三、运算符与基本数据类型
python开发IDE: pycharm、eclipse
# 专业版
# 不要汉化
1、运算符
1结果是值
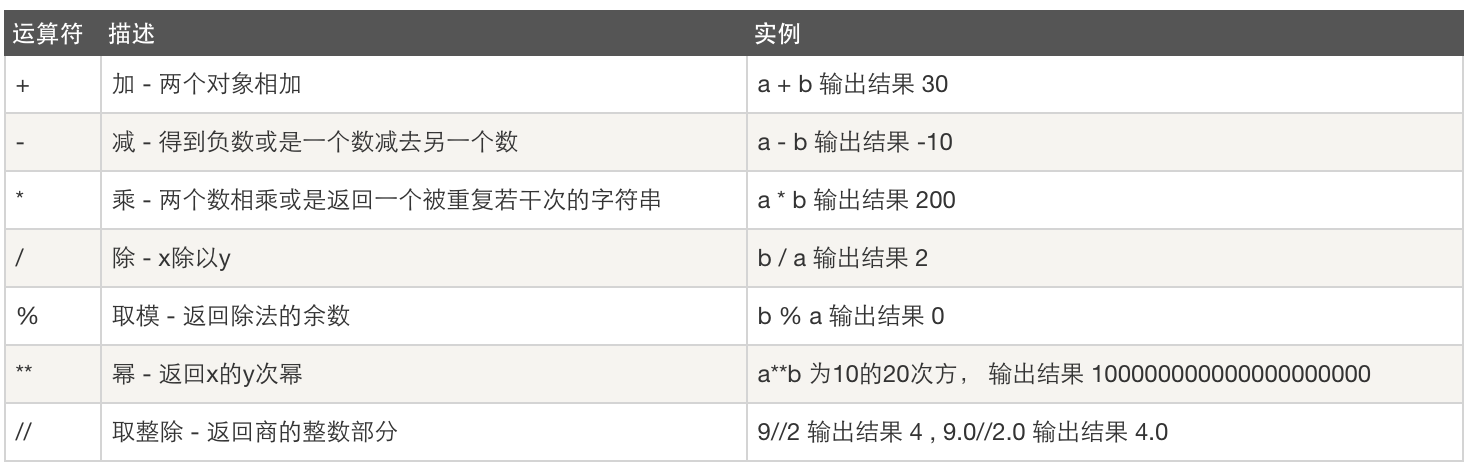
算数运算
a = 10 * 10
赋值运算
a = a + 1 a+=1

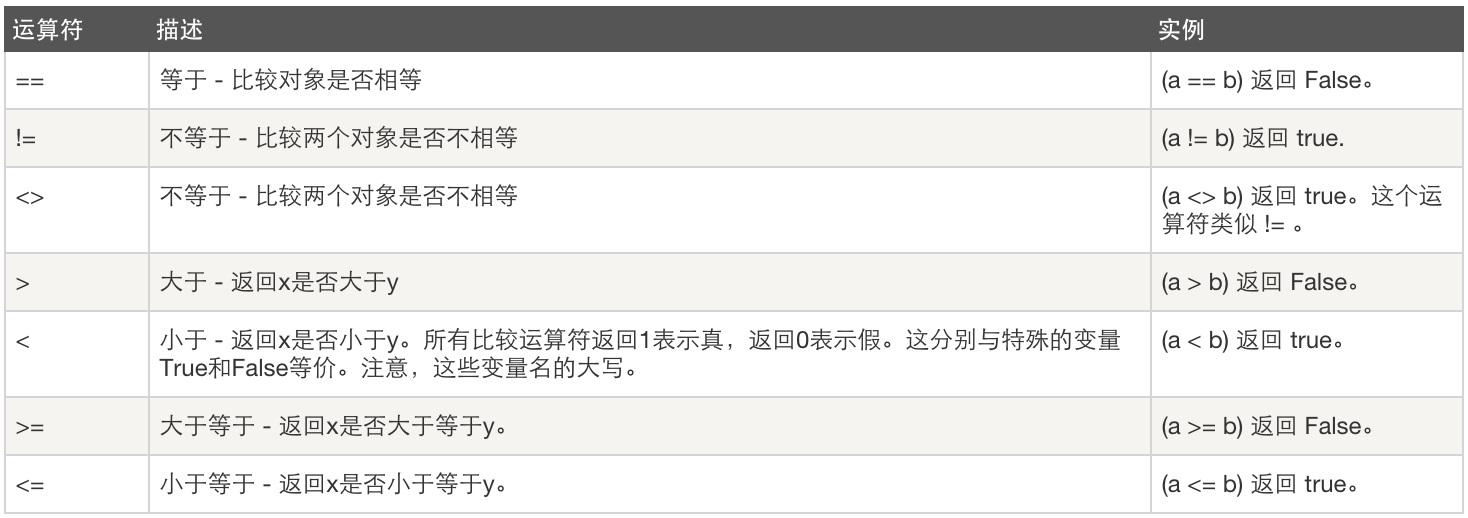
2结果是布尔值
比较运算
a = 1 > 5
逻辑运算
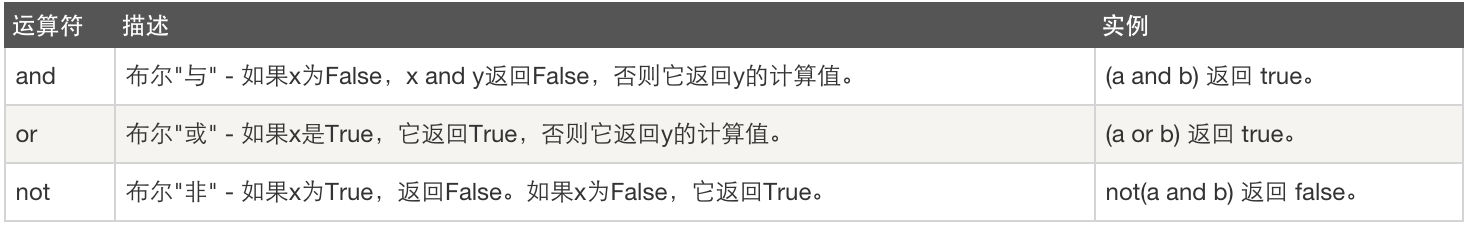
a = 1>6 or 1==1
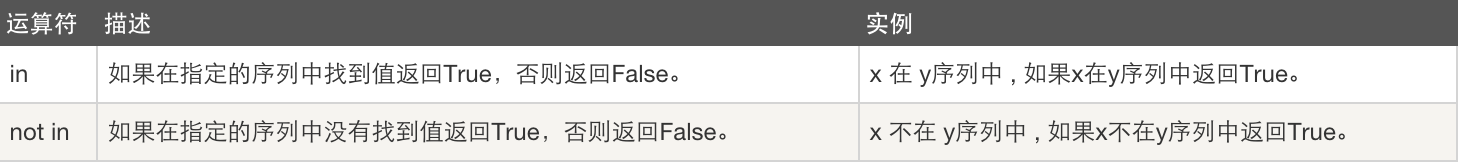
成员运算
a = "蚊" in "郑建文"
2、基本数据类型
基本数据类型:计算机顾名思义就是可以做数学计算的机器,因此,计算机程序理所当然地可以处理各种数值。但是,计算机能处理的远不止数值,还可以处理文本、图形、音频、视频、网页等各种各样的数据,不同的数据,需要定义不同的数据类型
1数字 int (整型),所有的功能,都放在int里
a1 = 123
a1 = 456
- int
将字符串转换为数字
a = "123"
print(type(a),a)
b = int(a)
print(type(b),b)
num = "0011"
v = int(num, base=16)
print(v)
- bit_lenght
# 当前数字的二进制,至少用n位表示
r = age.bit_length()
 int
int
2字符串 str
字符串:字符串是以单引号'或双引号"括起来的任意文本,比如'abc',"xyz"等等。请注意,''或""本身只是一种表示方式,不是字符串的一部分,因此,字符串'abc'只 有a,b,c这3个字符。如果'本身也是一个字符,那就可以用""括起来,比如"I'm OK"包含的字符是I,',m,空格,O,K这6个字符。
-
-
- 移除空白
- 分割
- 长度
- 索引
- 切片
-
s1 = "asdf"
s2 = "asdffas"
1.test = "aLex"
首字母大写
v = test.capitalize()
print(v)
2.所有变小写,casefold更牛逼,很多未知的对相应变小写
v1 = test.casefold()
print(v1)
v2 = test.lower()
print(v2)
3.设置宽度,并将内容居中,20 代指总长度
* 空白未知填充,一个字符,可有可无
v = test.center(20,"中")
print(v)
4.去字符串中寻找,寻找子序列的出现次数
test = "aLexalexr"
v = test.count('ex')
print(v)
test = "aLexalexr"
v = test.count('ex',5,6)
print(v)
5.以什么什么结尾
以什么什么开始
test = "alex"
v = test.endswith('ex')
v = test.startswith('ex')
print(v)
6.从开始往后找,找到第一个之后,获取其未知
> 或 >=
test = "alexalex"
未找到 -1
v = test.find('ex')
print(v)
index找不到,报错 忽略
test = "alexalex"
v = test.index('8')
print(v)
7.格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换为指定的值
test = 'i am {name}, age {a}'
print(test)
v = test.format(name='alex',a=19)
print(v)
test = 'i am {0}, age {1}'
print(test)
v = test.format('alex',19)
print(v)
8.格式化,传入的值 {"name": 'alex', "a": 19}
test = 'i am {name}, age {a}'
v1 = test.format(name='df',a=10)
v2 = test.format_map({"name": 'alex', "a": 19})
9.字符串中是否只包含 字母和数字
test = "123"
v = test.isalnum()
print(v)
10.是否是字母,汉子
test = "as2df"
v = test.isalpha()
print(v)
11.expandtabs,断句20,
test = "username\temail\tpassword\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123\nlaiying\tying@q.com\t123"
v = test.expandtabs(20)
print(v)
12 index找不到,报错 忽略
test = "alexalex"
v = test.index('8')
print(v)
13 当前输入是否是数字
test = "二" 1,②
v1 = test.isdecimal()
v2 = test.isdigit()
v3 = test.isnumeric()
print(v1,v2,v3)
14. 是否存在不可显示的字符
\t 制表符
\n 换行
test = "oiuas\tdfkj"
v = test.isprintable()
print(v)
15 判断是否全部是空格
test = ""
v = test.isspace()
print(v)
16 判断是否是标题
test = "Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is"
v1 = test.istitle()
print(v1)
v2 = test.title()
print(v2)
v3 = v2.istitle()
print(v3)
17 ***** 将字符串中的每一个元素按照指定分隔符进行拼接
test = "你是风儿我是沙"
print(test)
t = ' '
v = "_".join(test)
print(v)
18 判断是否全部是大小写 和 转换为大小写
test = "Alex"
v1 = test.islower()
v2 = test.lower()
print(v1, v2)
v1 = test.isupper()
v2 = test.upper()
print(v1,v2)
19移除指定字符串
有限最多匹配
test = "xa"
v = test.lstrip('xa')
v = test.rstrip('9lexxexa')
v = test.strip('xa')
print(v)
test.lstrip()
test.rstrip()
test.strip()
去除左右空白
v = test.lstrip()
v = test.rstrip()
v = test.strip()
print(v)
print(test)
去除\t \n
v = test.lstrip()
v = test.rstrip()
v = test.strip()
print(v)
20 对应关系替换
test = "aeiou"
test1 = "12345"
v = "asidufkasd;fiuadkf;adfkjalsdjf"
m = str.maketrans("aeiou", "12345")
new_v = v.translate(m)
print(new_v)
21 分割为三部分
test = "testasdsddfg"
v = test.partition('s')
print(v)
v = test.rpartition('s')
print(v)
22 分割为指定个数
v = test.split('s',2)
print(v)
test.rsplit()
23 分割,只能根据,true,false:是否保留换行
test = "asdfadfasdf\nasdfasdf\nadfasdf"
v = test.splitlines(False)
print(v)
24 以xxx开头,以xx结尾
test = "backend 1.1.1.1"
v = test.startswith('a')
print(v)
test.endswith('a)
25 大小写转换
test = "aLex"
v = test.swapcase()
print(v)
26 字母,数字,下划线 : 标识符 def class
a = "def"
v = a.isidentifier()
print(v)
27 将指定字符串替换为指定字符串
test = "alexalexalex"
v = test.replace("ex",'bbb')
print(v)
v = test.replace("ex",'bbb',2)
print(v)
7个基本魔法
join '_'.join("asdfasdf")
split
find
strip
upper
lower
replace
4个灰魔法
est = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来"
一、for循环
for 变量名 in 字符串:
变量名
break
continue
index = 0
while index < len(test):
v = test[index]
print(v)
index += 1
print('=======')
for zjw in test:
print(zjw)
test = "郑建文妹子有种冲我来"
for item in test:
print(item)
break
for item in test:
continue
print(item)
二、索引,下标,获取字符串中的某一个字符
v = test[3]
print(v)
三、切片
v = test[0:-1] 0=< <1
print(v)
四、获取长度
Python3: len获取当前字符串中由几个字符组成
v = len(test)
print(v)
注意:
len("asdf")
for循环
索引
切片
五、获取连续或不连续的数字,
Python2中直接创建在内容中
python3中只有for循环时,才一个一个创建
r1 = range(10)
r2 = range(1,10)
r3 = range(1,10,2)
帮助创建连续的数字,通过设置步长来指定不连续
v = range(0, 100, 5)
for item in v:
print(item)
练习题:根据用户输入的值,输出每一个字符以及当前字符所在的索引位置
test = input(">>>")
for item in test:
print(item)
将文字 对应的索引打印出来:
test = input(">>>")
print(test) test = qwe test[0] test[1]
l = len(test) l = 3
print(l)
r = range(0,l) 0,3
for item in r:
print(item, test[item]) 0 q,1 w,2 e
test = input(">>>")
for item in range(0, len(test)):
print(item, test[item])
1个深灰魔法
字符串一旦创建,不可修改
一旦修改或者拼接,都会造成重新生成字符串
name = "zhengjianwen"
age = "18"
info = name + age
print(info)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号