches("考察")) { 25 System.out.println("wrong format"); 26 continue; 27 } 28 if (str1[1].matches("必修") && str1[2].matches("考察")) { 29 System.out.println(str1[0] + " : course type & access mode mismatch"); 30 continue; 31 } 32 String type; 33 String examType; 34 if (str1[1].matches("必修")) { 35 type = "必修"; 36 examType = "考试"; 37 } else { 38 type = "选修"; 39 if (str1[2].matches("考试")) { 40 examType = "考试"; 41 } else { 42 examType = "考察"; 43 } 44 } 45 Course course2 = new Course(str1[0], type, examType); 46 Iterator<Course> courseIterator = course.iterator(); 47 boolean ishave = false; 48 while (courseIterator.hasNext()) { 49 Course course3 = courseIterator.next(); 50 if (course3.getCourse().equals(course2.getCourse())) { 51 ishave = true; 52 } 53 } 54 if (!ishave) { 55 course.add(course2); 56 } 57 } else if (str.matches("[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{2}")) { 58 59 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 60 String type = "必修"; 61 String examType = "考试"; 62 if (!str1[1].equals("必修")) { 63 System.out.println("wrong format"); 64 continue; 65 } 66 Course course2 = new Course(str1[0], type, examType); 67 Iterator<Course> courseIterator = course.iterator(); 68 boolean ishave = false; 69 while (courseIterator.hasNext()) { 70 Course course3 = courseIterator.next(); 71 if (course3.getCourse().equals(course2.getCourse())) { 72 ishave = true; 73 } 74 } 75 if (!ishave) course.add(course2); 76 77 } else if (str.matches("[0-9]{8}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s(0|100|[1-9][0-9])\\s(0|100|[1-9][0-9])")) { 78 79 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 80 Iterator<Course> courseIterator = course.iterator(); 81 boolean hasCourse = false; 82 Course course1 = new Course(); 83 while (courseIterator.hasNext()) { 84 Course course2 = courseIterator.next(); 85 if (course2.getCourse().equals(str1[2])) { 86 hasCourse = true; 87 course1 = course2; 88 break; 89 } 90 } 91 if (!hasCourse) { 92 System.out.println(str1[2] + " does not exist"); 93 classes.add(str1[0].substring(0, 6)); 94 student.put(Integer.valueOf(str1[0]), str1[1]); 95 continue; 96 } 97 ChooseCourse chooseCourse = new ChooseCourse(course1, str1[1], str1[0],Integer.parseInt(str1[3]),Integer.parseInt(str1[4])); 98 99 Iterator<ChooseCourse> hasStudent = chooseCourses.iterator(); 100 boolean ishave = false; 101 while (hasStudent.hasNext()) { 102 ChooseCourse chooseCourse1 = hasStudent.next(); 103 if (chooseCourse1.getStudent().getStudent().equals(chooseCourse1.getStudent())) { 104 ishave = true; 105 break; 106 } 107 } 108 if(ishave){ 109 continue; 110 } 111 classes.add(str1[0].substring(0, 6)); 112 student.put(Integer.valueOf(str1[0]), str1[1]); 113 ChooseCourse chooseCourse1 = new ChooseCourse(course1, str1[1], str1[0], Integer.parseInt(str1[3]), Integer.parseInt(str1[4])); 114 chooseCourses.add(chooseCourse1); 115 116 } else if (str.matches("[0-9]{8}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z]{1,11}\\s(0|100|[1-9][0-9])")) { 117 118 String[] str1 = str.split(" "); 119 Iterator<Course> courseIterator = course.iterator(); 120 boolean hasCourse = false; 121 Course course1 = new Course(); 122 while (courseIterator.hasNext()) { 123 Course course2 = courseIterator.next(); 124 if (course2.getCourse().equals(str1[2])) { 125 hasCourse = true; 126 course1 = course2; 127 break; 128 } 129 } 130 if (!hasCourse) { 131 System.out.println(str1[2] + " does not exist"); 132 classes.add(str1[0].substring(0, 6)); 133 student.put(Integer.valueOf(str1[0]), str1[1]); 134 continue; 135 } 136 ChooseCourse chooseCourse = new ChooseCourse(course1, str1[1], str1[0], 0, 0); 137 138 Iterator<ChooseCourse> hasStudent = chooseCourses.iterator(); 139 boolean ishave = false; 140 while (hasStudent.hasNext()) { 141 ChooseCourse chooseCourse1 = hasStudent.next(); 142 if (chooseCourse1.getStudent().getStudent().equals(chooseCourse1.getStudent())) { 143 ishave = true; 144 break; 145 } 146 } 147 if(ishave){ 148 continue; 149 } 150 classes.add(str1[0].substring(0, 6)); 151 student.put(Integer.valueOf(str1[0]), str1[1]); 152 ChooseCourse chooseCourse1 = new ChooseCourse(course1, str1[1], str1[0], Integer.parseInt(str1[3]), 0); 153 chooseCourses.add(chooseCourse1); 154 } else { 155 System.out.println("wrong format"); 156 } 157 158 159 } 160 161 //对学生排序 162 List<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> listStudent = new ArrayList<>(student.entrySet()); 163 listStudent.sort(Map.Entry.comparingByKey()); 164 //输出学生信息 165 Iterator<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> itStudent = listStudent.iterator(); 166 while (itStudent.hasNext()) { 167 Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry = itStudent.next(); 168 Iterator<ChooseCourse> iterator = chooseCourses.iterator(); 169 int number = 0; 170 double scoreAll = 0; 171 172 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 173 ChooseCourse chooseCourse = iterator.next(); 174 if (String.valueOf(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue()).equals(chooseCourse.getStudent().getClass1().getClass1() + chooseCourse.getStudent().getStudent())) { 175 if (chooseCourse.getScore1().getNormalscore() == 0) { 176 System.out.println(chooseCourses.get(0).getStudent().getClass1().getClass1() + " " + chooseCourses.get(0).getStudent().getStudent() + " : access mode mismatch"); 177 continue; 178 } 179 number++; 180 if (chooseCourse.getCourse().getType().equals("必修")) { 181 scoreAll += chooseCourse.getScore1().getNormalscore() * 0.3 + chooseCourse.getScore1().getFinalscore() * 0.7; 182 } else { 183 scoreAll += chooseCourse.getScore2().getFinalscore(); 184 } 185 } 186 } 187 if (number == 0) { 188 System.out.println(String.valueOf(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue()).substring(0, 8) + " " + String.valueOf(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue()).substring(8) + " did not take any exams"); 189 190 continue; 191 } 192 System.out.println(String.valueOf(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue()).substring(0, 8) + " " + String.valueOf(entry.getKey() + entry.getValue()).substring(8) + " " + (int) (scoreAll / number)); 193 } 194 195 HashMap<Integer, String> courseX = new HashMap<>(); 196 Iterator<Course> courseIterator = course.iterator(); 197 while(courseIterator.hasNext()) 198 199 { 200 Iterator<ChooseCourse> iterator = chooseCourses.iterator(); 201 int number = 0; 202 double scoreAll = 0; 203 double scoreScore1 = 0; 204 double scoreScore2 = 0; 205 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 206 ChooseCourse s = iterator.next(); 207 if (s.getCourse() == courseIterator.next()) { 208 number++; 209 if (s.getCourse().getType().equals("必修")) { 210 scoreAll += s.getScore1().normalscore*0.3+s.getScore2().finalscore*0.7; 211 scoreScore1 += s.getScore1().normalscore; 212 scoreScore2 += s.getScore2().finalscore; 213 } else { 214 scoreAll += s.getScore2().finalscore; 215 scoreScore1 += s.getScore2().finalscore; 216 } 217 } 218 219 } 220 if (number == 0) { 221 System.out.println(courseIterator.next().getCourse() + " has no grades yet"); 222 continue; 223 } 224 if (courseIterator.next().getType().equals("必修")) { 225 courseX.put((int) (scoreAll / number), courseIterator.next().getCourse() + " " + (int) (scoreScore1 / number) + " " + (int) (scoreScore2 / number)); 226 System.out.println(courseIterator.next().getCourse() + " " + (int) (scoreScore1 / number) + " " + (int) (scoreScore2 / number) + " " + (int) (scoreAll / number)); 227 } else { 228 courseX.put((int) (scoreAll / number), courseIterator.next().getCourse() + " " + (int) (scoreScore1 / number)); 229 System.out.println(courseIterator.next().getCourse() + " " + (int) (scoreScore1 / number) + " " + (int) (scoreAll / number)); 230 } 231 } 232 233 //对课程排序(按成绩高低) 234 List<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> listCourse = new ArrayList<>(courseX.entrySet()); 235 listCourse.sort(Map.Entry.comparingByKey()); 236 for(int i = 0; i<listCourse.size();i++) 237 238 { 239 System.out.println(listCourse.get(i).getValue() + " " + listCourse.get(i).getKey()); 240 } 241 242 HashMap<Integer, String> classX = new HashMap<>(); 243 Iterator<String> classIterator = classes.iterator(); 244 while(classIterator.hasNext()) 245 { 246 Iterator<ChooseCourse> iterator = chooseCourses.iterator(); 247 int number = 0; 248 double scoreAll = 0; 249 while (iterator.hasNext()) { 250 ChooseCourse s = iterator.next(); 251 if (s.getStudent().getClass1().getClass1().substring(0, 6).equals(classIterator.next())) { 252 253 if(s.getScore1().getFinalscore() == 0 && s.getScore1().getNormalscore() == 0){ 254 continue; 255 } 256 number++; 257 if (s.getCourse().getType().equals("必修")) { 258 scoreAll += s.getScore1().normalscore*0.3+s.getScore2().finalscore*0.7; 259 } else { 260 scoreAll += s.getScore2().finalscore; 261 } 262 } 263 } 264 if (number == 0) { 265 System.out.println(classIterator.next() + " has no grades yet"); 266 continue; 267 } 268 classX.put((int) (scoreAll / number), classIterator.next()); 269 System.out.println(classIterator.next() + " " + (int) (scoreAll / number)); 270 } 271 //对班级排序(按成绩高低) 272 List<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> listClass = new ArrayList<>(classX.entrySet()); 273 listClass.sort(Map.Entry.comparingByKey()); 274 for(int i = listClass.size() - 1; i >=0;i--) 275 { 276 System.out.println(listClass.get(i).getValue() + " " + listClass.get(i).getKey()); 277 } 278 } 279 } 280 class ChooseCourse{ 281 private Course course; 282 private Student student; 283 private Score score1; 284 private Score score2; 285 public ChooseCourse(){ 286 } 287 public ChooseCourse(Course course, String student, String class1, int score1, int score2) { 288 this.course = course; 289 this.student = new Student(student, class1); 290 this.score1 = new ExamScore(score1, score2); 291 this.score2 = new CheckScore(score1, score2); 292 } 293 public Score getScore2(){ 294 return score2; 295 } 296 297 298 public Course getCourse() { 299 return course; 300 } 301 public Score getScore1() { 302 return score1; 303 } 304 public Student getStudent() { 305 return student; 306 } 307 } 308 class Course{ 309 private String course; 310 private String type; 311 private String examtype; 312 public Course(){ 313 } 314 public Course(String course,String type,String examtype){ 315 this.course = course; 316 this.type = type; 317 this.examtype = examtype; 318 } 319 public String getCourse() { 320 return course; 321 } 322 323 public String getType() { 324 return type; 325 } 326 327 } 328 class Student{ 329 private String student; 330 private Class class1; 331 public Student(String student,String class1){ 332 this.student = student; 333 this.class1 = new Class(class1); 334 } 335 public String getStudent() { 336 return student; 337 } 338 339 public Class getClass1() { 340 return class1; 341 } 342 343 } 344 class Class{ 345 private String class1; 346 347 public Class(String class1){ 348 this.class1 = class1; 349 } 350 public String getClass1() { 351 return class1; 352 } 353 354 } 355 abstract class Score{ 356 protected int normalscore; 357 protected int finalscore; 358 public Score(){ 359 } 360 public Score(int normalscore,int finalscore) 361 { 362 this.normalscore = normalscore; 363 this.finalscore = finalscore; 364 } 365 public int getFinalscore() { 366 return finalscore; 367 } 368 public int getNormalscore() { 369 return normalscore; 370 } 371 public void setFinalscore(int finalscore) { 372 this.finalscore = finalscore; 373 } 374 public void setNormalscore(int normalscore) { 375 this.normalscore = normalscore; 376 } 377 } 378 class ExamScore extends Score{ 379 private int examscore; 380 public ExamScore(){ 381 } 382 public ExamScore(int normalscore ,int finalscore) 383 { 384 this.examscore = (int)((double)(normalscore*0.3+finalscore*0.7)); 385 } 386 387 } 388 class CheckScore extends Score{ 389 private int checkscore; 390 public CheckScore(){ 391 } 392 public CheckScore(int normalscore, int finalscore) 393 { 394 this.checkscore = finalscore; 395 } 396 397 }
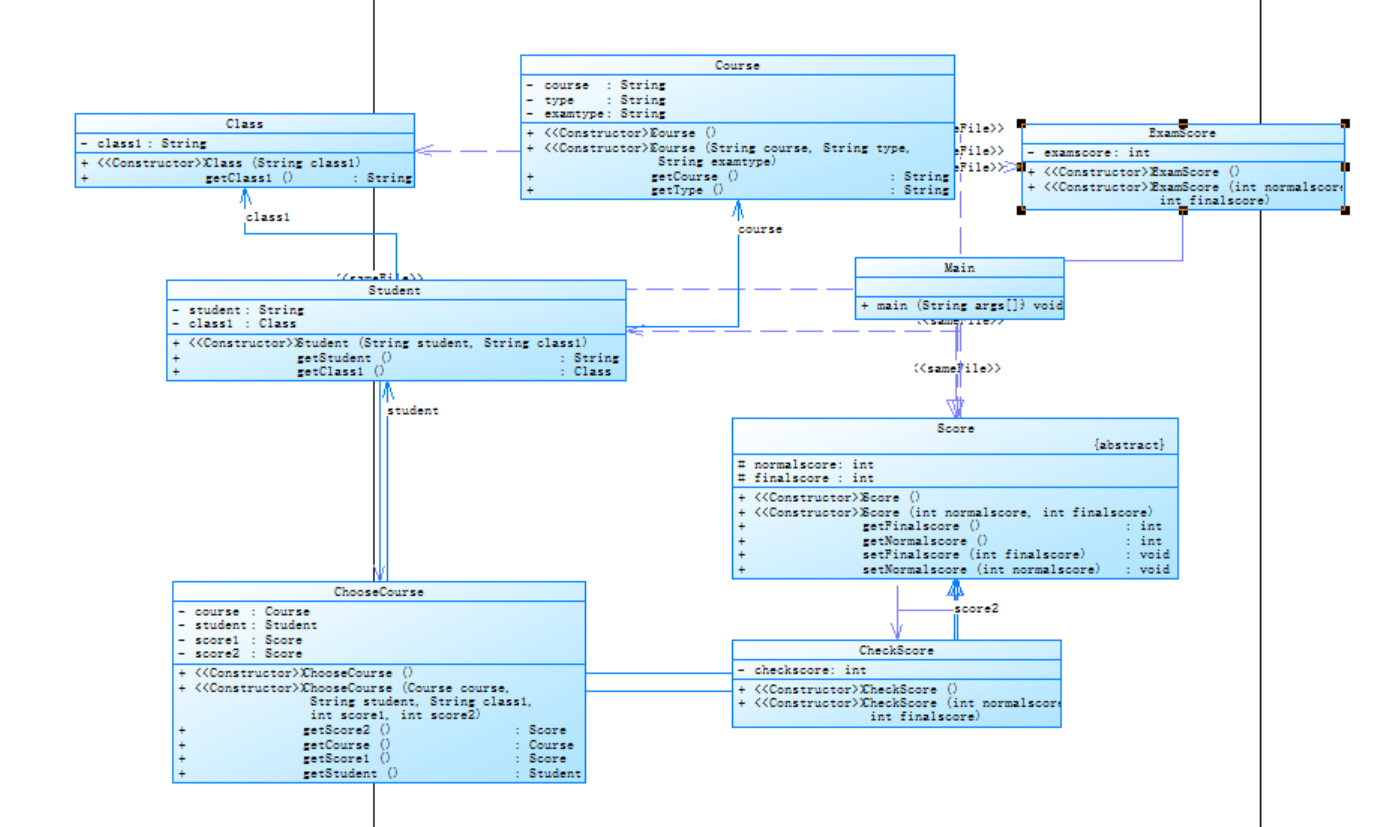
代码分析:信息分别分 ChooseCourse,Student,Class,Score 四个类,代码需要对键盘输入的信息先进行判断进而选择保存还是做出行为直到输入end为止,输出时输出所有课程信息,所有学生的成绩,以及班级的成绩信息。
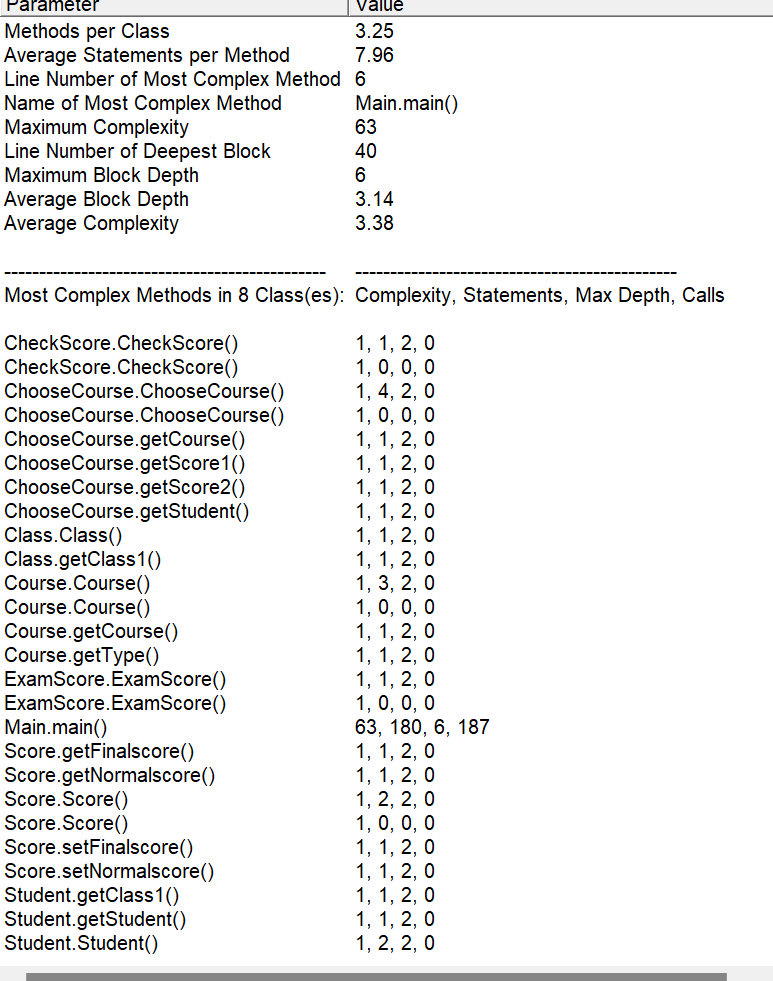
(3)踩坑心得
在题目集(10) 容器-HashMap-排序中,用了两个HashMap糅合到一起
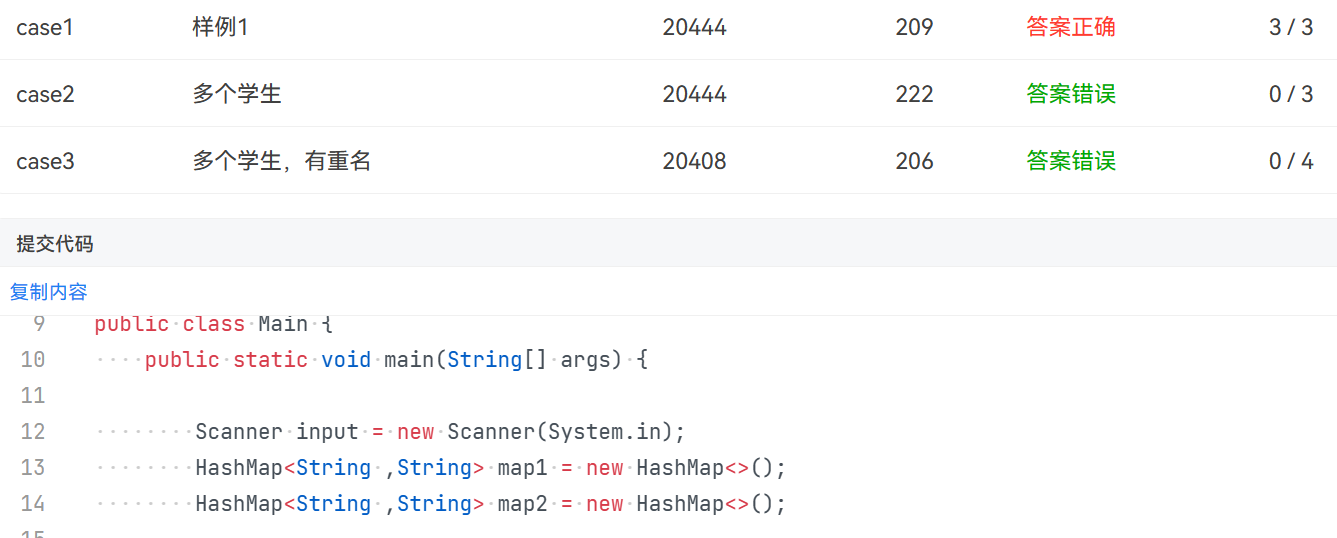
使用一个以后
在7-4 jmu-Java-04面向对象进阶-03-接口-自定义接口ArrayIntegerStack中未考虑空栈、满栈的状态,导致答案错误
(4)改进建议
在题目集(10) 容器-HashMap-排序中,原本在储存学生信息时,是用了两个HashMap,并没有将学生信息都整合在一个类里
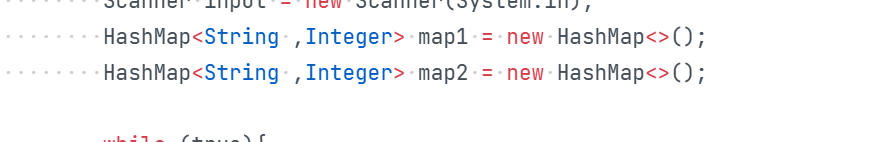
这样容易出错,而且查找的时候也很麻烦,后面就创建了一个Student类,方便了许多。
(5)总结
本阶段(10-16)周,我学到了很多东西,在前十周学习的Java基本语法及其用法,而在本阶段学习了许多开发规则和开发模式,虽然现在可能毫不沾边,但可能让以后的学习更轻松一些吧,我个人觉得在此阶段进行的翻转课堂活动让我学到了很多东西,受益匪浅,无论是在课前的准备,还是在源码编写以及ppt的制作还有表达能力,提升都是很大的!只是感觉PTA的作业难度有时太大然而时间又太短导致自己很难再规定的时间内完成,以及同时还有实验叠加在一起。
课程总结:本课程的教学理念可能还是偏向实践一点,但没有过度直接从c语言这门“水课”中到我认为高强度的学习可能刚开始有点难接受,教学方法觉得还是很好的,边讲边练使教学更加有效不只是嘴皮子功夫,使学习的东西熟记于心,教学组织即线上线下混合的方式让学习更加多元,教学过程即PTA是让我最痛苦的东西,本来就学东西慢意味着要花更多时间去学习题目中所不知道的内容,导致完成的总是不尽如人意!

