CSS 之 position
position 的 relative 和 absolute
如何正确理解 absolute:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/CSS/position
相对定位的元素并未脱离文档流,而绝对定位的元素则脱离了文档流。
在布置文档流中其它元素时,绝对定位元素不占据空间。绝对定位元素相对于最近的非 static 祖先元素定位。
当这样的祖先元素不存在时,则相对于ICB(inital container block, 初始包含块)
什么是 ICB:
The containing block in which the root element lives is a rectangle called the initial containing block. For continuous media,
it has the dimensions of the viewport and is anchored at the canvas origin;
下面是一个 demo:
样式如下:
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.wrapper {
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
background-color: gray;
}
.son1 {
position: relative;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: red;
}
.son2 {
position: absolute;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
html 如下:
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="son1"></div>
<div class="son2"></div>
</div>
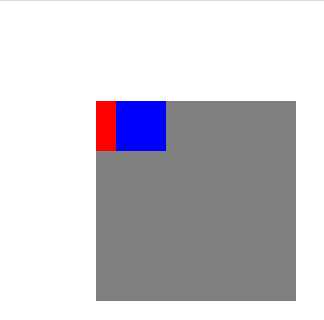
效果:

解释
父 relative,两个子,分别是 relative 和 absolute,可以看到,position 为 absolute 的子位于 position 为 relative 子的下面。
这会给人一种错觉,误以为 son2 是在根据 son1(兄弟元素) 进行定位。当为 son2 指定 top/left/right/bottom 之后,就可以明显的看到,它的定位依据确实是 wrapper。
参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/20109535
.son2 {
position: absolute;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
top: 0;
left: 20px;
background-color: blue;
}
效果:
所以,关键是 top/left/right/bottom 这几个定位属性的设置。
如果把 son2 的 position 改成 fixed(没有设置 top/left/right/bottom),可以看到其位置并没有根据浏览器窗口定位:
.son2 {
position: fixed;
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: blue;
}
只有加上了 top/left/right/bottom,fixed 的效果才能显示出来。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号