好久没有总结了,最近也一直在学习。今天就把spring boot与其它技术的整合做个小总结,主要是jpa、redis和swagger2。公司里有用到这些,整合起来也很简单。
首先,新建一个Spring Boot 的项目,我这里用的是之前一篇Spring Boot学习笔记---Spring Boot 基础及使用idea搭建项目
是同一个项目。这里我就不重新建项目了。
项目目录
1.Spring Boot整合JPA
JPA我用的不是很多,但是在学习springboot和cloud的时候,都是用的jpa进行数据库的操作,如果感觉兴趣可以去学习一下。
1. 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.38</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
2.配置数据源
之前项目的配置文件是application.properties格式的,这里我换成了application.yml格式的文件。作用是一样的。
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring-cloud?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&characterSetResults=utf8
username: root
password: 1111
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create #第一次建表 create 后面用update
show-sql: true
3.创建实体对象,jpa根据注解自动建表
package com.springboot.first.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* @Package main.java.com.jpa.jpastart.entity
* @Description: 用户
* @auther MZ
* @create 2018/5/30 21:11
*/
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String username;
@Column
private String password;
//……省略
}
4.创建Dao层
package com.springboot.first.dao;
import com.springboot.first.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
/**
*
*/
public interface UserDao extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByUsername(String username);
}
5.创建service层
package com.springboot.first.service;
import com.springboot.first.dao.UserDao;
import com.springboot.first.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Package main.java.com.jpa.jpastart.service
* @Description: 用户service
* @auther MZ
* @create 2018/5/30 21:21
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public User findUserByName(String username) {
return userDao.findByUsername(username);
}
}
6.创建controller层
package com.springboot.first.controller;
import com.springboot.first.entity.User;
import com.springboot.first.service.UserService;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Package main.java.com.jpa.jpastart.controller
* @Description: 控制器
* @auther MZ
* @create 2018/5/30 21:23
*/
@RequestMapping("/user")
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/{username}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable("username") String username) {
return userService.findUserByName(username);
}
}
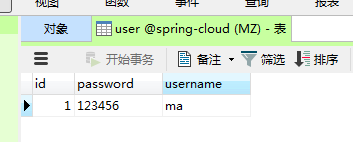
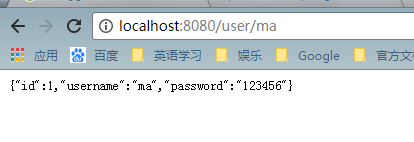
7.运行项目,查看结果,表建好后,可以插入几条测试数据,方便查看。
2.Spring Boot整合Redis
关于redis的安装,可以参考Redis学习-redis概述
1.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.添加配置信息
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password:
database: 1
pool:
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1
max-idle : 500
3.添加RedisDao类,通过注解@Repository注入Spring IoC容器中。
package com.springboot.first.dao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Package com.springboot.first.dao
* @Description: redis测试
* @auther MZ
* @create 2018/5/31 20:56
*/
@Repository
public class RedisDao {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate template;
public void setKey(String key, String value) {
ValueOperations<String, String > ops = template.opsForValue();
ops.set(key,value,1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
public String getValue(String key) {
ValueOperations<String, String> ops = this.template.opsForValue();
return ops.get(key);
}
}
4.在FirstApplicationTests 添加测试方法
package com.springboot.first;
import com.springboot.first.dao.RedisDao;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class FirstApplicationTests {
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
RedisDao redisDao;
@Test
public void testRedis(){
redisDao.setKey("name","ma");
redisDao.setKey("age","24");
System.out.println(redisDao.getValue("name"));
System.out.println(redisDao.getValue("age"));
}
}
5.运行

3.Spring Boot整合Swagger2,搭建Restful Api在线文档
Swagger是一个功能强大的在线API文档的框架,公司整合用来开发对外接口。
1.添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.6.1</version>
</dependency>
2.配置Swagger2,新建一个java类,做为配置类。
package com.springboot.first.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
/**
* @Package com.springboot.first.config
* @Description: swagger2配置
* @auther MZ
* @create 2018/6/1 21:12
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2 {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.springboot.first.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("springboot利用swagger构建api文档")
.description("学习使用,https://home.cnblogs.com/u/black-spike/")
.termsOfServiceUrl("https://home.cnblogs.com/u/black-spike/")
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
3.文档注解
Swagger2通过注解来生成API接口文档,文档信息包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息等。通常情况下生成的API文档,以下接口可以满足基本的需求:
- @Api:修饰整个类,用于描述Controller类。
- @ApiOperation:描述类的方法,或者说一个接口。
- @ApiParam:单个参数描述。
- @ApiModel:用于对象来接收参数。
- @ApiProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段。
- @ApiResponse:HTTP响应一个描述。
- @ApiResponses:HTTP响应的整体描述
- @APiIgnore:使用该注解,表述Swagger2忽略这个API。
- @ApiError:发生错误返回的信息。
- @ApiParamImplicit:一个请求参数。
11.@ApiParamsImplicit:多个请求参数。
4.在userservice中添加方法
public List<User> findAll() {
return userDao.findAll();
}
5.在UserController中添加一个RESTful风格的API接口
@ApiOperation(value = "用户列表", notes = "用户列表")
@RequestMapping(value = {""}, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> getUsers() {
List<User> users = userService.findAll();
return users;
}
6.运行,在页面输入http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
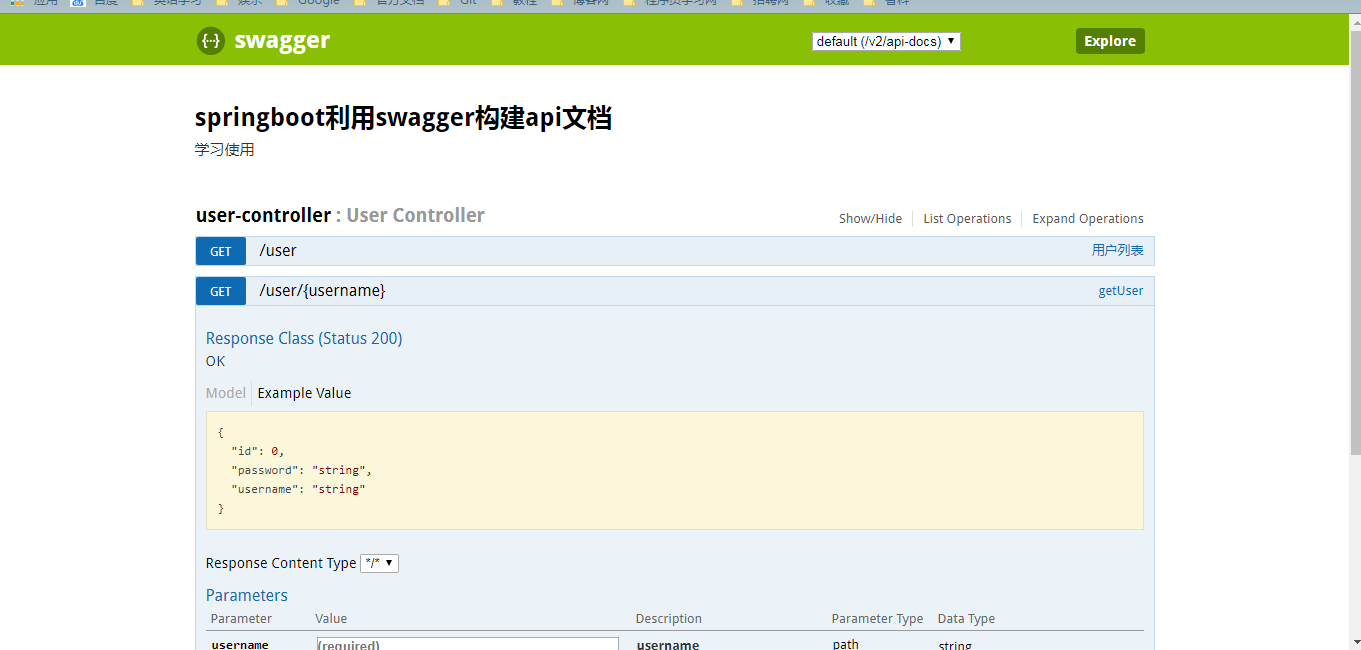
小结
一直学习,但是都没有好好的去总结。感觉这以后会用的到,到时候就方便一下了。



