1289 - LCM from 1 to n
http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/18507767
这个是位图的链接,这篇写的挺好。
模板:
1 #include<math.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<string.h> 7 #include<vector> 8 #include<map> 9 #include<math.h> 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long LL; 12 typedef unsigned long long ll; 13 int cmp(const void*p,const void*q); 14 const int N=1e8; 15 const int M=5; 16 const int V=(1<<M)-1; 17 int prime[(N>>M)+4]= {0}; 18 void setbit(LL x) 19 { 20 prime[x>>M]|=1<<(x&(V)); 21 } 22 bool getbit(LL x) 23 { 24 return prime[x>>M]&(1<<(x&V)); 25 } 26 int kp[7000000]; 27 int main(void) 28 { 29 int i,j,k;LL p; 30 for(i=2; i<=20000; i++) 31 { 32 if(!getbit(i)) 33 { 34 for(j=i; i*j<=100000000; j++) 35 { 36 setbit(i*j); 37 } 38 } 39 }int ans=0; 40 for(i=2;i<=100000000;i++) 41 { 42 if(!getbit(i)) 43 { 44 kp[ans++]=i; 45 } 46 } 47 return 0; 48 }
1289 - LCM from 1 to n
| Time Limit: 4 second(s) | Memory Limit: 64 MB |
Given an integer n, you have to find
lcm(1, 2, 3, ..., n)
lcm means least common multiple. For example lcm(2, 5, 4) = 20, lcm(3, 9) = 9, lcm(6, 8, 12) = 24.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 10000), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 108).
Output
For each case, print the case number and lcm(1, 2, 3, ..., n). As the result can be very big, print the result modulo 232.
Sample Input |
Output for Sample Input |
|
5 10 5 200 15 20 |
Case 1: 2520 Case 2: 60 Case 3: 2300527488 Case 4: 360360 Case 5: 232792560 |
Problem Setter: Jane Alam Jan
思路:
有个定理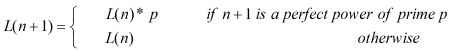
这个是如果n+1是素数的次方,那么当前的L(1+n)=L(n)*p,p为素数,否则就是L(n);
这个很好理解,如过n+1=(p)k,我们从最小公倍数的定义:Lcm=max(a1,a2,a3....)*max(b1,b2,b3...)*max(c1,c2,c3...)*....
其中a1是A1的某个素因数的个数,a2是A2的某个素因数的个数(这两个素因数相同).....
这样我们知道p这个素因数,在n时最大为k-1,所以当到n+1时就有L(n+1)=L(n)*p;否则的话如果n+1不是某个素数的次方那么代表着已经出现的所有素数的最大个数未被更新
那么就有L(n+1)=L(n);所以我们将【2,1e8】的素数全部筛选出来,由于内存限制所以只能用位图来筛选。
这样筛好后,然后我们把<=(1e8)的素数的次方打表出来,然后排序,这样再打表下到每个素数次方时(1,pk)的LCM;然后每次查找二分就行。
1 #include<math.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<string.h> 7 #include<vector> 8 #include<map> 9 #include<math.h> 10 #include<queue> 11 using namespace std; 12 typedef long long LL; 13 typedef unsigned long long ll; 14 const int N=1e8+2; 15 const int M=5; 16 const int V=(1<<M)-1; 17 const LL mod=4294967296; 18 typedef struct node 19 { 20 unsigned int id; 21 unsigned int NN; 22 23 } ss; bool cmp( struct node p,struct node q) 24 { 25 return p.NN<q.NN?true:false; 26 } 27 ss io[6000000]; 28 int prime[(N>>M)+4]= {0}; 29 void setbit(LL x) 30 { 31 prime[x>>M]|=1<<(x&(V)); 32 } 33 bool getbit(LL x) 34 { 35 return prime[x>>M]&(1<<(x&V)); 36 } 37 int er(int n,int m,int ans,int t); 38 int main(void) 39 { 40 int i,j,k;LL p; 41 for(i=2; i<=20000; i++) 42 { 43 if(!getbit(i)) 44 { 45 for(j=i; i*j<=100000000; j++) 46 { 47 setbit(i*j); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 int ans=0; 52 int cns=0; 53 for(i=2; i<100000000; i++) 54 { 55 if(!getbit(i)) 56 { 57 LL sum=i;ans++; 58 while(sum<=N) 59 { 60 io[cns].id=i; 61 io[cns++].NN=sum; 62 sum*=i; 63 } 64 } 65 }sort(io,io+cns,cmp); 66 for(i=1;i<cns;i++) 67 { 68 io[i].id=(io[i-1].id*io[i].id)%mod; 69 }//freopen("data.in","r",stdin); 70 //freopen("wrong.out","w",stdout); 71 scanf("%d",&k); 72 int s; 73 for(s=1; s<=k; s++) 74 { 75 scanf("%lld",&p);printf("Case %d: ",s); 76 {int l,r; 77 l=0; 78 r=cns-1; 79 int ak=0; 80 int uu; 81 while(l<=r) 82 { 83 int c=(l+r)>>1; 84 if(io[c].NN<=p) 85 { 86 ak=c; 87 l=c+1; 88 } 89 else 90 r=c-1; 91 } 92 unsigned int sum1=io[ak].id; 93 printf("%u\n",sum1);} 94 } 95 return 0; 96 } 97 int er(int n,int m,int ans,int t) 98 { int l=(n+m)/2;if(l<0)return -1; 99 if(io[l].NN==ans) 100 { 101 return l; 102 } 103 104 if(io[l-1].NN<ans&&io[l].NN>ans) 105 { 106 return l-1; 107 } else if(n==m&&m==t) 108 return m; 109 else if(n==m) 110 return n-1; 111 else if(io[l-1].NN>=ans&&io[l].NN>ans) 112 { 113 return er(n,l-1,ans,t); 114 } 115 else if(io[l-1].NN<ans&&io[l].NN<ans) 116 { 117 return er(l+1,m,ans,t); 118 } 119 }
我这里两种二分,下面函数式的比较难把喔,写起来很恶心。
油!油!you@



