最近工作中涉及到和app相关的测试工作,需要用到mock,特意网上查了些资料,发现有很多工具可以实现app的mock,但是经过我反复试用后,发现mitmproxy这个工具非常的强大
我认为mitmproxy的最大优势有2个
a、使用简单,上手成本极低
b、可以完美的python脚本集成,可以对http请求/websock请求做高度定制化且自动化的处理,更重要的是,他可以热加载
另外如果大家的工作涉及到app的测试,我强烈建议大家要使用代理抓包分析接口请求,有以下几个优势
a、可以比较不同平台app的接口处理逻辑,请求频率、触发条件 是否一样
b、可以观察app的请求频率是否合理,不合理的请求频率会浪费客户的流量
下面我们进入正题
一、前期准备
1、官网地址(有非常详细的介绍,建议去看下)
https://mitmproxy.org/
2、安装(直接使用pip安装即可)
1 | pip install mitmproxy |
安装后大家可以使用搜索工具搜索如下文件:mitmproxy.exe\mitmweb.exe\mitmweb.exe,然后执行下面的命令,有输出即可证明安装成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | >mitmdump.exe --versionMitmproxy: 8.0.0Python: 3.8.10OpenSSL: OpenSSL 1.1.1n 15 Mar 2022Platform: Windows-10-10.0.19045-SP0>mitmproxy.exe --versionMitmproxy: 8.0.0Python: 3.8.10OpenSSL: OpenSSL 1.1.1n 15 Mar 2022Platform: Windows-10-10.0.19045-SP0>mitmweb.exe --versionMitmproxy: 8.0.0Python: 3.8.10OpenSSL: OpenSSL 1.1.1n 15 Mar 2022Platform: Windows-10-10.0.19045-SP0 |
3、启动
其实3个命令的启动是一样的,这里我认为mitmweb.exe是最适合的最强大,既有web界面,也可以集成python脚本,所以今天以介绍mitmweb.exe这个命令为主
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 | >mitmweb.exe --helpusage: mitmweb [options]optional arguments: -h, --help show this help message and exit --version show version number and exit --options Show all options and their default values --commands Show all commands and their signatures --set option[=value] Set an option. When the value is omitted, booleans are set to true, strings and integers are set to None (if permitted), and sequences are emptied. Boolean values can be true, false or toggle. Sequences are set using multiple invocations to set for the same option. -q, --quiet Quiet. -v, --verbose Increase log verbosity. --mode MODE, -m MODE Mode can be "regular", "transparent", "socks5", "reverse:SPEC", or "upstream:SPEC". For reverse and upstream proxy modes, SPEC is host specification in the form of "http[s]://host[:port]". --no-anticache --anticache Strip out request headers that might cause the server to return 304-not-modified. --no-showhost --showhost Use the Host header to construct URLs for display. --rfile PATH, -r PATH Read flows from file. --scripts SCRIPT, -s SCRIPT Execute a script. May be passed multiple times. --stickycookie FILTER Set sticky cookie filter. Matched against requests. --stickyauth FILTER Set sticky auth filter. Matched against requests. --save-stream-file PATH, -w PATH Stream flows to file as they arrive. Prefix path with + to append. The full path can use python strftime() formating, missing directories are created as needed. A new file is opened every time the formatted string changes. --no-anticomp --anticomp Try to convince servers to send us un-compressed data.Mitmweb: --no-web-open-browser --web-open-browser Start a browser. --web-port PORT Web UI port. --web-host HOST Web UI host. --web-columns WEB_COLUMNS Columns to show in the flow list May be passed multiple times.Proxy Options: --listen-host HOST Address to bind proxy to. --listen-port PORT, -p PORT Proxy service port. --no-server, -n --server Start a proxy server. Enabled by default. --ignore-hosts HOST Ignore host and forward all traffic without processing it. In transparent mode, it is recommended to use an IP address (range), not the hostname. In regular mode, only SSL traffic is ignored and the hostname should be used. The supplied value is interpreted as a regular expression and matched on the ip or the hostname. May be passed multiple times. --allow-hosts HOST Opposite of --ignore-hosts. May be passed multiple times. --tcp-hosts HOST Generic TCP SSL proxy mode for all hosts that match the pattern. Similar to --ignore-hosts, but SSL connections are intercepted. The communication contents are printed to the log in verbose mode. May be passed multiple times. --upstream-auth USER:PASS Add HTTP Basic authentication to upstream proxy and reverse proxy requests. Format: username:password. --proxyauth SPEC Require proxy authentication. Format: "username:pass", "any" to accept any user/pass combination, "@path" to use an Apache htpasswd file, or "ldap[s]:url_server_ldap[:port]:dn_auth:password:dn_subtree" for LDAP authentication. --no-rawtcp --rawtcp Enable/disable raw TCP connections. TCP connections are enabled by default. --no-http2 --http2 Enable/disable HTTP/2 support. HTTP/2 support is enabled by default.SSL: --certs SPEC SSL certificates of the form "[domain=]path". The domain may include a wildcard, and is equal to "*" if not specified. The file at path is a certificate in PEM format. If a private key is included in the PEM, it is used, else the default key in the conf dir is used. The PEM file should contain the full certificate chain, with the leaf certificate as the first entry. May be passed multiple times. --cert-passphrase PASS Passphrase for decrypting the private key provided in the --cert option. Note that passing cert_passphrase on the command line makes your passphrase visible in your system's process list. Specify it in config.yaml to avoid this. --no-ssl-insecure --ssl-insecure, -k Do not verify upstream server SSL/TLS certificates. --key-size KEY_SIZE TLS key size for certificates and CA.Client Replay: --client-replay PATH, -C PATH Replay client requests from a saved file. May be passed multiple times.Server Replay: --server-replay PATH, -S PATH Replay server responses from a saved file. May be passed multiple times. --no-server-replay-kill-extra --server-replay-kill-extra Kill extra requests during replay (for which no replayable response was found). --no-server-replay-nopop --server-replay-nopop Don't remove flows from server replay state after use. This makes it possible to replay same response multiple times. --no-server-replay-refresh --server-replay-refresh Refresh server replay responses by adjusting date, expires and last-modified headers, as well as adjusting cookie expiration.Map Remote: --map-remote PATTERN, -M PATTERN Map remote resources to another remote URL using a pattern of the form "[/flow-filter]/url- regex/replacement", where the separator can be any character. May be passed multiple times.Map Local: --map-local PATTERN Map remote resources to a local file using a pattern of the form "[/flow-filter]/url- regex/file-or-directory-path", where the separator can be any character. May be passed multiple times.Modify Body: --modify-body PATTERN, -B PATTERN Replacement pattern of the form "[/flow-filter]/regex/[@]replacement", where the separator can be any character. The @ allows to provide a file path that is used to read the replacement string. May be passed multiple times.Modify Headers: --modify-headers PATTERN, -H PATTERN Header modify pattern of the form "[/flow-filter]/header-name/[@]header-value", where the separator can be any character. The @ allows to provide a file path that is used to read the header value string. An empty header-value removes existing header-name headers. May be passed multiple times.Filters: See help in mitmproxy for filter expression syntax. --intercept FILTER Intercept filter expression. |
说实话有这么命令参数,其实我们常用的就2个
1 | mitmweb.exe -p 8888 -s D:\code\test\mitm4.py |
-p指定代理服务的启动端口
-s指定我们执行的脚本
4、配置代理
正常情况下,我们app和笔记本连在同一个wifi就可以代理抓包,但是在我实际测试工程中,会发现有的时候会抓不到包。所以这个时候建议大家在笔记本上开热点,然后手机连这个热点,然后在配置代理,就基本上没问题
5、安装证书
由于目前的请求基本上都是https,所以我们需要安装证书,以便mitmproxy可以帮我们解密https的报文
如果mitmweb已经启动成功,我们就可以访问下面这个地址
1 | http://mitm.it/ |

如果出现这个,就说明我们的代理还没有配置对
如果出现下面的窗口,则证明正常,我们根据当前的客户端类型安装证书即可

二、进入实战(这里我们用51cto这个app来做测试)
1、脚本的模板(当然还有其他钩子方法,但是基本不常用,我也没有去使用,所以这里不讲,这里只讲request和response,其他可以看官网)
import mitmproxy.http
from mitmproxy import ctx, http
class Mit():
def request(self,flow:mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow):
#在这里写对request请求的流程处理
pass
def response(self,flow:mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow):
#在这里写对response请求的流程处理
pass
addons = [
Mit(),
]
1、修改请求的报文(ctx.log是proxy自己写的一个日志工具,可以根据日志的级别在控制台打印不同的颜色,你也可以用print打印)
a、先用下面的方法获取请求这个对象有什么方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | class Mit(): def request(self,flow:mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): #在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if flow.request.url == "edu.51cto.com/app.php": ctx.log.error("匹配到请求报文") ctx.log.error(dir(flow.request)) def response(self,flow:mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): #在这里写对response请求的流程处理 passaddons = [ Mit(),] |
可以看到控制台输出,request这个请求有如下方法,所有大家可想而知mitmproxy这个工具有多强大了,也就是说我们几乎可以对请求字任何字段删除和更改,甚至可以对新增字段
1 | ['__abstractmethods__', <br>'__annotations__', <br>'__class__', <br>'__delattr__', <br>'__dict__', <br>'__dir__', <br>'__doc__', <br>'__eq__', <br>'__format__', <br>'__ge__', <br>'__getattribute__', <br>'__gt__', <br>'__hash__', <br>'__init__', <br>'__init_subclass__',<br> '__le__', <br>'__lt__', <br>'__module__', <br>'__ne__', <br>'__new__', <br>'__reduce__', <br>'__reduce_ex__', <br>'__repr__', <br>'__setattr__', <br>'__sizeof__', <br>'__str__', <br>'__subclasshook__', <br>'__weakref__', <br>'_abc_impl', <br>'_get_content_type_charset', <br>'_get_cookies', <br>'_get_multipart_form', <br>'_get_query', <br>'_get_urlencoded_form', <br>'_guess_encoding', <br>'_set_cookies', <br>'_set_multipart_form', <br>'_set_query', <br>'_set_urlencoded_form', <br>'anticache', <br>'anticomp', <br>'authority', <br>'constrain_encoding', <br>'content', <br>'cookies', <br>'copy', <br>'data', <br>'decode', <br>'encode', <br>'first_line_format', <br>'from_state', <br>'get_content', <br>'get_state', <br>'get_text', <br>'headers', <br>'host', <br>'host_header', <br>'http_version', <br>'is_http10', <br>'is_http11', <br>'is_http2', <br>'json', <br>'make', <br>'method', <br>'multipart_form', <br>'path', <br>'path_components', <br>'port', <br>'pretty_host', <br>'pretty_url', <br>'query', <br>'raw_content', <br>'scheme', <br>'set_content', <br>'set_state', <br>'set_text', <br>'stream', <br>'text', <br>'timestamp_end', <br>'timestamp_start', <br>'trailers', <br>'url', <br>'urlencoded_form'] |
b、获取参数和修改参数的例子
我们常用用法,下面的代码我演示了获取参数和修改的参数的用法,大家注意看我的注释
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | def request(self,flow:mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): #在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: ctx.log.error("匹配到请求报文") # ctx.log.error(dir(flow.request)) ctx.log.error(flow.request.query) # 返回url的参数的值 ctx.log.error(flow.request.query.items()) # 返回url参数值的dict形式 ctx.log.debug(flow.request.query.keys()) # url参数的key ctx.log.info(flow.request.query.values()) # url参数的values值 ctx.log.info(flow.request.method) # 获取请求的方法 ctx.log.info(flow.request.scheme) # 获取请求的类型,http还是https ctx.log.info(flow.request.host) # 获取请求的host ctx.log.info(flow.request.headers) # 获取请求的头部 ctx.log.info(flow.request.url) # 获取请求的url flow.request.url = "https://www.baidu.com" #修改url flow.request.query.set_all("wd",["test"]) #设置url参数 |
大家看到我在app上请求51cto的地址,被代理到了百度,且新增了url的参数
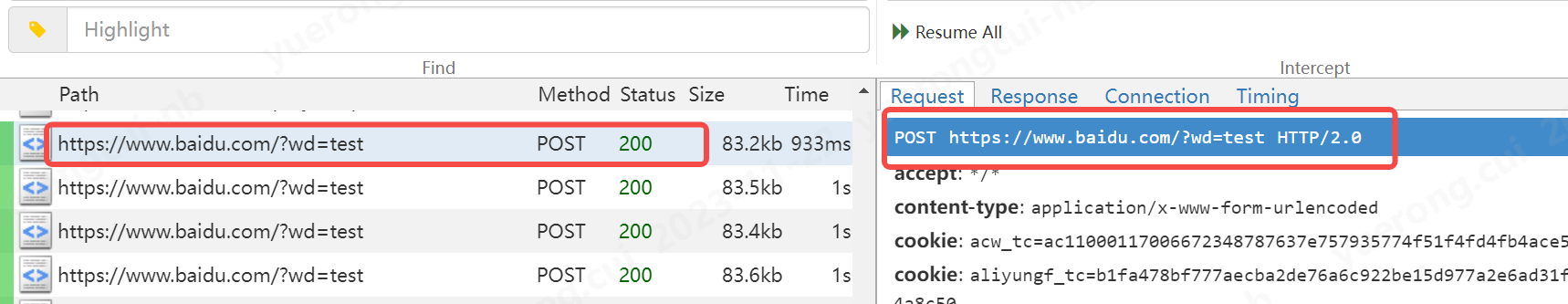
c、新增参数的例子
另外,我们不仅仅可以修改已有参数,还可以给请求头新增参数
1 | flow.request.headers["test"] = "abc" |
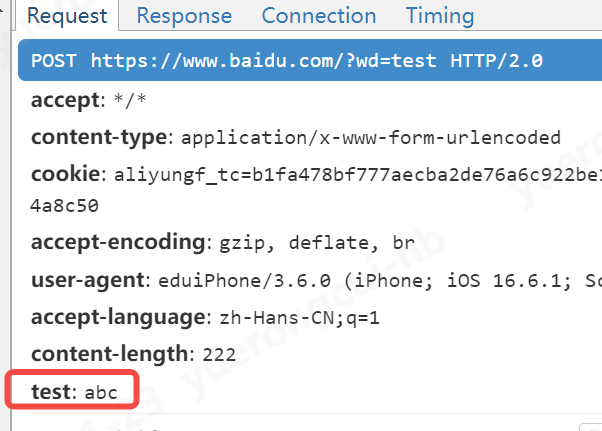
2、修改响应
a、先用下面的方法看下响应请求有什么属性和方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | class Mit(): def request(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: pass def response(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对response请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: ctx.log.error(dir(flow.response))addons = [ Mit(),] |
可以看到控制台输出,response这个请求有如下方法,所有大家可想而知mitmproxy这个工具有多强大了,也就是说我们几乎可以对请求的任何做增删改
1 | ['__abstractmethods__',<br> '__annotations__', <br>'__class__', <br>'__delattr__', <br>'__dict__', <br>'__dir__', <br>'__doc__', <br>'__eq__', <br>'__format__', <br>'__ge__', <br>'__getattribute__', <br>'__gt__', <br>'__hash__', <br>'__init__', <br>'__init_subclass__', <br>'__le__', <br>'__lt__', <br>'__module__', <br>'__ne__', <br>'__new__', <br>'__reduce__', <br>'__reduce_ex__', <br>'__repr__', <br>'__setattr__', <br>'__sizeof__', <br>'__str__', <br>'__subclasshook__', <br>'__weakref__', <br>'_abc_impl', <br>'_get_content_type_charset', <br>'_get_cookies', <br>'_guess_encoding', <br>'_set_cookies', <br>'content', <br>'cookies', <br>'copy', <br>'data', <br>'decode', <br>'encode', <br>'from_state', <br>'get_content', <br>'get_state', <br>'get_text', <br>'headers', <br>'http_version', <br>'is_http10', <br>'is_http11', <br>'is_http2', <br>'json', <br>'make', <br>'raw_content', <br>'reason', <br>'refresh', <br>'set_content', <br>'set_state', <br>'set_text', <br>'status_code', <br>'stream', <br>'text', <br>'timestamp_end', <br>'timestamp_start',<br>'trailers'] |
b、演示一个拒绝响应的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | class Mit(): def request(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: pass def response(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对response请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: ctx.log.error(dir(flow.response)) ctx.log.error("测试拒绝响应") flow.response = flow.response.make(status_code=404, content="<h1>被代理</h1>", headers={"content-type":"text/html"} )addons = [ Mit(),] |
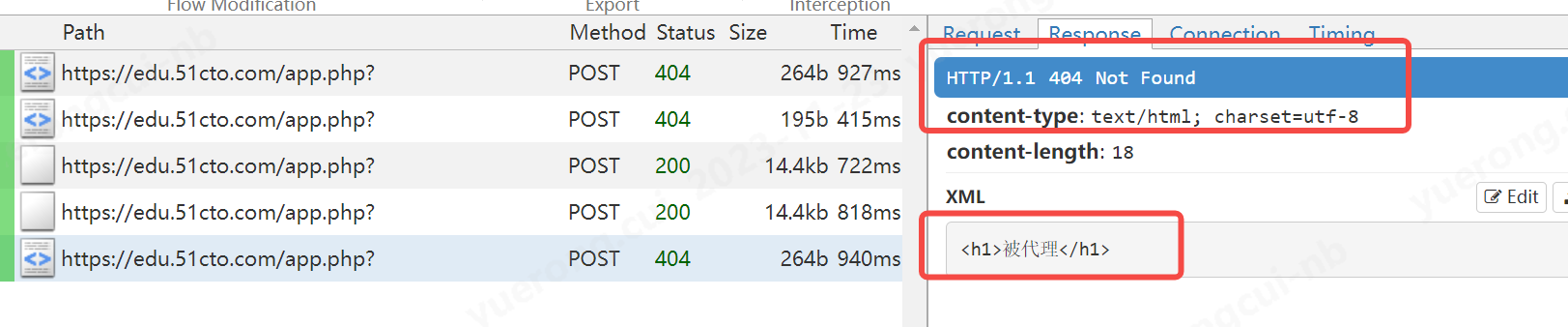
c、演示一个获取参数的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | import jsonclass Mit(): def request(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: pass def response(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对response请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: res_text = json.loads(flow.response.text,encoding="utf-8") ctx.log.info(res_text) res_get_text = flow.response.get_text("result") ctx.log.warn(res_get_text) res_get_header = flow.response.headers ctx.log.error(res_get_header)addons = [ Mit(),] |
看一下返回的结果
flow.response.text的值,也就是响应体的值
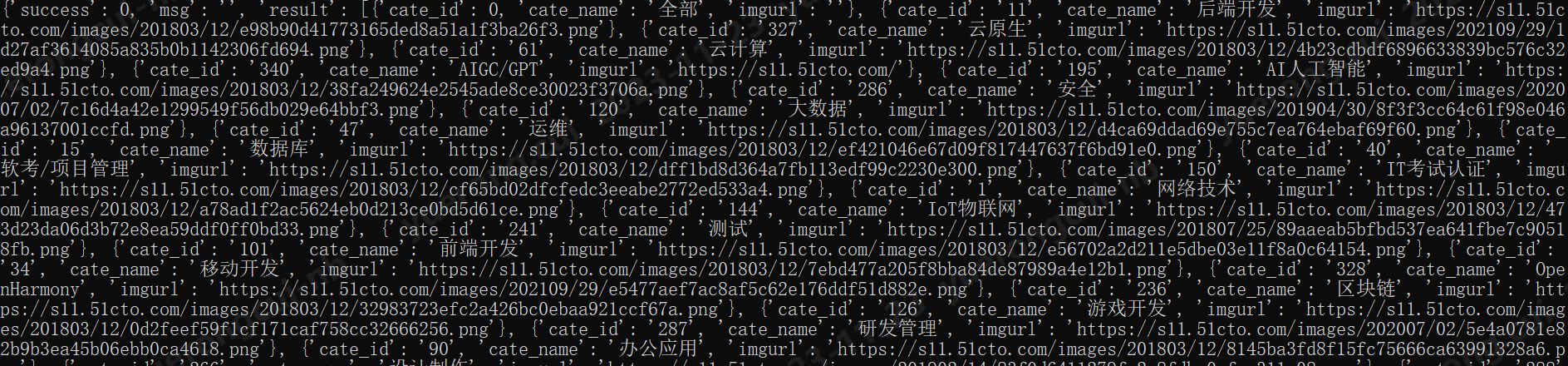
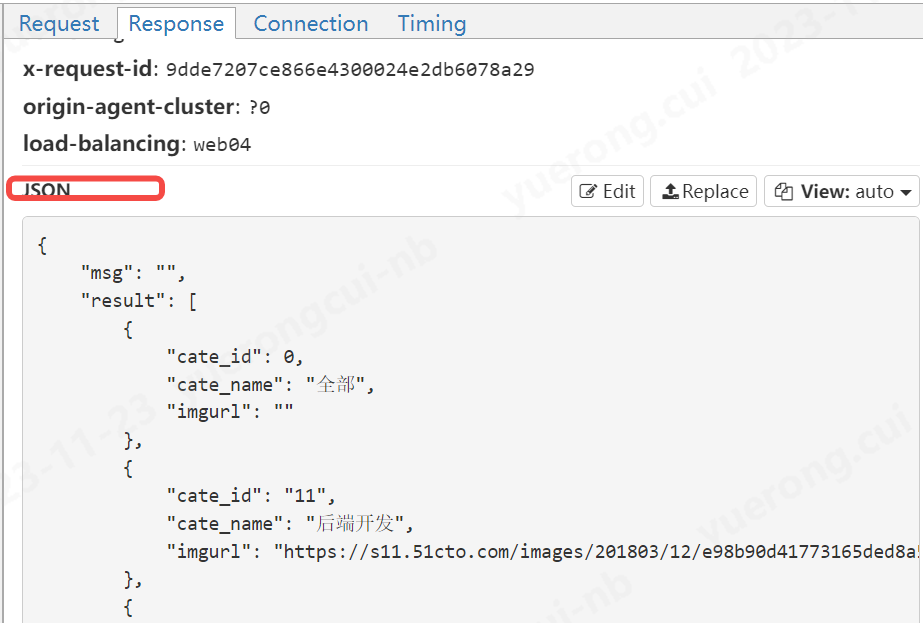
d、演示一个修改参数的例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | import jsonclass Mit(): def request(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对request请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: pass def response(self, flow: mitmproxy.http.HTTPFlow): # 在这里写对response请求的流程处理 if "edu.51cto.com/app.php" in flow.request.url: res_text = json.loads(flow.response.text,encoding="utf-8") res_text["msg"] = "test_mitmproxy" flow.response.text = json.dumps(res_text,ensure_ascii=True) addons = [ Mit(),] |
我们修改了msg的信息
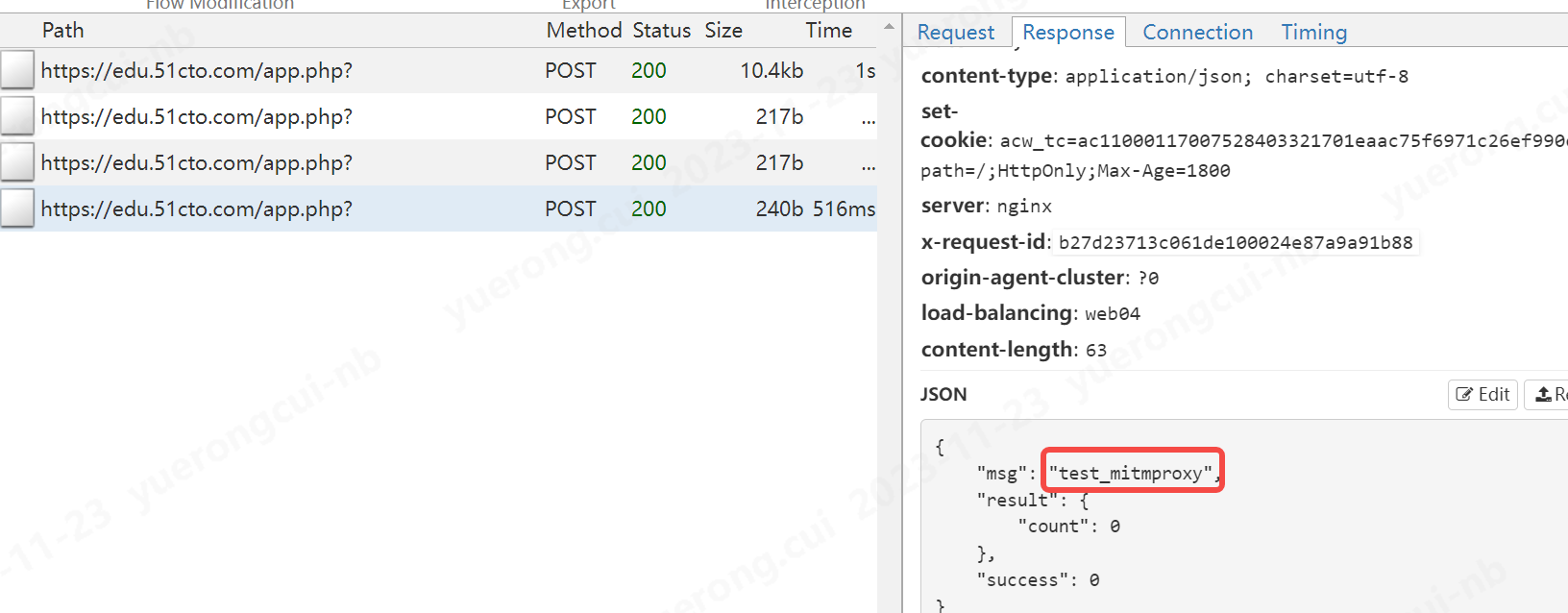
至此我认为主要的作用已经讲完了





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
2018-11-23 Django的Rbac介绍1