20145206 《信息安全系统设计基础》第十周学习总结
代码运行情况
1、cp1.c
#include <stdio.h> //标准输入输出头文件
#include <stdlib.h> //标准库头文件
#include <unistd.h> //unix类系统定义符号常量的头文件
#include <fcntl.h> //定义了一组基于C的非缓冲的文件操作函数,可用于文件和设备(及socket等)的I/O操作
#define BUFFERSIZE 4096 //缓冲区大小
#define COPYMODE 0644 // 新文件的访问权限位
void oops(char *, char *); //错误处理函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int in_fd, out_fd, n_chars;
char buf[BUFFERSIZE]; //定义缓冲区
if (argc != 3) //当输入参数不足时
{
fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s source destination\n", *argv);
exit(1);
}
if ((in_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1) /打开文件失败
oops("Cannot open ", argv[1]);
if ((out_fd = creat(argv[2], COPYMODE)) == -1) //创建新文件失败
oops("Cannot creat", argv[2]);
while ((n_chars = read(in_fd, buf, BUFFERSIZE)) > 0) //缓冲区不空时,开始写文件
if (write(out_fd, buf, n_chars) != n_chars) //写文件出错
oops("Write error to ", argv[2]);
if (n_chars == -1) //从文件中读数据出错
oops("Read error from ", argv[1]);
if (close(in_fd) == -1 || close(out_fd) == -1) //关闭输入文件出错或关闭输出文件出错
oops("Error closing files", "");
}
void oops(char *s1, char *s2) //错误处理
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s ", s1);
perror(s2);
exit(1);
}
首先,进入week10文件夹,用vim编辑器编辑cp1.c的代码并编译:
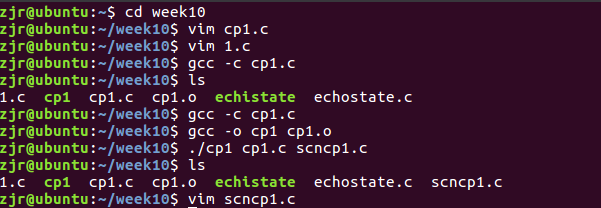
再次查看scncp1.c中的内容,发现和cp1.c中的内容完全一致:
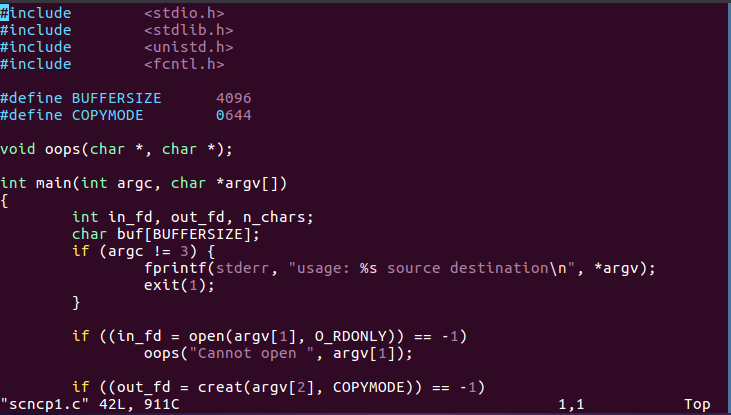
说明此代码的功能是:复制文件或目录
2、echostate.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <termios.h>
int main()
{
struct termios info;
int rv;
rv = tcgetattr( 0, &info ); /* read values from driver */
if ( rv == -1 ){
perror( "tcgetattr");
exit(1);
}
if ( info.c_lflag & ECHO )
printf(" echo is on , since its bit is 1\n");
else
printf(" echo is OFF, since its bit is 0\n");
return 0;
}
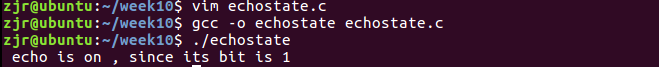
功能:查看在命令行中输入命令时是否可见,可见返回1,否则返回0
3、fileinfo.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h> //基本系统数据类型
#include <sys/stat.h> //文件属性结构体
void show_stat_info(char *, struct stat *);
//显示文件属性函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat info;
if (argc>1) //运行时有参数
{
if( stat(argv[1], &info) != -1 ) //显示文件状态
{
show_stat_info( argv[1], &info );
return 0;
}
else
perror(argv[1]); //错误处理
}
return 1;
}
void show_stat_info(char *fname, struct stat *buf)
{
printf(" mode: %o\n", buf->st_mode);
printf(" links: %d\n", buf->st_nlink);
printf(" user: %d\n", buf->st_uid);
printf(" group: %d\n", buf->st_gid);
printf(" size: %d\n", (int)buf->st_size);
printf("modtime: %d\n", (int)buf->st_mtime);
printf(" name: %s\n", fname );
}
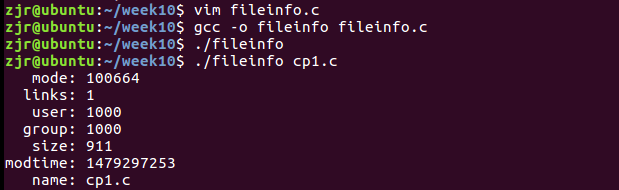
功能:查看文件信息
4、filesize.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h> //文件属性结构体
int main()
{
struct stat infobuf;
if ( stat( "/etc/passwd", &infobuf) == -1 )
//查看文件属性函数
perror("/etc/passwd"); //错误处理
else
printf(" The size of /etc/passwd is %d\n", infobuf.st_size );
}
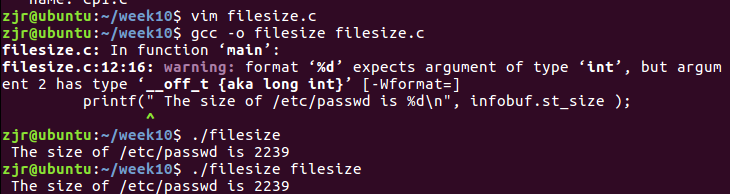
功能:查看文件大小
5、ls1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h> //基本系统数据类型
#include <dirent.h>
void do_ls(char []);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if ( argc == 1 ) //没有参数是,显示 当前万人当
do_ls( "." );
else
while ( --argc ){
printf("%s:\n", *++argv ); //显示参数
do_ls( *argv );
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls( char dirname[] )
{
DIR *dir_ptr; //DIR表示目录类型
struct dirent *direntp; //目录结构体
if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL )
fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname);
else
{
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL )
printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name );
closedir(dir_ptr);
}
}
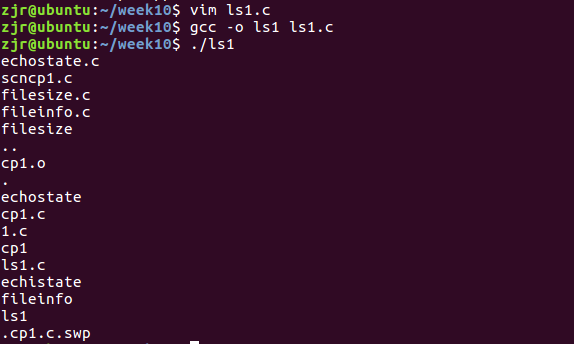
功能:显示当前目录下的所有文件
6、ls2.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
void do_ls(char[]); //显示指定目录下的文件
void dostat(char *); //显示文件属性
void show_file_info( char *, struct stat *); //显示文件读取详细信息
void mode_to_letters( int , char [] ); //显示文件读取权限信息
char *uid_to_name( uid_t );
char *gid_to_name( gid_t );
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if ( argc == 1 )
do_ls( "." );
else
while ( --argc ){
printf("%s:\n", *++argv );
do_ls( *argv );
}
return 0;
}
void do_ls( char dirname[] )
{
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *direntp;
if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL )
fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname);
else
{
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL )
dostat( direntp->d_name );
closedir(dir_ptr);
}
}
void dostat( char *filename )
{
struct stat info;
if ( stat(filename, &info) == -1 )
perror( filename );
else
show_file_info( filename, &info );
}
void show_file_info( char *filename, struct stat *info_p )
{
char *uid_to_name(), *ctime(), *gid_to_name(), *filemode();
void mode_to_letters();
char modestr[11];
mode_to_letters( info_p->st_mode, modestr );
printf( "%s" , modestr );
printf( "%4d " , (int) info_p->st_nlink);
printf( "%-8s " , uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid) );
printf( "%-8s " , gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid) );
printf( "%8ld " , (long)info_p->st_size);
printf( "%.12s ", 4+ctime(&info_p->st_mtime));
printf( "%s\n" , filename );
}
void mode_to_letters( int mode, char str[] )
{
strcpy( str, "----------" );
if ( S_ISDIR(mode) ) str[0] = 'd';
if ( S_ISCHR(mode) ) str[0] = 'c';
if ( S_ISBLK(mode) ) str[0] = 'b';
if ( mode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r';
if ( mode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXUSR ) str[3] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r';
if ( mode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXGRP ) str[6] = 'x';
if ( mode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r';
if ( mode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w';
if ( mode & S_IXOTH ) str[9] = 'x';
}
#include <pwd.h> //定义口令结构体
char *uid_to_name( uid_t uid )
{
struct passwd *getpwuid(), *pw_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if ( ( pw_ptr = getpwuid( uid ) ) == NULL ){
sprintf(numstr,"%d", uid);
return numstr;
}
else
return pw_ptr->pw_name ;
}
#include <grp.h> //包含组结构的定义
char *gid_to_name( gid_t gid )
{
struct group *getgrgid(), *grp_ptr;
static char numstr[10];
if ( ( grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid) ) == NULL ){
sprintf(numstr,"%d", gid);
return numstr;
}
else
return grp_ptr->gr_name; //返回组名
}
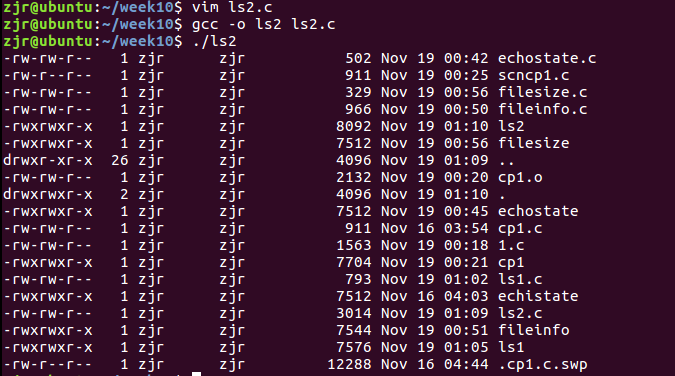
功能:显示指定目录下的文件详细信息
7、setcho.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <termios.h> //串口配置中,终端的工作模式,是一个结构体
#define oops(s,x) { perror(s); exit(x); }
//用于错误处理的宏
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct termios info;
if ( argc == 1 )
exit(0);
if ( tcgetattr(0,&info) == -1 ) /* 获取文件属性 */
oops("tcgettattr", 1);
if ( argv[1][0] == 'y' )
info.c_lflag |= ECHO ; /* 设置打开标志位 */
else
info.c_lflag &= ~ECHO ; /* 设置关闭标志位 */
if ( tcsetattr(0,TCSANOW,&info) == -1 ) /* 设置文件属性 */
oops("tcsetattr",2);
return 0;
}
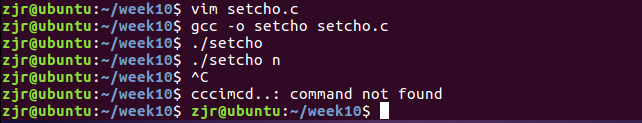
功能:设置echo的状态
8、spwd.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
ino_t get_inode(char *); // 获取i-node节点号
void printpathto(ino_t); // 打印当前目录路径
void inum_to_name(ino_t , char *, int ); //根据i-node节点找到对应文件名
int main()
{
printpathto( get_inode( "." ) );
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
void printpathto( ino_t this_inode )
{
ino_t my_inode ;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
if ( get_inode("..") != this_inode )
{
chdir( ".." );
inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ);
my_inode = get_inode( "." );
printpathto( my_inode );
printf("/%s", its_name );
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find , char *namebuf, int buflen)
{
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *direntp;
dir_ptr = opendir( "." );
if ( dir_ptr == NULL ){
perror( "." );
exit(1);
}
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL )
if ( direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find )
{
strncpy( namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen);
namebuf[buflen-1] = '\0';
closedir( dir_ptr );
return;
}
fprintf(stderr, "error looking for inum %d\n", (int) inode_to_find);
exit(1);
}
ino_t get_inode( char *fname )
{
struct stat info;
if ( stat( fname , &info ) == -1 ){
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot stat ");
perror(fname);
exit(1);
}
return info.st_ino; //返回i-node节点号
}
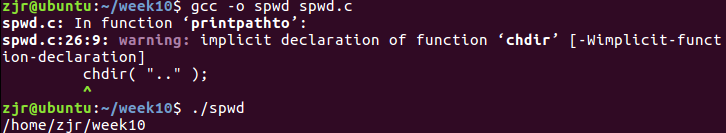
功能:显示当前目录路径
9、testioctl.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int main()
{
struct winsize size;
if( isatty(STDOUT_FILENO) == 0) //判断一个文件描述符是否指向一个终端
exit(1);
if (ioctl(STDOUT_FILENO, TIOCGWINSZ, &size) < 0) //控制驱动器
{
perror("ioctl TIOCGWINSZ error");
exit(1);
}
printf("%d rows %d columns\n", size.ws_row, size.ws_col);
return 0;
}
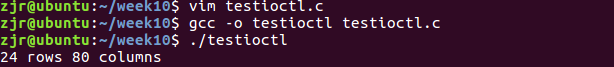
功能:查看窗体大小信息
9、who1.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <utmp.h> // 定义用户信息结构体
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h> //对 POSIX 操作系统 API 的访问功能的头文件
#define SHOWHOST
int show_info( struct utmp *utbufp )
{
printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_line);
printf(" ");
printf("%10ld", utbufp->ut_time);
printf(" ");
#ifdef SHOWHOST
printf("(%s)", utbufp->ut_host);
#endif
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
int main()
{
struct utmp current_record;
int utmpfd;
int reclen = sizeof(current_record);
if ( (utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE, O_RDONLY)) == -1 ){
perror( UTMP_FILE );
exit(1);
}
while ( read(utmpfd, ¤t_record, reclen) == reclen )
show_info(¤t_record);
close(utmpfd);
return 0;
}
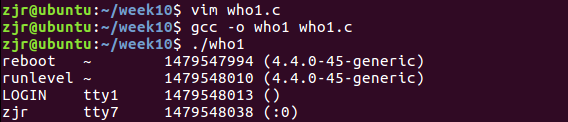
功能:查看当前登录用户信息
本周代码托管截图
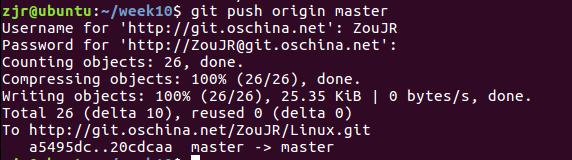
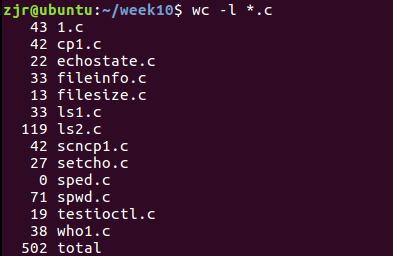
代码行数统计:
代码托管链接:
代码托管链接
感悟体会
本周还是继续第十章的学习,主要学习代码的部分,经过自己的探索以及看往届学长学姐的代码,了解了每个代码的具体含义,并把每个代码都进行了实际操作,达到了正确的结果,不足之处在于细节上还不是很理解,还需要慢慢消化。
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 20/30 | 学习了一些Linux核心命令 |
| 第二周 | 250/250 | 1/3 | 20/50 | 学习了vim编辑器基础 |
| 第三周 | 280/530 | 1/4 | 18/68 | 熟练在vim里编程并运行 |
| 第五周 | 300/830 | 1/5 | 15/83 | 学会生成汇编文件并查看 |
| 第六周 | 200/1030 | 1/6 | 12/95 | 了解Y86指令 |
| 第七周 | 139/1169 | 1/7 | 10/105 | 了解存储器层次结构 |
| 第八周 | 0/1169 | 2/9 | 8/113 | 复习前面所学内容 |
| 第九周 | 182/1351 | 2/11 | 9/122 | 了解Unix I/O |
| 第十周 | 502/1853 | 2/13 | 8/130 | 对代码进行理解 |



