C++ C# Java 异步对比
开发工具:Visual Studio 2019、Visual Studio Code
C++
这里不是C++ 20,C++ 20 的 Coroutine 会另外写
#include<iostream>
#include<future>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include <windows.h>
std::string Func_01();
void Func_02();
unsigned long long GetThreadId(std::thread::id tid);
void Print(std::string s);
int main()
{
DWORD start = GetTickCount();
auto task = std::async(Func_01);
Print("In Main,ThreadId:");
Print("In Main,Before Func_01,ThreadId:");
std::cout << task.get();
std::cout << "\n\n";
Print("In Main,After Func_01,ThreadId:");
std::cout << "Done\n";
DWORD end = GetTickCount();
std::cout << end - start << std::endl;
return 0;
}
std::string Func_01()
{
Print("In Func_01,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_01,Before Task,ThreadId:");
std::async([]()
{
Print("In Func_01 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_01 Task,Before Func_02,ThreadId:");
std::async(Func_02).get();
Print("In Func_01 Task,After Func_02,ThreadId:");
}).get();
Print("In Func_01,After Task,ThreadId:");
return "Hello World";
}
void Func_02()
{
Print("In Func_02,ThreadId:");
std::async([]()
{
Print("In Func_02 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_02 Task,Before Delay,ThreadId:");
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(3000));
Print("In Func_02 Task,After Delay,ThreadId:");
}).get();
Print("In Func_02,After Task,ThreadId:");
}
unsigned long long GetThreadId(std::thread::id tid)
{
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << std::this_thread::get_id();
std::string stid = oss.str();
return std::stoull(stid);
}
void Print(std::string s)
{
std::string str = s + std::to_string(GetThreadId(std::this_thread::get_id())) + "\n\n";
std::cout << str;
}
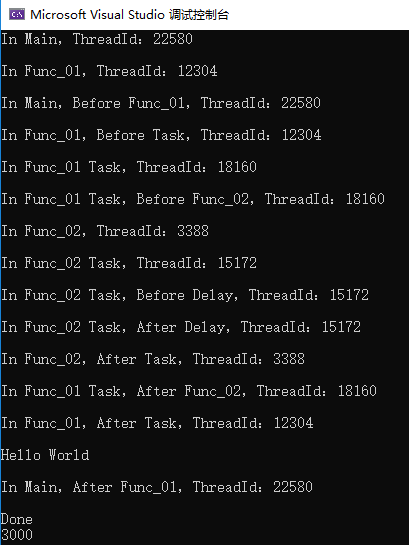
结果,调用std::async()就会创建线程,通过future.get()等待线程执行完毕就回调,最后回到主线程
C#
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
var task = Func_01();
Print("In Main");
Print("In Main,Before Func_01");
Console.WriteLine(await task);
Console.WriteLine();
Print("In Main,After Func_01");
Console.WriteLine("Done");
stopwatch.Stop();
TimeSpan timespan = stopwatch.Elapsed;
Console.WriteLine(timespan.TotalMilliseconds);
}
async static Task<string> Func_01()
{
Print("In Func_01");
Print("In Func_01,Before Task");
var task = Task.Run(async () =>
{
Print("In Func_01 Task");
Print("In Func_01 Task,Before Func_02");
await Func_02();
Print("In Func_01 Task,After Func_02");
return "Hello World";
});
string str = await task;
Print("In Func_01,After Task");
return str;
}
async static Task Func_02()
{
Print("In Func_02");
Print("In Func_02,Before Task");
await Task.Run(() =>
{
Print("In Func_02 Task,Before Delay");
//await Task.Delay(3000);
Thread.Sleep(3000);
Print("In Func_02 Task,After Delay");
});
Print("In Func_02,After Task");
}
static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s},Thread:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}\n");
}
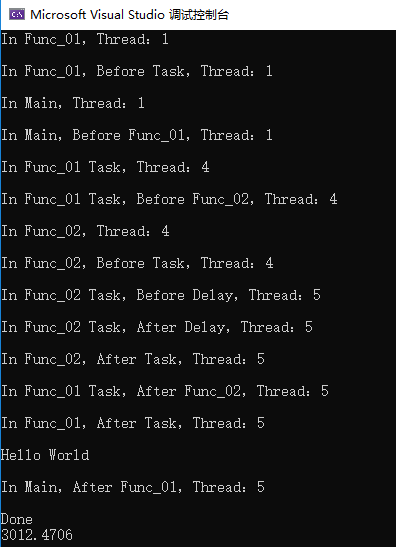
结果,可以看到,在Func_01()和Func_02()中,async如果不使用await,那么就会同步执行,VS也会提示“缺少await,将以同步方式运行”,async函数只有await之后才会创建线程
其实我感觉不是await创建的线程,而是Task.Run()或Task.Delay()之类的方法创建的线程,但是在一些地方感觉await有创建线程,有点难说明白,还是看官方文档吧
await 运算符暂停对其所属的 async 方法的求值,直到其操作数表示的异步操作完成。 异步操作完成后,await 运算符将返回操作的结果(如果有)。 当 await 运算符应用到表示已完成操作的操作数时,它将立即返回操作的结果,而不会暂停其所属的方法。
异步方法同步运行,直至到达其第一个 await 表达式,此时会将方法挂起,直到等待的任务完成。
至于为什么Task结束之后线程标识不变,因为await就是Task.ContinueWith()回调,这个就去看Help Viewer吧,我觉得跟同步上下文SynchronizationContext也有关系
还有一点要注意,尽量不要使用Thread.Sleep(),尽量使用await Task.Delay(),这样多个Task同时并发时就不会阻塞到同一个线程
也可以有另外的写法,在函数中直接返回Task.Run(),这应该才是常用的写法,毕竟async只是标识符,被async标识的函数可以使用await
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
var task = Func_01();
Print("In Main");
Print("In Main,Before Func_01");
Console.WriteLine(await task);
Console.WriteLine();
Print("In Main,After Func_01");
Console.WriteLine("Done");
stopwatch.Stop();
TimeSpan timespan = stopwatch.Elapsed;
Console.WriteLine(timespan.TotalMilliseconds);
}
static Task<string> Func_01()
{
return Task.Run(async () =>
{
Print("In Func_01");
Print("In Func_01,Before Task");
var task = Task.Run(async () =>
{
Print("In Func_01 Task");
Print("In Func_01 Task,Before Func_02");
await Func_02();
Print("In Func_01 Task,After Func_02");
return "Hello World";
});
string str = await task;
Print("In Func_01,After Task");
return str;
});
}
static Task Func_02()
{
return Task.Run(async () =>
{
Print("In Func_02");
Print("In Func_02,Before Task");
await Task.Run(() =>
{
Print("In Func_02 Task,Before Delay");
//await Task.Delay(3000);
Thread.Sleep(3000);
Print("In Func_02 Task,After Delay");
});
Print("In Func_02,After Task");
});
}
static void Print(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{s},Thread:{Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}\n");
}

结果就是会在每个Task.Run()之后创建新的线程,与C++类似,但不会返回主线程,毕竟await是Task.ContinueWith()
如果这里的方法添加了async就需要在返回时使用await
Java
static ExecutorService service=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
var task=Func_01();
Print("In Main");
Print("In Main,Before Func_01");
System.out.println(task.get());
System.out.println();
Print("In Main,After Func_01");
System.out.println("Done");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
}
public static Future<String> Func_01()
{
Print("In Func_01");
Print("In Func_01,Before Task");
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_01 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_01 Task,Before Func_02");
Func_02().get();
Print("In Func_01 Task,After Func_02");
return "Hello World";
});
}
public static Future Func_02()
{
Print("In Func_02,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_02,Before Task");
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_02 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_02 Task,Before Delay");
try
{
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
Print("In Func_02 Task,After Delay");
});
}
public static void Print(String s)
{
System.out.println(s+",Thread:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n");
}

结果,必须调用ExecutorService.submit()才会创建线程,Future.get()是回调,最后会回到主线程
与C++和C#都有一些相同,却也有一些不同
ExecutorService.submit()应该是对应C#里的Task.Run(),所以也可以直接返回
static ExecutorService service=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
var task=Func_01();
Print("In Main");
Print("In Main,Before Func_01");
System.out.println(task.get());
System.out.println();
Print("In Main,After Func_01");
System.out.println("Done");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("共耗时"+(end-start)+"毫秒");
}
public static Future<String> Func_01()
{
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_01");
Print("In Func_01,Before Task");
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_01 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_01 Task,Before Func_02");
Func_02().get();
Print("In Func_01 Task,After Func_02");
return "Hello World";
}).get();
});
}
public static Future Func_02()
{
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_02,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_02,Before Task");
return service.submit(()->
{
Print("In Func_02 Task,ThreadId:");
Print("In Func_02 Task,Before Delay");
try
{
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
}
Print("In Func_02 Task,After Delay");
}).get();
});
}
public static void Print(String s)
{
System.out.println(s+",Thread:"+Thread.currentThread().getId()+"\n");
}

C++ C# Java 异步对比 结束
C++ 和 Java 是阻塞式的异步(我觉得只是多线程),强调非阻塞异步并发的一般都是使用协程,C# 是非阻塞式的异步





