numpy是一个数组分析工具。
- python获取函数的帮助文档,通过help()函数
help(numpy.genfromtxt)
Help on function genfromtxt in module numpy:
genfromtxt(fname, dtype=<class 'float'>, comments='#', delimiter=None, skip_header=0, skip_footer=0, converters=None, missing_values=None, filling_values=None, usecols=None, names=None, excludelist=None, deletechars=" !#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^{|}~", replace_space='_', autostrip=False, case_sensitive=True, defaultfmt='f%i', unpack=None, usemask=False, loose=True, invalid_raise=True, max_rows=None, encoding='bytes', *, like=None)
Load data from a text file, with missing values handled as specified.
Each line past the first `skip_header` lines is split at the `delimiter`
character, and characters following the `comments` character are discarded.
Parameters
----------
fname : file, str, pathlib.Path, list of str, generator
File, filename, list, or generator to read. If the filename
extension is `.gz` or `.bz2`, the file is first decompressed. Note
that generators must return byte strings. The strings
in a list or produced by a generator are treated as lines.
。。。
1、numpy.genfromtxt()函数,从文件中读取数据,并解析成多维数组。
import numpy # 当NumPy不能将非数值型值转换为float或integer类型,数据会标识为nan # 从文件中读取数据到多维数组中 world_alcohol = numpy.genfromtxt('world_alcohol.txt', delimiter=',',skip_header=1) # 返回多维数组 print(type(world_alcohol)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> 多维数组 # 查看[0,8)行的数据 print(world_alcohol[0:8])
2、numpy.array() 构造一维或多维数组
# numpy.array()函数,可以生成一维数组和多维数组,当入参是一个list时,我们生成一维数组 vector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20]) print(vector) # [ 5 10 15 20] print(type(vector)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # 通过shape属性,可以查看向量的大小 print(vector.shape) # (4,) # 传入多层嵌套list,得到是矩阵 matrix = numpy.array([[[5,10,15],[20,25,30],[35,40,45]],[[5,10,15],[20,25,30],[35,40,45]]]) # 通过shape属性,可以查看矩阵数组的维度大小(形状) print(matrix.shape) # (2, 3, 3) print(type(matrix)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> print('----------') print(matrix)----------
[[[ 5 10 15] [20 25 30] [35 40 45]] [[ 5 10 15] [20 25 30] [35 40 45]]]
3、属性dtype可以查看多维数组元素的数据类型
numbers = numpy.array([1,2,3,4]) numbers.dtype # dtype('int32')
4、numpy.genfromtxt(dtype='U75')指定值类型,默认是float。
在不指定dtype=‘’参数时,默认是float值类型。在文本字符串值场景下,需要指定值类型。
# 指定值类型‘U75’ world_alcohol = numpy.genfromtxt("world_alcohol.txt",delimiter=',',dtype='U75',skip_header=1) print(world_alcohol) print('--------------') # 值类型默认float,会导致非数值型转换成nan world_alcohol_nan = numpy.genfromtxt('world_alcohol.txt', delimiter=',',skip_header=1) # 返回多维数组 print(type(world_alcohol_nan)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> 多维数组 print(world_alcohol_nan[0:3])
[['1986' 'Western Pacific' 'Viet Nam' 'Wine' '0'] ['1986' 'Americas' 'Uruguay' 'Other' '0.5'] ['1985' 'Africa' "Cte d'Ivoire" 'Wine' '1.62'] ... ['1987' 'Africa' 'Malawi' 'Other' '0.75'] ['1989' 'Americas' 'Bahamas' 'Wine' '1.5'] ['1985' 'Africa' 'Malawi' 'Spirits' '0.31']] -------------- <class 'numpy.ndarray'> [[1.986e+03 nan nan nan 0.000e+00] [1.986e+03 nan nan nan 5.000e-01] [1.985e+03 nan nan nan 1.620e+00]]
# 查看22-28行的float值,可见[24行,4列]的值为空'',即nan sub_world_alcohol_nan = world_alcohol_nan[22:28] print(sub_world_alcohol_nan) #help(numpy.isnan)
[[1.984e+03 nan nan nan 2.670e+00] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 4.400e-01] [1.985e+03 nan nan nan nan] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 0.000e+00] [1.985e+03 nan nan nan 1.360e+00] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 2.220e+00]]
# 第四列所有行是否nan值,返回vector
vector_is_value_empty = numpy.isnan(sub_world_alcohol_nan[:,4]) print(vector_is_value_empty)
[False False True False False False]
# 将nan批量替换为0 sub_world_alcohol_nan[vector_is_value_empty,4] = '0' print(sub_world_alcohol_nan)
[[1.984e+03 nan nan nan 2.670e+00] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 4.400e-01] [1.985e+03 nan nan nan 0.000e+00] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 0.000e+00] [1.985e+03 nan nan nan 1.360e+00] [1.984e+03 nan nan nan 2.220e+00]]
# 矩阵第4列,全量进行批量替换为0 vector_all_is_value_empty = numpy.isnan(world_alcohol_nan[:,4]) world_alcohol_nan[vector_all_is_value_empty,4] = '0' # 取出矩阵第4列(酒精消费),函数astype(float)转换为float,sum()求和,mean()求均值 alcohol_consumption = world_alcohol_nan[:,4] alcohol_consumption = alcohol_consumption.astype(float) total_alcohol = alcohol_consumption.sum() len_alcohol = len(alcohol_consumption) average_alcohol = alcohol_consumption.mean() #print(total_alcohol, len_alcohol, average_alcohol) print(total_alcohol) # 1137.7800000000002 print(len_alcohol) # 997 print(average_alcohol) # 1.1412036108324977
1137.7800000000002 997 1.1412036108324977
5、寻址一个值,用[n,m]方式。 区别于分片子集的操作,[n:m,x:y]。
uruguay_other_1986 = world_alcohol[1,4] print(uruguay_other_1986) # 0.5 print(type(uruguay_other_1986)) # <class 'numpy.str_'> third_country = world_alcohol[2,2] print(third_country) # Cte d'Ivoire
# 分片子集[a:b] vector = numpy.array([5,10,15,20]) print(vector[0:3]) # [ 5 10 15] print(type(vector)) # <class 'numpy.ndarray'> print(vector.dtype) # int32
6、矩阵,子集分片
matrix = numpy.array([ [5,10,15], [20,25,30], [35,40,45] ]) # 矩阵截取所有行,1列的值 print(matrix[:,1]) print('---------') # 矩阵所有行,[0,2)列的值 print(matrix[:, 0:2]) print('---------') # 矩阵[1,3)行,[0,2)列的值 print(matrix[1:3,0:2])
7、numpy值计算: 变量 操作符 值
matrix = numpy.array([ [5,10,15], [20,25,30], [35,40,45] ]) new_matrix = matrix % 10 == 0 print(new_matrix)
[[False True False] [ True False True] [False True False]]
7.1 寻址所有true的值,到一个vector中
matrix[ bool_matrix ]
print(matrix[new_matrix]) # [10 20 30 40]
7.2 列运算
matrix[:,1] 第[1]列
matrix = numpy.array([ [5,10,15], [20,25,30], [35,40,45] ]) # 对比列[1]值是否等于25 second_column_25 = (matrix[:,1] == 25) print(matrix[:,1]) # [10 25 40] print(second_column_25) # [False True False] # 寻址true的行,所有列 print(matrix[second_column_25, :]) # [[20 25 30]]
7.3 多条件判断
# 多条件判断 vector = numpy.array([5,10,15,20]) # 条件 与 equal_to_ten_and_five = (vector == 10) & (vector == 5) print(equal_to_ten_and_five) # [False False False False] # 条件 或 equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5) print(equal_to_ten_or_five) # [ True True False False]
7.4 通过bool类型的矩阵或者向量,进行批量操作True位置的元素
# 将true位置的值进行,批量修改 vector = numpy.array([5,10,15,20]) equal_to_ten_or_five = (vector == 10) | (vector == 5) # [ True True False False] vector[equal_to_ten_or_five] = 50 print(vector) #[50 50 15 20]
7.5 通过bool类型的矩阵或者向量,进行批量操作True位置的元素:取出所有true位置的的值
matrix = numpy.array([ [5,10,15], [20,25,30], [35,40,45] ]) new_matrix = matrix % 10 == 0 print(new_matrix) print('----------------') # 寻址所有true的值,到一个vector中 print(matrix[new_matrix]) # [10 20 30 40]
[[False True False] [ True False True] [False True False]] ---------------- [10 20 30 40]
7.6 matrix[:,1] 语义操作矩阵第[1]列(一维数组) 和 matrix[ vector_bool , : ] 语义操作vector_bool为Tru的行所有列(多维数组)
matrix = numpy.array([ [5,10,15], [20,25,30], [35,40,45] ]) # 对比列[1]值是否等于25 second_column_25 = (matrix[:,1] == 25) print(matrix[:,1]) # [10 25 40] print(second_column_25) # [False True False] # 寻址true的行,所有列 print(matrix[second_column_25, :]) # [[20 25 30]]
7.6.1 matrix[start:end:step, 1] 语义:操作第[1]列,[start, end)步长为stetp的元素;
8*8棋盘矩阵,其中1、3、5、7行&&0、2、4、6列的元素置为1 1 ,3,5,7列&&0,2,4,6行也是1
import numpy as np # 8*8棋盘矩阵,其中1、3、5、7行&&0、2、4、6列的元素置为1 1 ,3,5,7列&&0,2,4,6行也是1 z = np.zeros((8,8),dtype=int) # 1、3、5、7行&&0、2、4、6列的元素置为1 z[1::2,::2] = 1 # 0、2、4、6行&&1、3、5、7列的元素置为1 z[::2,1::2] = 1 #print ("z:\n",z) z
array([[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]])
7.6.2 arr[[k0,k1,..,ki],:]数组[k0,k1,..,ki]行,arr[:,[l0,l1,..,li]]数组[l0,l1,..,li]]列
import numpy as np #交换矩阵的其中两行 a = np.arange(25).reshape(5,5) print ("a:\n",a) print("数组2、0行 a[[2,0]] : \n",a[[2,0]]) print("数组2、0列 a[:,[2,0]] : \n",a[:,[2,0]]) #0、1行,赋值为3、0行的值 a[[0,1]] = a[[3,0]] print ("0、1行,赋值为3、0行的值:\n",a)
a: [[ 0 1 2 3 4] [ 5 6 7 8 9] [10 11 12 13 14] [15 16 17 18 19] [20 21 22 23 24]] 数组2、0行 a[[2,0]] : [[10 11 12 13 14] [ 0 1 2 3 4]] 数组2、0列 a[:,[2,0]] : [[ 2 0] [ 7 5] [12 10] [17 15] [22 20]] 0、1行,赋值为3、0行的值: [[15 16 17 18 19] [ 0 1 2 3 4] [10 11 12 13 14] [15 16 17 18 19] [20 21 22 23 24]]
7.7 vector.astype(float): 多维数组类型转换之string转float
# dtype数据类型有:
# b boolean
# i signed integer
# u unsigned integer
# f floating-point
# c complex floating-point
# m timedelta
# M datetime
# O object
# S (byte-)string
# U Unicode
# V void
vector = numpy.array(["123","2","3"]) print(vector.dtype) # <U3 :Unicode 3位 #help(numpy.dtype) print(vector) # ['123' '2' '3'] print('------------') vector_conv = vector.astype(float) print(vector_conv.dtype) # float64 :float 64位 print(vector_conv) #[123. 2. 3.]
7.8 多维数组求和:vector.sum() matrix.sum()
# axis指示我们在哪个维度上执行操作
# axis=1表示我们想在每一行上执行操作,axis=0表示在每列上执行操作
# 多维数组求和:vector.sum() matrix.sum() # axis指示我们在哪个维度上执行操作 # axis=1表示我们想在每一行上执行操作,axis=0表示在每列上执行操作
# 向量 vector = numpy.array([5, 10, 15, 20]) print(vector.shape) # (4,) 向量 print(vector.sum()) # 50 #等同于vector.sum(axis=0) print(vector.sum(axis=0)) # 50 #等同于vector.sum() #print(vector.sum(axis=1)) # vector向量不可axis=1按行执行操作
# 矩阵 matrix_4_1 = numpy.array([[5], [10], [15], [20]]) print(matrix_4_1.shape) # (4,1) 矩阵 print(matrix_4_1.sum(axis=0)) # [50] 按列加 print(matrix_4_1.sum(axis=1)) # [ 5 10 15 20] 按行加 print(matrix_4_1.sum()) # 50 matrix_3_3 = numpy.array([ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ]) print(matrix_3_3.sum()) # 225 print(matrix_3_3.sum(axis=0)) # [60 75 90] 按列加 print(matrix_3_3.sum(axis=1)) # [ 30 75 120] 按行加
7.8.1 矩阵的运算:2x3x3矩阵
matrix_2_3_3 = numpy.array([ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ]) print(matrix_2_3_3.sum(axis=0).shape) print(matrix_2_3_3.sum(axis=0)) print(matrix_2_3_3.sum(axis=1).shape) print(matrix_2_3_3.sum(axis=1))
(3, 3) [[10 20 30] [40 50 60] [70 80 90]] (2, 3) [[60 75 90] [60 75 90]]
7.8.2 矩阵的运算:4x3x3矩阵
matrix_4_3_3 = numpy.array([ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] , [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] , [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ]) print(matrix_4_3_3.shape) print('------------------') print(matrix_4_3_3.sum(axis=0)) print('------------------') print(matrix_4_3_3.sum(axis=0).shape) print('------------------') print(matrix_4_3_3.sum(axis=1)) print('------------------') print(matrix_4_3_3.sum(axis=1).shape)
(4, 3, 3) ------------------ [[ 20 40 60] [ 80 100 120] [140 160 180]] ------------------ (3, 3) ------------------ [[60 75 90] [60 75 90] [60 75 90] [60 75 90]] ------------------ (4, 3)
7.8.3 矩阵的运算:2x4x3x3矩阵
matrix_2_4_3_3_3 = numpy.array([ [ [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ] ], [ [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ], [ [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ], [ [5, 10, 15], [20, 25, 30], [35, 40, 45] ] ] ] ]) print(matrix_2_4_3_3_3.shape) print('------------------') #print(matrix_2_4_3_3_3.sum(axis=0)) print('------------------') print(matrix_2_4_3_3_3.sum(axis=0).shape) print('------------------') #print(matrix_2_4_3_3_3.sum(axis=1)) print('------------------') print(matrix_2_4_3_3_3.sum(axis=1).shape)
8、数组变维
8.1 数组变维函数 reshape()
reshape:在不改变原数组数据的情况下,将它reshape成一个新的维度。
如果给定的数组数据和需要reshape的形状不符合时,将会报错。
# 数组形状(维度)
a.shape
(2, 3, 5)
8.3 ndim属性:数组坐标轴数(维度)
a.ndim
3
8.4 dtypes属性:数组的数据类型
a.dtype.name
'int32'
8.5 size属性:数组中元素的总数
a.size
15
8.6 zeros()构建一个由0填充的给定形状(3,4)和类型的新数组
#help(np.zeros)
np.zeros ((3,4))
array([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.]])
8.7 ones()构建一个由1填充的给定形状(2,,3,4)和类型 int32 的新数组
#help(np.ones) np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 )
array([[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]],
[[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1]]])
8.9 arrange(end) / arrange(start,end,step) 创建数值序列数值
# 10-30范围内,步长为5,构建序列
np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
array([10, 15, 20, 25])
# 0-2范围内,步长为0.3,构建序列
np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
array([ 0. , 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, 1.5, 1.8])
# 0-12,构建(4行,3列)数组 np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
8.10 numpy.random.random( (n,m) ) 构建(n行,m列)随机值 [0.0, 1.0) 数组
print(np.random.random((2,3))) #help(np.random.random)
[[0.75551497 0.12664133 0.66382302] [0.17664593 0.59902515 0.79439341]]
8.11 linspace(start, end, num) 构建[start, end)区间内均匀num个元素的数组
np.linspace主要用来创建等差数列。
from numpy import pi np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ) #help(np.linspace)
array([0. , 0.06346652, 0.12693304, 0.19039955, 0.25386607,
0.31733259, 0.38079911, 0.44426563, 0.50773215, 0.57119866,
0.63466518, 0.6981317 , 0.76159822, 0.82506474, 0.88853126,
0.95199777, 1.01546429, 1.07893081, 1.14239733, 1.20586385,
1.26933037, 1.33279688, 1.3962634 , 1.45972992, 1.52319644,
1.58666296, 1.65012947, 1.71359599, 1.77706251, 1.84052903,
1.90399555, 1.96746207, 2.03092858, 2.0943951 , 2.15786162,
2.22132814, 2.28479466, 2.34826118, 2.41172769, 2.47519421,
2.53866073, 2.60212725, 2.66559377, 2.72906028, 2.7925268 ,
2.85599332, 2.91945984, 2.98292636, 3.04639288, 3.10985939,
3.17332591, 3.23679243, 3.30025895, 3.36372547, 3.42719199,
3.4906585 , 3.55412502, 3.61759154, 3.68105806, 3.74452458,
3.8079911 , 3.87145761, 3.93492413, 3.99839065, 4.06185717,
4.12532369, 4.1887902 , 4.25225672, 4.31572324, 4.37918976,
4.44265628, 4.5061228 , 4.56958931, 4.63305583, 4.69652235,
4.75998887, 4.82345539, 4.88692191, 4.95038842, 5.01385494,
5.07732146, 5.14078798, 5.2042545 , 5.26772102, 5.33118753,
5.39465405, 5.45812057, 5.52158709, 5.58505361, 5.64852012,
5.71198664, 5.77545316, 5.83891968, 5.9023862 , 5.96585272,
6.02931923, 6.09278575, 6.15625227, 6.21971879, 6.28318531])
#生成0~10之间均匀分布的11个数,包括0和10 z = np.linspace(0,10,11,endpoint=True,retstep=True) print (z)
(array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.]), 1.0)
8.12 np.sin()对ndarray多维数组中每个元素取正弦
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 10 )) np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 10 ))
# help(np.sin)
[0. 0.6981317 1.3962634 2.0943951 2.7925268 3.4906585 4.1887902 4.88692191 5.58505361 6.28318531]
array([ 0.00000000e+00, 6.42787610e-01, 9.84807753e-01, 8.66025404e-01,
3.42020143e-01, -3.42020143e-01, -8.66025404e-01, -9.84807753e-01,
-6.42787610e-01, -2.44929360e-16])
8.13 np.array( array_like )生成多维数组,多维数组计算:向量计算
a = np.array( [20,30,40,50] ) b = np.arange( 4 ) print('a : ', a ) print('b : ', b ) #b c = a-b print ('c : ',c) b**2 print ('b**2 : ',b**2) print('(a<35 : ', a<35)
# help(np.array)
8.14 np.array( array_like )生成多维数组,多维数组计算:矩阵计算
8.14.1 矩阵叉乘 : 必须是 (n,m) 叉乘 (n,m) 得到(n,m)
A = np.array( [[1,1], [2,2], [0,1]] ) B = np.array( [[2,0], [2,0], [3,4]] ) print ('A : \n\n', A) print ('B : \n\n', B) # 矩阵 叉 乘 : 必须是 (n,m) 叉乘 (n,m) 得到(n,m) print ('A*B : \n\n', A*B)
A : [[1 1] [2 2] [0 1]] B : [[2 0] [2 0] [3 4]] A*B : [[2 0] [4 0] [0 4]]
8.14.2 矩阵点乘 : 必须是 (i,k) 点乘 (k,j) 得到(i, j)
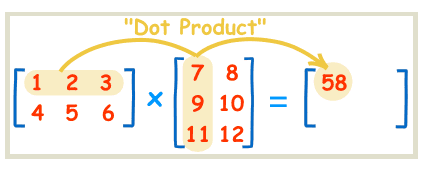
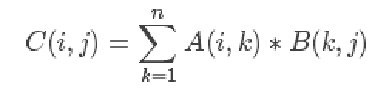
A = np.array( [[1,1], [2,2], [0,1]] ) B = np.array( [[2,0,1], [3,4,1]] ) print ('A : \n\n', A) print ('B : \n\n', B) # 矩阵 点 乘 : 必须是 (i,k) 点乘 (k,j) 得到(i, j) print('A.dot(B) : \n\n', A.dot(B)) print('np.dot(A, B) : \n\n', np.dot(A, B))
A : [[1 1] [2 2] [0 1]] B : [[2 0 1] [3 4 1]] A.dot(B) : [[ 5 4 2] [10 8 4] [ 3 4 1]] np.dot(A, B) : [[ 5 4 2] [10 8 4] [ 3 4 1]]
9 数组运算
9.1 numpy.exp(B):返回e的幂次方,e是一个常数为2.71828 : e的B次方
import numpy as np B = np.arange(3) print(B) # [0 1 2] print(np.exp(B)) # [1. 2.71828183 7.3890561 ]
9.2 np.sqrt(B):求B的开方,根号B
print(B) # [0 1 2] print(np.sqrt(B)) # [0. 1. 1.41421356]
9.3 求B的平方
# 对B求平方 print(B**2) # [0 1 4]
9.4 np.floor()返回不大于输入参数的最大整数。(向下取整)
# numpy.random.random( (n,m) ) 构建(n行,m列)随机值 [0.0, 1.0) 数组 # 构建(3行,4列)随机值的多维数组,值乘以10,用floor向下取整 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random(3,4)) print(a)
[[8. 8. 1. 5.] [1. 7. 7. 0.] [3. 3. 6. 9.]]
# 数组a的形状 : (3行,4列) print(a.shape) # (3, 4)
# 重新设置多维数组a的形状 a.shape = (6, 2) print (a)
ndarray.T 数组属性:矩阵的置
print(a.T)
9.5 numpy.ravel() 数组扁平化
# arr.ravel()
b = a.ravel() print(b) # [0. 0. 2. 1. 8. 9. 0. 0. 7. 0. 6. 6.]
9.6 numpy.resize( arr, (n,m) )新建 和 arr.resize( (n,m) )自定义形状
如果新数组比源数组大,则将会copy原数组的值对新数组进行填充
# a.resize是重塑自己的形状,返回None;希望返回新数组用np.resize(a, (2,6)) print (a.resize((2,7))) print(a) # 如果新数组比源数组大,则将会copy原数组的值对新数组进行填充 b = np.array([[0,1],[2,3]]) # np.resize : 给定一个数组,和特定维度,将返回一个给定维度形式的新数组 c = np.resize(b,(3,2))
9.7 np.vstack()和np.hstack()
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1,2,3]) arr2 = np.array([4,5,6]) # np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺 print("np.hstack : \n", np.hstack((arr1, arr2))) # np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠 print("np.vstack : \n", np.vstack((arr1, arr2)))
np.hstack : [1 2 3 4 5 6] np.vstack : [[1 2 3] [4 5 6]]
9.8 np.hsplit(a,x) 和 np.vsplit(a,x)
np.hsplit(a,x)函数的作用是将数组a横向等分成x个数组。列数必须能平分
np.vsplit(a,x)函数的作用是将数组a纵向等分成x个数组。行数必须能平分
import numpy as np #help(np.arange) a = np.arange(40).reshape((10,-1)) print(a)
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11] [12 13 14 15] [16 17 18 19] [20 21 22 23] [24 25 26 27] [28 29 30 31] [32 33 34 35] [36 37 38 39]]
# 将a等分为2列,列数必须能平分 b = np.hsplit(a,2) b
[array([[ 0, 1],
[ 4, 5],
[ 8, 9],
[12, 13],
[16, 17],
[20, 21],
[24, 25],
[28, 29],
[32, 33],
[36, 37]]),
array([[ 2, 3],
[ 6, 7],
[10, 11],
[14, 15],
[18, 19],
[22, 23],
[26, 27],
[30, 31],
[34, 35],
[38, 39]])]
# 将a等分为4列,列数必须能平分 b = np.hsplit(a,4) b
[array([[ 0],
[ 4],
[ 8],
[12],
[16],
[20],
[24],
[28],
[32],
[36]]),
array([[ 1],
[ 5],
[ 9],
[13],
[17],
[21],
[25],
[29],
[33],
[37]]),
array([[ 2],
[ 6],
[10],
[14],
[18],
[22],
[26],
[30],
[34],
[38]]),
array([[ 3],
[ 7],
[11],
[15],
[19],
[23],
[27],
[31],
[35],
[39]])]
# 将a等分为2行,行必须能平分 b = np.vsplit(a,2) b
[array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19]]),
array([[20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27],
[28, 29, 30, 31],
[32, 33, 34, 35],
[36, 37, 38, 39]])]
# 将a等分为5行,行必须能平分 b = np.vsplit(a,5) b
[array([[0, 1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6, 7]]),
array([[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15]]),
array([[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]),
array([[24, 25, 26, 27],
[28, 29, 30, 31]]),
array([[32, 33, 34, 35],
[36, 37, 38, 39]])]
9.9 id(obj, /) 返回一个对象的标识
a = np.arange(12) b = a # a和b是同一个ndarray对象的两个名称 print(b is a) b.shape = 3,4 print (a.shape) # 对象的标识 print (id(a)) print (id(b))
True (3, 4) 2212586013488 2212586013488
9.10 view()方法创建一个查看相同数据的新数组对象。
view方法创建一个相同数据的新数组对象。且,指向同一个数据存储的内存地址。
# view方法创建一个相同数据的新数组对象。且,指向同一个数据存储的内存地址 a = np.arange(12) c = a.view() print(c is a) c.shape = 2,6 print ("a.shape: ",a.shape) print("c.shape:",c.shape) c[0,4] = 1234 print("c: \n", c) print("a: \n", a) print("a~c 共享内存:", np.may_share_memory(a,c))
False a.shape: (12,) c.shape: (2, 6) c: [[ 0 1 2 3 1234 5] [ 6 7 8 9 10 11]] a: [ 0 1 2 3 1234 5 6 7 8 9 10 11] a~c 共享内存: True
9.11 copy()方法对数组及其数据进行完整的复制。不共享内存。
a = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4) d = a.copy() print("d is a : ",d is a) d[0,0] = 9999 print ("d: \n", d) print ("a: \n", a)
9.12 numpy.argmax(array, axis)、numpy.argmin(array, axis) 用于返回一个numpy数组中最大(小)值的索引值。
axis=0每列最大值索引,axis=1每行最大值索引
axis=None : 给出水平方向最小(大)值的下标;即数组拉平后水平方向。
import numpy as np # numpy.argmax(array, axis) 用于返回一个numpy数组中最大值的索引值。axis=0每列最大值索引,axis=1每行最大值索引 # 一维数组:直接返回索引值 one_dim_arr = np.array([1,4,5,3,7,2,6]) print(np.argmax(one_dim_arr))
4
# 引用博客:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42755982/article/details/104542538
# 多维argmax: 以三维为例,三维计算之后降维,将返回一个二维数组。 # 一个(m×n×p)维的矩阵, # axis为0,舍去m,返回一个 n×p 维的矩阵 # axis为1,舍去n,返回一个 m×p 维的矩阵 # axis为2,舍去p,返回一个 m×n 维的矩阵 #three_dim_arr = np.floor(10*np.random.random(24)).reshape((3,2,4)) three_dim_arr = [ [[1,2,3,5],[-3,0,6,8]], [[3,9,-3,6],[0,6,33,22]], [[62,1,0,18],[6,3,-2,16]] ] #print(three_dim_arr) a = np.argmax(three_dim_arr, axis=0) print("a: \n", a) b = np.argmax(three_dim_arr, axis=1) print("b: \n", b) c = np.argmax(three_dim_arr, axis=2) print("c: \n", c)
import numpy as np three_dim_arr = np.array([ [[1,2,3,5],[-3,0,6,8]], [[3,9,-3,6],[0,6,33,22]], [[62,1,0,18],[6,3,-2,16]] ]) print(three_dim_arr.argmin()) print(three_dim_arr.argmax())
4 16
找出数组中与给定值最接近的数的下标索引
#找出数组中与给定值最接近的数的下标索引 z = np.array([[0,1,8,2,3],[4,9,5,6,7]]) a = 5.1 #print (np.abs(z-a)) print (np.abs(z-a).argmin())
7
9.13 np.tile() 将原矩阵横向、纵向地复制。
tile 是瓷砖的意思,顾名思义,这个函数就是把数组像瓷砖一样铺展开来。
a = np.arange(0, 40, 10) # [0,10,20,30] b = np.tile(a, (2, 3, 3)) print (b)
[[[ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30]] [[ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30] [ 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30 0 10 20 30]]]
9.14 np.sort() 对给定的数组的元素进行排序
a = np.array([[4, 3, 5], [1, 2, 9], [8,6,7]]) #a.sort(axis=1) # 自排序 #print (a) b = np.sort(a, axis=1) # 等于np.sort(a,axis=-1) # 等于 np.sort(a) print ("b : \n",b) c = np.sort(a, axis=0) print("c : \n", c)
9.15 np.argsort() 输出排序后的下标索引
a = np.array([4, 3, 1, 2, 9]) j = np.argsort(a) print ("j: \n",j) print ("a[j]: \n",a[j])
j: [2 3 1 0 4] a[j]: [1 2 3 4 9]
9.16 np.min(z)、z.min()数组最小值 和 np.max(z)、z.max()数组最大值
z = np.floor(np.random.random((3,5))*10) print("z:\n",z) zmin,zmax = z.min(),z.max() print("zmin: ",zmin,"\nzmax: ",zmax)
z: [[3. 9. 1. 6. 5.] [1. 8. 3. 6. 3.] [8. 6. 5. 9. 5.]] zmin: 1.0 zmax: 9.0
归一化,将矩阵规格化到0~1,即最小的变成0,最大的变成1,最小与最大之间的等比缩放
#归一化,将矩阵规格化到0~1,即最小的变成0,最大的变成1,最小与最大之间的等比缩放 z = np.floor(10*np.random.random((5,5))) print ("z:\n",z) zmin,zmax = z.min(),z.max() print("zmin: ",zmin,"\nzmax: ",zmax) z1 = (z-zmin)/(zmax-zmin) print ("z1:\n",z1)
z: [[1. 5. 6. 1. 7.] [6. 0. 0. 3. 4.] [9. 3. 1. 5. 4.] [4. 7. 7. 3. 9.] [3. 6. 4. 1. 6.]] zmin: 0.0 zmax: 9.0 z1: [[0.11111111 0.55555556 0.66666667 0.11111111 0.77777778] [0.66666667 0. 0. 0.33333333 0.44444444] [1. 0.33333333 0.11111111 0.55555556 0.44444444] [0.44444444 0.77777778 0.77777778 0.33333333 1. ] [0.33333333 0.66666667 0.44444444 0.11111111 0.66666667]]
矩阵相加: 每行,对应列相加,列数必须相等
#矩阵相加: 每行,对应列相加,列数必须相等 z = np.ones((3,5)) print ("z:\n",z) z1 = z + np.arange(5) print ("np.arange(5):\n",np.arange(5)) print ("z1:\n",z1)
z: [[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.] [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]] np.arange(5): [0 1 2 3 4] z1: [[1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] [1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] [1. 2. 3. 4. 5.]]
9.17 np.random.randint()函数
# numpy.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype=’l’)
# 返回随机整数或整型数组,范围区间为[low,high),包含low,不包含high;
# high没有填写时,默认生成随机数的范围是[0,low)
# low=1 输出[0,1)内的一个整数 print(np.random.randint(1)) # 0 # low=1, high=none, size=2行2列,输出范围[0,1)内的一个整数数组 print(np.random.randint(1,size=(2,2))) # array([[0,0],[0,0]]) print(np.random.randint(0,2)) # 输出[0,2)之间的整数 np.random.randint(1,20,size=(4,4),dtype='uint8')
array([[16, 8, 15, 4],
[ 3, 3, 8, 8],
[ 5, 5, 7, 6],
[19, 14, 8, 15]], dtype=uint8)
9.18 NumPy.all()与any()函数
9.18.1 all(a, axis=None, out=None, keepdims=np._NoValue)
判断给定轴向上的***所有元素是否都为True***
零为False,其他情况为True
如果axis为None,返回单个布尔值True或False
9.18.2 any(a, axis=None, out=None, keepdims=np._NoValue)
判断给定轴向上***是否有任意一个元素为True***
如果axis为None,返回单个布尔值True或False
# numpy all()判断矩阵中所有元素是否都为True # numpy any()判断矩阵中任意一元素是否都为True a2 = np.arange(5) # array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]) print('np.all(a2): ', np.all(a2)) # 是否全为True,np.all(a2): False print('np.any(a2): ', np.any(a2)) # 是否任意为True,np.any(a2): True # 随手写一个矩阵 [0 3 0 0 0] a3 = np.array([0,3,0,0,0]) print('np.all(a3): ', np.all(a3)) # 是否全为True,np.all(a3): False print('np.any(a3): ', np.any(a3)) # 是否任意为True,np.any(a3): True # 生产一个全是0的矩阵,形状与a3一样 a4 = np.zeros_like(a3) # [0 0 0 0 0] print('np.all(a4): ', np.all(a4)) # 是否全为True,np.all(a4): False print('np.any(a4): ', np.any(a4)) # 是否任意为True,np.any(a4): False # 生成一个全是False的矩阵,形状与a3一样 a5 = np.full_like(a3, False) # array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) a5 print('np.all(a5): ', np.all(a5)) # 是否全为True,np.all(a5): False print('np.any(a5): ', np.any(a5)) # 是否任意为True,np.any(a5): False # 生产一个全是True的矩阵,形状和a3一样 a6 = np.full_like(a3, True) a6 # array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) print('np.all(a6): ', np.all(a6)) # 是否全为True,np.all(a6): True print('np.any(a6): ', np.any(a6)) # 是否任意为True,np.any(a6): True
9.19 numpy.meshgrid(*xi, **kwargs) 从两个或多个坐标向量返回坐标矩阵。
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #x = np.array([[0,1,2],[0,1,2]]) #y = np.array([[0,0,0],[1,1,1]]) x,y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(-1,1,10),np.linspace(-1,1,10)) plt.plot(x,y, color='red', marker='.', linestyle='') plt.grid(True) plt.show()



