今天,主要学习MyBatis的动态SQL。这是MyBatis的强大特性之一。
动态SQL的作用
MyBatis的动态SQL主要就是为了解决手动拼接SQL的麻烦
动态SQL中的元素
动态SQL是MyBatis的强大特性之一,MyBatis3采用了功能强大的基于OGNL的表达式来完成动态SQL。动态SQL主要元素如下表所示:
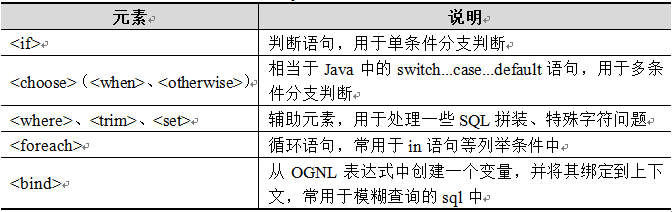
1.<if> 元素
在MyBatis中,<if>元素是最常用的判断语句,它类似于Java中的if语句,主要用于实现某些简单的条件选择。其基本使用示例如下:
<select id="findCustomerByNameAndJobs" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs !=''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
</select>
2.<choose>、<when>、<otherwise>元素
如果是java语言,这种情况就相当于switch...case...default语句。
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="username !=null and username !=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username}, '%')
</when>
<when test="jobs !=null and jobs !=''">
and jobs= #{jobs}
</when>
<otherwise>
and phone is not null
</otherwise>
</choose>
3. <where>、<trim>元素
在前面案例中,映射文件中编写的SQL后面都加入了“where 1=1”的条件,那么到底为什么要这么写呢?如果将where后“1=1”的条件去掉,那么MyBatis所拼接出来的SQL将会如下所示
select * from t_customer where and username like '%'? '%'
可以看出上面SQL语句明显存在SQL语法错误,而加入了条件“1=1”后,既保证了where后面的条件成立,又避免了where后面第一个词是and或者or之类的关键词。
不过“where 1=1”这种写法对于初学者来将不容易理解,并且也不够雅观。
针对上述情况中“where 1=1”,在MyBatis的SQL中就可以使用
select * from t_customer
<where>
<if test="username !=null and username !=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username}, '%')
</if>
<if test="jobs !=null and jobs !=''">
and jobs= #{jobs}
</if>
</where>
上述代码中,使用<where>元素对“where 1=1”条件进行了替换,<where>元素会自动判断组合条件下拼装的SQL语句,只有<where>内的条件成立时,才会在拼接SQL中加入where关键字,否则将不会添加;
即使where之后的内容有多余的“AND”或“OR”,<where>元素也会自动将它们去除。
select * from t_customer
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="username !=null and username !=''">
and username like concat('%',#{username}, '%')
</if>
<if test="jobs !=null and jobs !=''">
and jobs= #{jobs}
</if>
</trim>
<trim>的作用是去除特殊的字符串,它的prefix属性代表语句的前缀,prefixOverrides属性代表需要去除的哪些特殊字符串,功能和<where>基本是等效的。
4.<set>元素
在Hibernate中,想要更新某个对象,就需要发送所有的字段给持久化对象,这种想更新的每一条数据都要将其所有的属性都更新一遍的方法,其执行效率是非常差的。为此,在MyBatis中可以使用动态SQL中的<set>元素进行处理:
<update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
update t_customer
<set>
<if test="username !=null and username !=''">
username=#{username},
</if>
<if test="jobs !=null and jobs !=''">
jobs=#{jobs},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
上述配置中,使用了<set>和<if>元素结合来组装update语句。其中<set>元素会动态前置SET关键字,同时也会消除SQL语句中最后一个多余的逗号;
<if>元素用于判断相应的字段是否为空,如果不为空,就将此字段进行动态SQL组装,并更新此字段,否则不执行更新。
5.<foreach>元素
<foreach>元素是一个循环语句,它的作用是遍历集合,它能够很好地支持数组和List、Set接口的集合,对此提供遍历功能。它往往用于SQL中的in关键字。其基本使用示例如下所示:
<select id="findCustomerByIds" parameterType="List"
resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where id in
-- 判断为空可以用 list.size>0
<foreach item="id" index="index" collection="list"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
关于上述示例中
-
item:配置的是循环中当前的元素。
-
index:配置的是当前元素在集合的位置下标。
-
collection:配置的list是传递过来的参数类型(首字母小写),它可以是一个array、list(或collection)、Map集合的键、POJO包装类中数组或集合类型的属性名等。
-
open和close:配置的是以什么符号将这些集合元素包装起来。
-
separator:配置的是各个元素的间隔符。
注意:
在使用<foreach>时最关键也是最容易出错的就是collection属性,该属性是必须指定的,而且在不同情况下,该属性的值是不一样的。主要有以下3种情况:
1.如果传入的是单参数且参数类型是一个数组或者List的时候,collection属性值分别为array和list(或collection)。
2.如果传入的参数是多个的时候,就需要把它们封装成一个Map了,当然单参数也可以封装成Map集合,这时候collection属性值就为Map的键。
3.如果传入的参数是POJO包装类的时候,collection属性值就为该包装类中需要进行遍历的数组或集合的属性名。
6.<bind>元素
首先,看一下这条sql:
select * from t_customer where username like '%${value}%'
1.如果使用“${}”进行字符串拼接,则无法防止SQL注入问题;
2.如果改用concat函数进行拼接,则只针对MySQL数据库有效;
3.如果改用“||”进行字符串拼接,则只针对Oracle数据库有效。
这样,映射文件中的SQL就要根据不同的情况提供不同形式的实现,这显然是比较麻烦的,且不利于项目的移植。为了减少这种麻烦,就可以使用MyBatis的
MyBatis的
<select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="com.itheima.po.Customer"
resultType="com.itheima.po.Customer">
<!--_parameter.getUsername()表示传递进来的参数(也可以直接写成对应的参数变量名,如username)-->
<bind name="pattern_username" value="'%'+_parameter.getUsername()+'%'" />
select * from t_customer
where
<!--需要的地方直接引用<bind>元素的name属性值即可-->
username like #{pattern_username}
</select>
案例
开发工具:idea
Java环境: jdk1.8.0_121
数据库:SQLServer
项目结构:
jar包:
实体类Customer
public class Customer {
private Integer id; //主键
private String username; //客户名称
private String jobs; //职业
private String phone; //电话
//省略setter和getter方法
}
CustomerMapper.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace表示命名空间-->
<mapper namespace="com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper">
<!--if元素使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByNameAndJobs" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs !=''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
</select>
<!--choose when otherwise使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByNameOrJobs" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="username != null and username !=''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</when>
<when test="jobs != null and jobs != ''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</when>
<otherwise>
and phone is not null
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
<!--where trim 使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByNameAndJobs1" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer
<where>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs !=''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!--where trim 使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByNameAndJobs2" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs !=''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
</trim>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs !=''">
and jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
</select>
<!--set使用-->
<update id="updateCustomer" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer">
update t_customer
<set>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
username = #{username}
</if>
<if test="jobs != null and jobs != ''">
jobs = #{jobs}
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
phone = #{phone},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>
<!--foreach元素使用-->
<select id="findCustomerByIds" parameterType="List" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
select * from t_customer where id in
<foreach item="id" collection="list" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
<!--bind元素使用,根据客户名模糊查询信息-->
<select id="findCustomerByName" parameterType="com.ma.po.Customer" resultType="com.ma.po.Customer">
<!--_parameter.getUsername()也可以直接写成传入的字段属性名,即username-->
<bind name="pattern_username" value="'%'+_parameter.getUsername()+'%'"/>
select * from t_customer
where
username like #{pattern_username}
</select>
</mapper>
MybatisTest
package com.ma.test;
import com.ma.po.Customer;
import com.ma.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author mz
* @version V1.0
* @Description: Mybatis测试
* @create 2017-11-01 15:20
*/
public class MybatisTest {
/**
* 根据姓名和职业查询客户if
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameAndJobsTest() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("jack");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer>customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByNameAndJobs", customer);
//输出结果
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 根据客户名或职业查询客户信息choose when otherwise
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameOrJobsTest() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("jack");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByNameOrJobs", customer);
for (Customer customer1 : list) {
System.out.println(customer1);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 根据姓名和职业查询客户where
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameAndJobs1Test() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("jack");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer>customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByNameAndJobs1", customer);
//输出结果
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 根据姓名和职业查询客户trim
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameAndJobs2Test() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("jack");
customer.setJobs("teacher");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer>customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByNameAndJobs2", customer);
//输出结果
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 更新数据,set测试
*/
@Test
public void updateCustomerTest() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(3);
customer.setPhone("1254587855");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回影响行数
int rows = sqlSession.update("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.updateCustomer", customer);
if (rows > 0) {
System.out.println("修改了"+ rows +"条数据!");
} else {
System.out.println("failed");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* foreach测试
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByIdsTest() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建List集合,封装查询id
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByIds", ids);
for (Customer customer : customers) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
/**
* 模糊查询bind
*/
@Test
public void findCustomerByNameTest() {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSession();
//创建Customer对象,封装需要组合查询的条件
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setUsername("j");
//执行SqlSession的查询方法,返回结果集
List<Customer> customers = sqlSession.selectList("com.ma.mapper.CustomerMapper.findCustomerByName", customer);
for (Customer customer1 : customers) {
System.out.println(customer1);
}
//关闭SqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
}
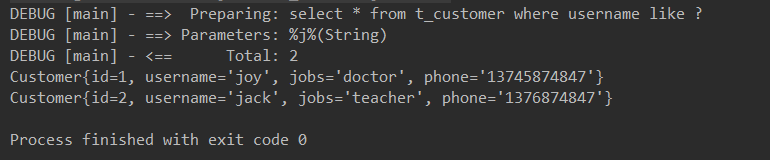
部分运行结果
小结
首先对MyBatis框架的动态SQL元素作了简要了解,然后分别对这些主要的动态SQL元素进行了详细说明。
通过学习可以了解常用动态SQL元素的主要作用,并能够掌握这些元素在实际开发中如何使用。
在MyBatis框架中,这些动态SQL元素的使用十分重要,熟练的掌握它们能够极大的提高开发效率。
以上内容是根据Java EE企业级应用开发教程(Spring+Spring MVC+MyBatis)做的一些笔记和总结。



