CCS - Analog Modulation - Amplitude Modulation (AM) - Demodulation of AM Signals - DSB-AM Demodulation
Demodulation of AM Signals
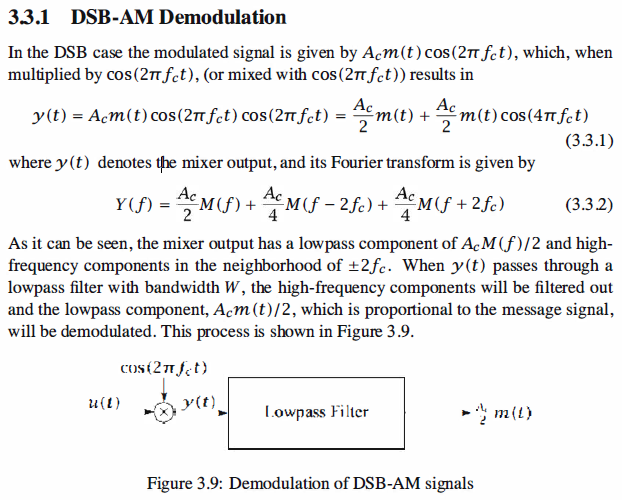
Demodulation is the process of extracting the message signal from the modulated signal.
The demodulation process depends on the type of modulation employed. For
DSB-AM and SSB-AM, the demodulation method is coherent demodulation, which
requires the existence of a signal with the same frequency and phase of the carrier at
the receiver. For conventional AM, envelope detectors are used for demodulation. In
this case precise knowledge of the frequency and the phase of the carrier at the receiver
is not crucial, so the demodulation process is much easier. Coherent demodulation for
DSB-AM and SSB-AM consists of multiplying (mixing) the modulated signal by a sinusoidal
with the same frequency and phase of the carrier and then passing the product
through a lowpass filter. The oscillator that generates the required sinusoidal at the
receiver is called the local oscillator.
Matlab Coding


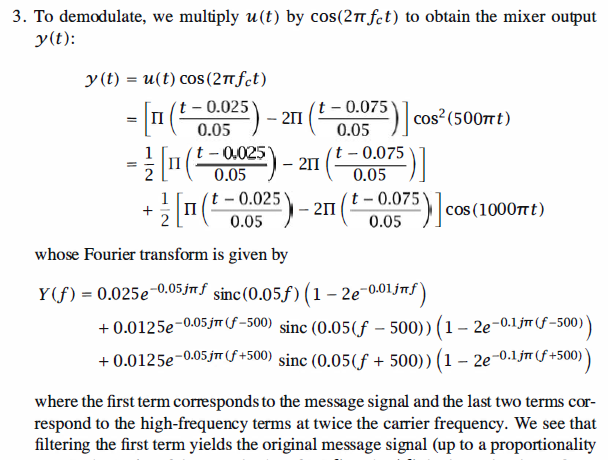
1 % MATLAB script for Illustrative Problem 3.5.
2 % Demonstration script for DSB-AM demodulation. The message signal 3 % is +1 for 0 < t < t0/3, -2 for t0/3 < t < 2t0/3, and zero otherwise. 4 echo on 5 t0=.15; % signal duration 6 ts=1/1500; % sampling interval 7 fc=250; % carrier frequency 8 fs=1/ts; % sampling frequency 9 t=[0:ts:t0]; % time vector 10 df=0.3; % desired frequency resolution 11 % message signal 12 m=[ones(1,t0/(3*ts)),-2*ones(1,t0/(3*ts)),zeros(1,t0/(3*ts)+1)]; 13 c=cos(2*pi*fc.*t); % carrier signal 14 u=m.*c; % modulated signal 15 y=u.*c; % mixing 16 [M,m,df1]=fftseq(m,ts,df); % Fourier transform 17 M=M/fs; % scaling 18 [U,u,df1]=fftseq(u,ts,df); % Fourier transform 19 U=U/fs; % scaling 20 [Y,y,df1]=fftseq(y,ts,df); % Fourier transform 21 Y=Y/fs; % scaling 22 f_cutoff=150; % cutoff freq. of the filter 23 n_cutoff=floor(150/df1); % Design the filter. 24 f=[0:df1:df1*(length(y)-1)]-fs/2; 25 H=zeros(size(f)); 26 H(1:n_cutoff)=2*ones(1,n_cutoff); 27 H(length(f)-n_cutoff+1:length(f))=2*ones(1,n_cutoff); 28 DEM=H.*Y; % spectrum of the filter output 29 dem=real(ifft(DEM))*fs; % filter output 30 pause % Press a key to see the effect of mixing. 31 clf 32 subplot(3,1,1) 33 plot(f,fftshift(abs(M))) 34 title('Spectrum of the Message Signal') 35 xlabel('Frequency') 36 subplot(3,1,2) 37 plot(f,fftshift(abs(U))) 38 title('Spectrum of the Modulated Signal') 39 xlabel('Frequency') 40 subplot(3,1,3) 41 plot(f,fftshift(abs(Y))) 42 title('Spectrum of the Mixer Output') 43 xlabel('Frequency') 44 pause % Press a key to see the effect of filtering on the mixer output. 45 clf 46 subplot(3,1,1) 47 plot(f,fftshift(abs(Y))) 48 title('Spectrum of the Mixer Output') 49 xlabel('Frequency') 50 subplot(3,1,2) 51 plot(f,fftshift(abs(H))) 52 title('Lowpass Filter Characteristics') 53 xlabel('Frequency') 54 subplot(3,1,3) 55 plot(f,fftshift(abs(DEM))) 56 title('Spectrum of the Demodulator output') 57 xlabel('Frequency') 58 pause % Press a key to compare the spectra of the message and the received signal. 59 clf 60 subplot(2,1,1) 61 plot(f,fftshift(abs(M))) 62 title('Spectrum of the Message Signal') 63 xlabel('Frequency') 64 subplot(2,1,2) 65 plot(f,fftshift(abs(DEM))) 66 title('Spectrum of the Demodulator Output') 67 xlabel('Frequency') 68 pause % Press a key to see the message and the demodulator output signals. 69 subplot(2,1,1) 70 plot(t,m(1:length(t))) 71 title('The Message Signal') 72 xlabel('Time') 73 subplot(2,1,2) 74 plot(t,dem(1:length(t))) 75 title('The Demodulator Output') 76 xlabel('Time')
The effect of mixing
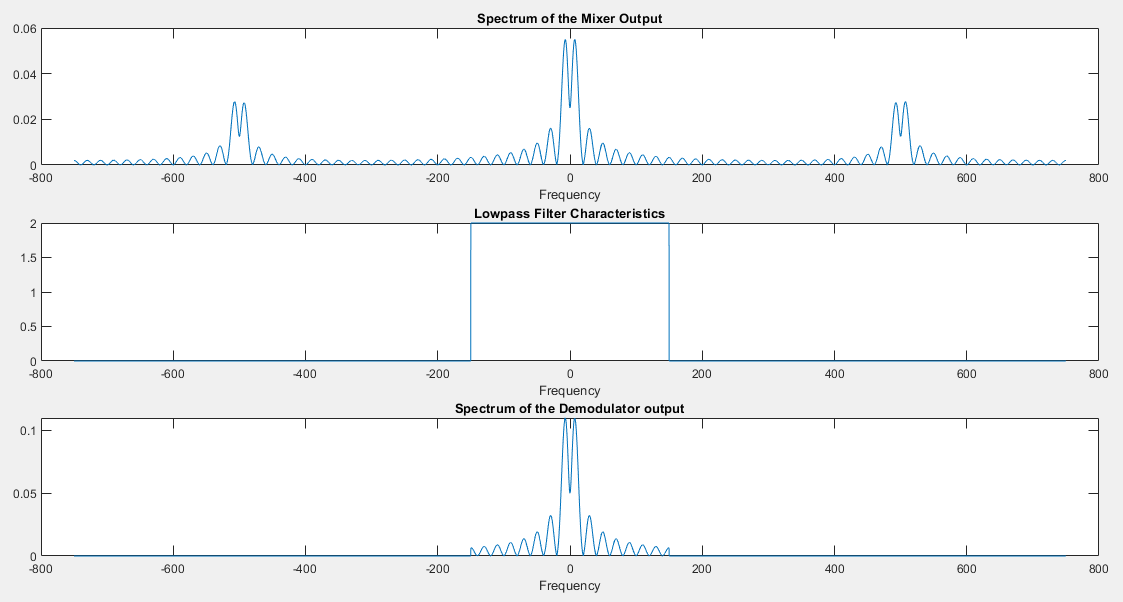
The effect of filtering on the mixer output
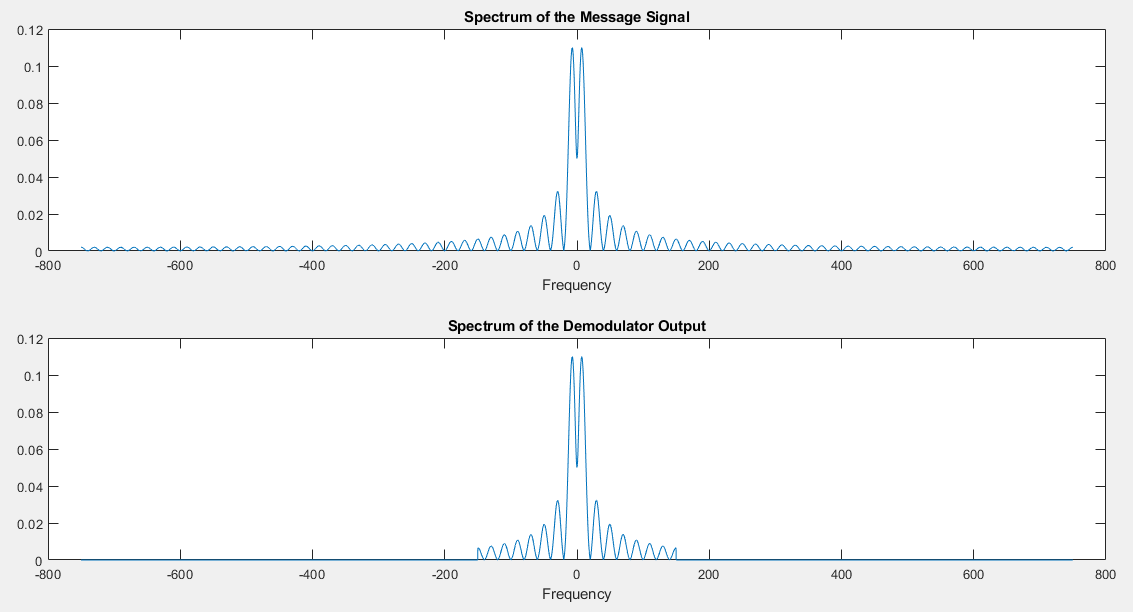
Compare the spectra of the message and the received signal
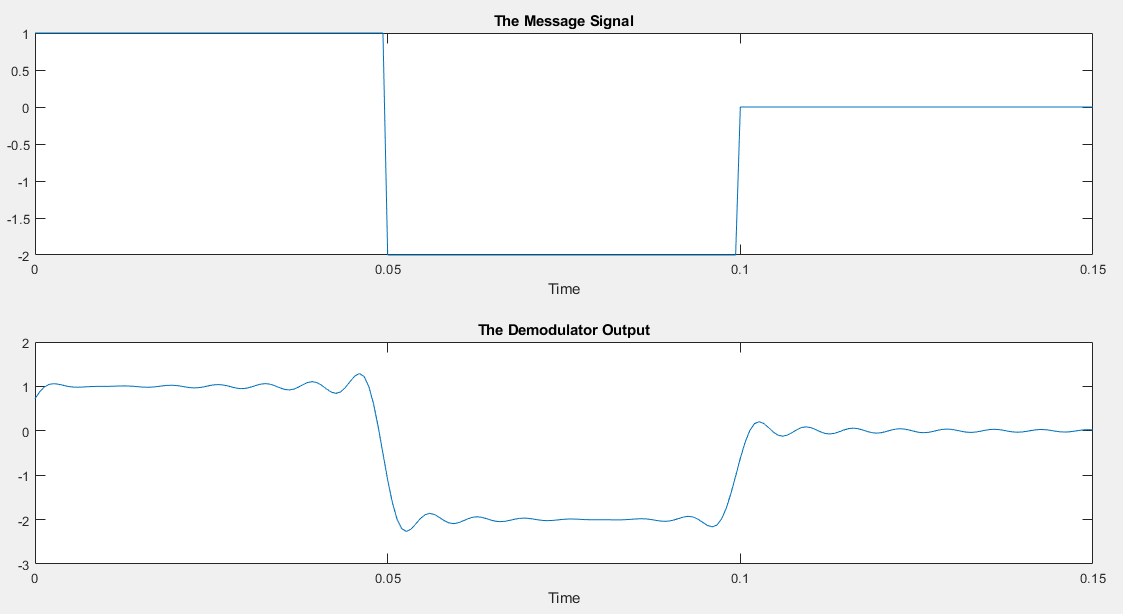
The message and the demodulator output signals
Reference,
1. <<Contemporary Communication System using MATLAB>> - John G. Proakis




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号